Table of Contents
- 23.1. MySQL Connector/ODBC
- 23.2. MySQL Connector/NET
- 23.3. MySQL Connector/J
- 23.4. MySQL Connector/MXJ
- 23.4.1. Introduction
- 23.4.2. Supported Platforms
- 23.4.3. JUnit Test Requirements
- 23.4.4. Running the JUnit Tests
- 23.4.5. Running as part of the JDBC Driver
- 23.4.6. Running within a Java Object
- 23.4.7. The MysqldResource API
- 23.4.8. Running within a JMX Agent (custom)
- 23.4.9. Deployment in a standard JMX Agent environment (JBoss)
- 23.4.10. Installation
- 23.5. Connector/PHP
This chapter describes MySQL Connectors, drivers that provide connectivity to the MySQL server for client programs. There are currently five MySQL Connectors:
Connector/ODBC provides driver support for connecting to a MySQL server using the Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) API. Support is available for ODBC connectivity from Windows, Unix and Mac OS X platforms.
Connector/NET enables developers to create .NET applications that use data stored in a MySQL database. Connector/NET implement a fully-functional ADO.NET interface and provides support for use with ADO.NET aware tools. Applications that want to use Connector/NET can be written in any of the supported .NET languages.
Connector/J provides driver support for connecting to MySQL from a Java application using the standard Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) API.
Connector/MXJ is a tool that enables easy deployment and management of MySQL server and database through your Java application.
Connector/PHP is a Windows-only connector for PHP that provides the
mysqlandmysqliextensions for use with MySQL 5.0.18 and later.
For information on connecting to a MySQL server using other languages and interfaces than those detailed above, including Perl, Python and PHP for other platforms and environments, please refer to the Chapter 22, APIs and Libraries chapter.
The MySQL Connector/ODBC is the name for the family of MySQL ODBC drivers (also called MyODBC drivers) that provide access to a MySQL database using the industry standard Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) API. This reference covers Connector/ODBC 3.51, a version of the API that provides ODBC 3.5x compliant access to a MySQL database.
The manual for versions of MyODBC older than 3.51 can be located in the corresponding binary or source distribution.
For more information on the ODBC API standard and how to use it, refer to http://www.microsoft.com/data/.
The application development part of this reference assumes a good working knowledge of C, general DBMS knowledge, and finally, but not least, familiarity with MySQL. For more information about MySQL functionality and its syntax, refer to http://dev.mysql.com/doc/.
Typically, you need to install MyODBC only on Windows machines. For Unix and Mac OS X you can use the native MySQL network or named pipe to communicate with your MySQL database. You may need MyODBC for Unix or Mac OS X if you have an application that requires an ODBC interface to communicate with database.. Applications that require ODBC to communicate with MySQL include ColdFusion, Microsoft Office, and Filemaker Pro.
If you want to install the MyODBC connector on a Unix host, then you must also install an ODBC manager.
If you have questions that are not answered in this document, please
send a mail message to <myodbc@lists.mysql.com>.
ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) provides a way for client programs to access a wide range of databases or data sources. ODBC is a standardized API that allows connections to SQL database servers. It was developed according to the specifications of the SQL Access Group and defines a set of function calls, error codes, and data types that can be used to develop database-independent applications. ODBC usually is used when database independence or simultaneous access to different data sources is required.
For more information about ODBC, refer to http://www.microsoft.com/data/.
There are currently two version of MyODBC available:
MyODBC 5.0, currently in beta status, has been designed to extend the functionality of the MyODBC 3.51 driver and incorporate full support for the functionality in the MySQL 5.0 server release, including stored procedures and views. Applications using MyODBC 3.51 will be compatible with MyODBC 5.0, while being able to take advantage of the new features. Features and functionality of the MyODBC 5.0 driver are not currently included in this guide.
MyODBC 3.51 is the current release of the 32-bit ODBC driver, also known as the MySQL ODBC 3.51 driver. This version is enhanced compared to the older MyODBC 2.50 driver. It has support for ODBC 3.5x specification level 1 (complete core API + level 2 features) in order to continue to provide all functionality of ODBC for accessing MySQL.
MyODBC 2.50 is the previous version of the 32-bit ODBC driver from MySQL AB that is based on ODBC 2.50 specification level 0 (with level 1 and 2 features). Information about the MyODBC 2.50 driver is included in this guide for the purposes of comparison only.
Note: From this section onward, the primary focus of this guide is the MyODBC 3.51 driver. More information about the MyODBC 2.50 driver in the documentation included in the installation packages for that version. If there is a specific issue (error or known problem) that only affects the 2.50 version, it may be included here for reference.
Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a widely accepted application-programming interface (API) for database access. It is based on the Call-Level Interface (CLI) specifications from X/Open and ISO/IEC for database APIs and uses Structured Query Language (SQL) as its database access language.
A survey of ODBC functions supported by MyODBC is given at Section 23.1.5.1, “MyODBC API Reference”. For general information about ODBC, see http://www.microsoft.com/data/.
The MyODBC architecture is based on five components, as shown in the following diagram:
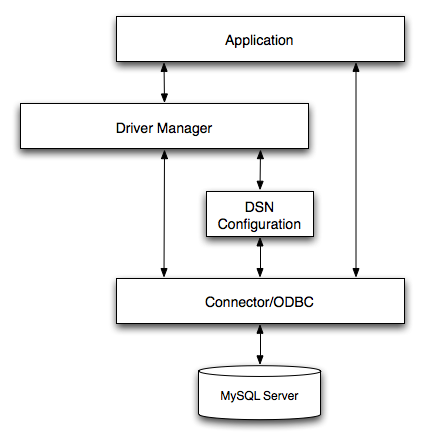
Application:
The Application uses the ODBC API to access the data from the MySQL server. The ODBC API in turn uses the communicates with the Driver Manager. The Application communicates with the Driver Manager using the standard ODBC calls. The Application does not care where the data is stored, how it is stored, or even how the system is configured to access the data. It needs to know only the Data Source Name (DSN).
A number of tasks are common to all applications, no matter how they use ODBC. These tasks are:
Selecting the MySQL server and connecting to it
Submitting SQL statements for execution
Retrieving results (if any)
Processing errors
Committing or rolling back the transaction enclosing the SQL statement
Disconnecting from the MySQL server
Because most data access work is done with SQL, the primary tasks for applications that use ODBC are submitting SQL statements and retrieving any results generated by those statements.
Driver manager:
The Driver Manager is a library that manages communication between application and driver or drivers. It performs the following tasks:
Resolves Data Source Names (DSN). The DSN is a configuration string that identifies a given database driver, database, database host and optionally authentication information that enables an ODBC application to connect to a database using a standardized reference.
Because the database connectivity information is identified by the DSN, any ODBC compliant application can connect to the data source using the same DSN reference. This eliminates the need to separately configure each application that needs access to a given database; instead you instruct the application to use a pre-configured DSN.
Loading and unloading of the driver required to access a specific database as defined within the DSN. For example, if you have configured a DSN that connects to a MySQL database then the driver manager will load the MyODBC driver to enable the ODBC API to communicate with the MySQL host.
Processes ODBC function calls or passes them to the driver for processing.
MyODBC Driver:
The MyODBC driver is a library that implements the functions supported by the ODBC API. It processes ODBC function calls, submits SQL requests to MySQL server, and returns results back to the application. If necessary, the driver modifies an application's request so that the request conforms to syntax supported by MySQL.
DSN Configuration:
The ODBC configuration file stores the driver and database information required to connect to the server. It is used by the Driver Manager to determine which driver to be loaded according to the definition in the DSN. The driver uses this to read connection parameters based on the DSN specified. For more information, Section 23.1.3, “MyODBC Configuration”.
MySQL Server:
The MySQL database where the information is stored. The database is used as the source of the data (during queries) and the destination for data (during inserts and updates).
An ODBC Driver Manager is a library that manages communication between the ODBC-aware application and any drivers. Its main functionality includes:
Resolving Data Source Names (DSN).
Driver loading and unloading.
Processing ODBC function calls or passing them to the driver.
Both Windows and Mac OS X include ODBC driver managers with the operating system. Most ODBC Driver Manager implementations also include an administration application that makes the configuration of DSN and drivers easier. Examples and information on these managers, including Unix ODBC driver managers are listed below:
Microsoft Windows ODBC Driver Manager (
odbc32.dll), http://www.microsoft.com/data/.Mac OS X includes
ODBC Administrator, a GUI application that provides a simpler configuration mechanism for the Unix iODBC Driver Manager. You can configure DSN and driver information either through ODBC Administrator or through the iODBC configuration files. This also means that you can test ODBC Administrator configurations using theiodbctestcommand. http://www.apple.com.unixODBCDriver Manager for Unix (libodbc.so). See http://www.unixodbc.org, for more information. TheunixODBCDriver Manager includes the MyODBC driver 3.51 in the installation package, starting with versionunixODBC2.1.2.iODBCODBC Driver Manager for Unix (libiodbc.so), see http://www.iodbc.org, for more information.
You can install the MyODBC drivers using two different methods, a binary installation and a source installation. The binary installation is the easiest and most straightforward method of installation. Using the source installation methods should only be necessary on platforms where a binary installation package is not available, or in situations where you want to customize or modify the installation process or MyODBC drivers before installation.
MySQL AB distributes all its products under the General Public License (GPL). You can get a copy of the latest version of MyODBC binaries and sources from the MySQL AB Web site http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/.
For more information about MyODBC, visit http://www.mysql.com/products/myodbc/.
For more information about licensing, visit http://www.mysql.com/company/legal/licensing/.
MyODBC can be used on all major platforms supported by MySQL. You can install it on:
Windows 95, 98, Me, NT, 2000, XP, and 2003
All Unix-like Operating Systems, including: AIX, Amiga, BSDI, DEC, FreeBSD, HP-UX 10/11, Linux, NetBSD, OpenBSD, OS/2, SGI Irix, Solaris, SunOS, SCO OpenServer, SCO UnixWare, Tru64 Unix
Mac OS X and Mac OS X Server
If a binary distribution is not available for a particular
platform, see Section 23.1.2.4, “Installing MyODBC from a source distribution”, to
build the driver from the original source code. You can
contribute the binaries you create to MySQL by sending a mail
message to <myodbc@lists.mysql.com>, so that it
becomes available for other users.
Using a binary distribution offers the most straightforward method for installing MyODBC. If you want more control over the driver, the installation location and or to customize elements of the driver you will need to build and install from the source. See the Section 23.1.2.4, “Installing MyODBC from a source distribution”.
Before installing the MyODBC drivers on Windows you should ensure that your Microsoft Data Access Components (MDAC) are up to date. You can obtain the latest version from the Microsoft Data Access and Storage website.
There are three available distribution types to use when installing for Windows. The contents in each case are identical, it is only the installation method which is different.
Zipped installer consists of a Zipped package containing a standalone installation application. To install from this package, you must unzip the installer, and then run the installation application. See Section 23.1.2.3.1.1, “Installing the Windows MyODBC Driver using an installer” to complete the installation.
MSI installer, an installation file that can be used with the installer included in Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. See Section 23.1.2.3.1.1, “Installing the Windows MyODBC Driver using an installer” to complete the installation.
Zipped DLL package, containing the DLL files that need must be manually installed. See Section 23.1.2.3.1.2, “Installing the Windows MyODBC Driver using the Zipped DLL package” to complete the installation.
The installer packages offer a very simple method for installing the MyODBC drivers. If you have downloaded the zipped installer then you must extract the installer application. The basic installation process is identical for both installers.
You should follow these steps to complete the installation:
Double click on the standalone installer that you extracted, or the MSI file you downloaded.
The MySQL Connector/ODBC 3.51 - Setup Wizard will start. Click the button to begin the installation process.
You will need to choose the installation type. The Typical installation provides the standard files you will need to connect to a MySQL database using ODBC. The Complete option installs all the available files, including debug and utility components. It is recommended you choose one of these two options to complete the installation. If choose one of these methods, click and then proceed to step 5.
You may also choose a Custom installation, which enables you to select the individual components that you want to install. You have chosen this method, click and then proceed to step 4.
If you have chosen a custom installation, use the popups to select which components to install and then click to install the necessary files.
Once the files have copied to your machine, the installation is complete. Click to exit the installer.
Now the installation is complete, you can continue to configure your ODBC connections using Section 23.1.3, “MyODBC Configuration”.
If you have downloaded the Zipped DLL package then you must install the individual files required for MyODBC operation manually. Once you have unzipped the installation files, you can either perform this operation by hand, executing each statement individually, or you can use the included Batch file to perform an installation to the default locations.
To install using the Batch file:
Unzip the MyODBC Zipped DLL package.
Open a Command Prompt.
Change to the directory created when you unzipped the MyODBC Zipped DLL package.
Run
Install.bat:C:\>
Install.batThis will copy the necessary files into the default location, and then register the MyODBC driver with the Windows ODBC manager.
If you want to copy the files to an alternative location - for example, to run or test different versions of the MyODBC driver on the same machine, then you must copy the files by hand. It is however not recommended to install these files in a non-standard location. To copy the files by hand to the default installation location use the following steps:
Unzip the MyODBC Zipped DLL package.
Open a Command Prompt.
Change to the directory created when you unzipped the MyODBC Zipped DLL package.
Copy the library files to a suitable directory. The default is to copy them into the default Windows system directory
\Windows\System32:C:\>
copy lib\myodbc3S.dll \Windows\System32C:\>copy lib\myodbc3S.lib \Windows\System32C:\>copy lib\myodbc3.dll \Windows\System32C:\>copy lib\myodbc3.lib \Windows\System32Copy the MyODBC tools. These must be placed into a directory that is in the system
PATH. The default is to install these into the Windows system directory\Windows\System32:C:\>
copy bin\myodbc3i.exe \Windows\System32C:\>copy bin\myodbc3m.exe \Windows\System32C:\>copy bin\myodbc3c.exe \Windows\System32Optionally copy the help files. For these files to be accessible through the help system, they must be installed in the Windows system directory:
C:\>
copy doc\*.hlp \Windows\System32Finally, you must register the MyODBC driver with the ODBC manager:
C:\>
myodbc3i -a -d -t"MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver;\ DRIVER=myodbc3.dll;SETUP=myodbc3S.dll"You must change the references to the DLL files and command location in the above statement if you have not installed these files into the default location.
On Windows, you may get the following error when trying to install the older MyODBC 2.50 driver:
An error occurred while copying C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM\MFC30.DLL. Restart Windows and try installing again (before running any applications which use ODBC)
The reason for the error is that another application is
currently using the ODBC system. Windows may not allow you
to complete the installation. In most cases, you can
continue by pressing Ignore to copy the
rest of the MyODBC files and the final installation should
still work. If it doesn't, the solution is to re-boot your
computer in “safe mode.” Choose safe mode by
pressing F8 just before your machine starts Windows during
re-booting, install the MyODBC drivers, and re-boot to
normal mode.
There are two methods available for installing MyODBC on Unix from a binary distribution. For most Unix environments you will need to use the tarball distribution. For Linux systems, there is also an RPM distribution available.
To install the driver from a tarball distribution
(.tar.gz file), download the latest
version of the driver for your operating system and follow
these steps that demonstrate the process using the Linux
version of the tarball:
shell>su rootshell>gunzip MyODBC-3.51.11-i686-pc-linux.tar.gzshell>tar xvf MyODBC-3.51.11-i686-pc-linux.tarshell>cd MyODBC-3.51.11-i686-pc-linux
Read the installation instructions in the
INSTALL-BINARY file and execute these
commands.
shell>cp libmyodbc* /usr/local/libshell>cp odbc.ini /usr/local/etcshell>export ODBCINI=/usr/local/etc/odbc.ini
Then proceed on to
Section 23.1.3.4, “Configuring a MyODBC DSN on Unix”,
to configure the DSN for MyODBC. For more information, refer
to the INSTALL-BINARY file that comes
with your distribution.
To install or upgrade MyODBC from an RPM distribution on
Linux, simply download the RPM distribution of the latest
version of MyODBC and follow the instructions below. Use
su root to become
root, then install the RPM file.
If you are installing for the first time:
shell>su rootshell>rpm -ivh MyODBC-3.51.12.i386.rpm
If the driver exists, upgrade it like this:
shell>su rootshell>rpm -Uvh MyODBC-3.51.12.i386.rpm
If there is any dependency error for MySQL client library,
libmysqlclient, simply ignore it by
supplying the --nodeps option, and then
make sure the MySQL client shared library is in the path or
set through LD_LIBRARY_PATH.
This installs the driver libraries and related documents to
/usr/local/lib and
/usr/share/doc/MyODBC, respectively.
Proceed onto
Section 23.1.3.4, “Configuring a MyODBC DSN on Unix”.
To uninstall the driver,
become root and execute an
rpm command:
shell>su rootshell>rpm -e MyODBC
Mac OS X is based on the FreeBSD operating system, and you can normally use the MySQL network port for connecting to MySQL servers on other hosts. Installing the MyODBC driver enables you to connect to MySQL databases on any platform through the ODBC interface. You should only need to install the MyODBC driver when your application requires an ODBC interface. Applications that require or can use ODBC (and therefore the MyODBC driver) include ColdFusion, Filemaker Pro, 4th Dimension and many other applications.
Mac OS X includes its own ODBC manager, based on the
iODBC manager. Mac OS X includes an
administration tool that provides easier administration of
ODBC drivers and configuration, updating the underlying
iODBC configuration files.
You can install MyODBC on a Mac OS X or Mac OS X Server
computer by using the binary distribution. The package is
available as a compressed disk image
(.dmg) file. To install MyODBC on your
computer using this method, follow these steps:
Download the file to your computer and double-click on the downloaded image file.
Within the disk image you will find an installer package (with the
.pkgextension). Double click on this file to start the Mac OS X installer.You will be presented with the installer welcome message. Click the button to begin the installation process.
Please take the time to read the Important Information as it contains guidance on how to complete the installation process. Note that if you want to test a connection to a MySQL database, you will need location of your MySQL server, and a user and password to use to create a suitable DSN to test your installation. Testing the connection is not required to complete the installation. Once you have read the notice and collected the necessary information, click .
MyODBC drivers are made available under the GNU General Public License. Please read the license if you are not familiar with it before continuing installation. Click to approve the license (you will be asked to confirm that decision) and continue the installation.
Choose a location to install the MyODBC drivers and the ODBC Administrator application. You must install the files onto a drive with an operating system and you may be limited in the choices available. Select the drive you want to use, and then click .
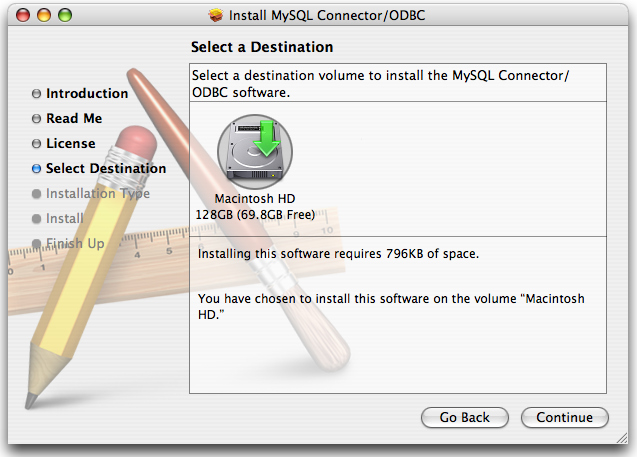
The installer will automatically select the files that need to be installed on your machine. Click to continue. The installer will copy the necessary files to your machine. A progress bar will be shown indicating the installation progress.
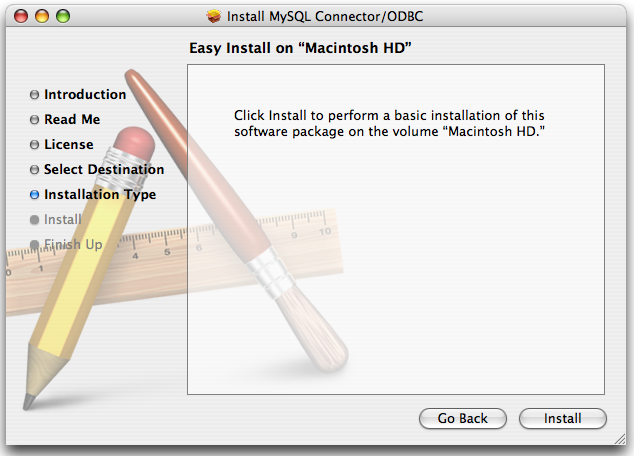
When installation has been completed you will get a window like the one shown below. Click to close and quit the installer.
Installing MyODBC from a source distribution gives you greater flexibility in the contents and installation location of the MyODBC components. It also enables you to build and install MyODBC on platforms where a pre-compiled binary is not available.
MyODBC sources are available either as a downloadable package, or through the revision control system used by the MyODBC developers.
You should only need to install MyODBC from source on Windows if you want to change or modify the source or installation. If you are unsure whether to install from source, please use the binary installation detailed in Section 23.1.2.3.1, “Installing MyODBC from a Binary Distribution on Windows”.
Installing MyODBC from source on Windows requires a number of different tools and packages:
MDAC, Microsoft Data Access SDK from http://www.microsoft.com/data/.
Suitable C compiler, such as Microsoft Visual C++ or the C compiler included with Microsoft Visual Studio.
Compatible
maketool. Microsoft'snmakeis used in the examples in this section.MySQL client libraries and include files from MySQL 4.0.0 or higher. (Preferably MySQL 4.0.16 or higher). This is required because MyODBC uses new calls and structures that exist only starting from this version of the library. To get the client libraries and include files, visit http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/.
MyODBC source distributions include
Makefiles that require the
nmake or other make
utility. In the distribution, you can find
Makefile for building the release
version and Makefile_debug for building
debugging versions of the driver libraries and DLLs.
To build the driver, use this procedure:
Download and extract the sources to a folder, then change directory into that folder. The following command assumes the folder is named
myodbc3-src:C:\>
cd myodbc3-srcEdit
Makefileto specify the correct path for the MySQL client libraries and header files. Then use the following commands to build and install the release version:C:\>
nmake -f MakefileC:\>nmake -f Makefile installnmake -f Makefile builds the release version of the driver and places the binaries in subdirectory called
Release.nmake -f Makefile install installs (copies) the driver DLLs and libraries (
myodbc3.dll,myodbc3.lib) to your system directory.To build the debug version, use
Makefile_Debugrather thanMakefile, as shown below:C:\>
nmake -f Makefile_debugC:\>nmake -f Makefile_debug installYou can clean and rebuild the driver by using:
C:\>
nmake -f Makefile cleanC:\>nmake -f Makefile install
Note:
Make sure to specify the correct MySQL client libraries and header files path in the Makefiles (set the
MYSQL_LIB_PATHandMYSQL_INCLUDE_PATHvariables). The default header file path is assumed to beC:\mysql\include. The default library path is assumed to beC:\mysql\lib\optfor release DLLs andC:\mysql\lib\debugfor debug versions.For the complete usage of nmake, visit http://msdn.microsoft.com/library/default.asp?url=/library/en-us/dv_vcce4/html/evgrfRunningNMAKE.asp.
If you are using the Subversion tree for compiling, all Windows-specific
Makefilesare named asWin_Makefile*.
After the driver libraries are copied/installed to the
system directory, you can test whether the libraries are
properly built by using the samples provided in the
samples subdirectory:
C:\>cd samplesC:\>nmake -f Makefile all
- 23.1.2.4.2.1. Typical configure Options
- 23.1.2.4.2.2. Additional configure Options
- 23.1.2.4.2.3. Building and Compilation
- 23.1.2.4.2.4. Building Shared Libraries
- 23.1.2.4.2.5. Installing Driver Libraries
- 23.1.2.4.2.6. Testing MyODBC on Unix
- 23.1.2.4.2.7. Building MyODBC from Source on Mac OS X
- 23.1.2.4.2.8. Building MyODBC from Source on HP-UX
- 23.1.2.4.2.9. Building MyODBC from Source on AIX
You need the following tools to build MySQL from source on Unix:
A working ANSI C++ compiler. gcc 2.95.2 or later, egcs 1.0.2 or later or egcs 2.91.66, SGI C++, and SunPro C++ are some of the compilers that are known to work.
A good make program. GNU make is always recommended and is sometimes required.
MySQL client libraries and include files from MySQL 4.0.0 or higher. (Preferably MySQL 4.0.16 or higher). This is required because MyODBC uses new calls and structures that exist only starting from this version of the library. To get the client libraries and include files, visit http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/.
If you have built your own MySQL server and/or client libraries from source then you must have used the
--enable-thread-safe-clientoption toconfigurewhen the libraries were built.You should also ensure that the
libmysqlclientlibrary were built and installed as a shared library.A compatible ODBC manager must be installed. MyODBC is known to work with the
iODBCandunixODBCmanagers. See Section 23.1.1.2.2, “ODBC Driver Managers”, for more information.If you are using a character set that isn't compiled into the MySQL client library then you need to install the MySQL character definitions from the
charsetsdirectory intoSHAREDIR(by default,/usr/local/mysql/share/mysql/charsets). These should be in place if you have installed the MySQL server on the same machine. See Chapter 10, Character Set Support, for more information on character set support.
Once you have all the required files, unpack the source files to a separate directory, you then have to run configure and build the library using make.
The configure script gives you a great deal of control over how you configure your MyODBC build. Typically you do this using options on the configure command line. You can also affect configure using certain environment variables. For a list of options and environment variables supported by configure, run this command:
shell> ./configure --help
Some of the more commonly used configure options are described here:
To compile MyODBC, you need to supply the MySQL client include and library files path using the
--with-mysql-path=option, whereDIRDIRis the directory where MySQL is installed.MySQL compile options can be determined by running
DIR/bin/mysql_configSupply the standard header and library files path for your ODBC Driver Manager (
iODBCorunixODBC).If you are using
iODBCandiODBCis not installed in its default location (/usr/local), you might have to use the--with-iodbc=option, whereDIRDIRis the directory whereiODBCis installed.If the
iODBCheaders do not reside inDIR/include--with-iodbc-includes=option to specify their location.INCDIRThe applies to libraries. If they are not in
DIR/lib--with-iodbc-libs=option.LIBDIRIf you are using
unixODBC, use the--with-unixODBC=option (case sensitive) to make configure look forDIRunixODBCinstead ofiODBCby default,DIRis the directory whereunixODBCis installed.If the
unixODBCheaders and libraries aren't located inDIR/includeDIR/lib--with-unixODBC-includes=andINCDIR--with-unixODBC-libs=options.LIBDIR
You might want to specify an installation prefix other than
/usr/local. For example, to install the MyODBC drivers in/usr/local/odbc/lib, use the--prefix=/usr/local/odbcoption.
The final configuration command looks something like this:
shell>./configure --prefix=/usr/local \--with-iodbc=/usr/local \--with-mysql-path=/usr/local/mysql
There are a number of other options that you need, or want, to set when configuring the MyODBC driver before it is built.
To link the driver with MySQL thread safe client libraries
libmysqlclient_r.soorlibmysqlclient_r.a, you must specify the following configure option:--enable-thread-safe
and can be disabled (default) using
--disable-thread-safe
This option enables the building of the driver thread-safe library
libmyodbc3_r.sofrom by linking with MySQL thread-safe client librarylibmysqlclient_r.so(The extensions are OS dependent).If the compilation with the thread-safe option fails, it may be because the correct thread-libraries on the system could not be located. You should set the value of
LIBSto point to the correct thread library for your system.LIBS="-lpthread" ./configure ..
You can enable or disable the shared and static versions of MyODBC using these options:
--enable-shared[=yes/no] --disable-shared --enable-static[=yes/no] --disable-static
By default, all the binary distributions are built as non-debugging versions (configured with
--without-debug).To enable debugging information, build the driver from source distribution and use the
--with-debugoption when you run configure.This option is available only for source trees that have been obtained from the Subversion repository. This option does not apply to the packaged source distributions.
By default, the driver is built with the
--without-docsoption. If you would like the documentation to be built, then execute configure with:--with-docs
To build the driver libraries, you have to just execute make.
shell> make
If any errors occur, correct them and continue the build
process. If you aren't able to build, then send a detailed
email to <myodbc@lists.mysql.com> for further
assistance.
On most platforms, MySQL does not build or support
.so (shared) client libraries by
default. This is based on our experience of problems when
building shared libraries.
In cases like this, you have to download the MySQL distribution and configure it with these options:
--without-server --enable-shared
To build shared driver libraries, you must specify the
--enable-shared option for
configure. By default,
configure does not enable this option.
If you have configured with the
--disable-shared option, you can build the
.so file from the static libraries
using the following commands:
shell>cd MyODBC-3.51.01shell>makeshell>cd drivershell>CC=/usr/bin/gcc \$CC -bundle -flat_namespace -undefined error \-o .libs/libmyodbc3-3.51.01.so \catalog.o connect.o cursor.o dll.o error.o execute.o \handle.o info.o misc.o myodbc3.o options.o prepare.o \results.o transact.o utility.o \-L/usr/local/mysql/lib/mysql/ \-L/usr/local/iodbc/lib/ \-lz -lc -lmysqlclient -liodbcinst
Make sure to change -liodbcinst to
-lodbcinst if you are using
unixODBC instead of
iODBC, and configure the library paths
accordingly.
This builds and places the
libmyodbc3-3.51.01.so file in the
.libs directory. Copy this file to the
MyODBC library installation directory
(/usr/local/lib (or the
lib directory under the installation
directory that you supplied with the
--prefix).
shell>cd .libsshell>cp libmyodbc3-3.51.01.so /usr/local/libshell>cd /usr/local/libshell>ln -s libmyodbc3-3.51.01.so libmyodbc3.so
To build the thread-safe driver library:
shell>CC=/usr/bin/gcc \$CC -bundle -flat_namespace -undefined error-o .libs/libmyodbc3_r-3.51.01.socatalog.o connect.o cursor.o dll.o error.o execute.ohandle.o info.o misc.o myodbc3.o options.o prepare.oresults.o transact.o utility.o-L/usr/local/mysql/lib/mysql/-L/usr/local/iodbc/lib/-lz -lc -lmysqlclient_r -liodbcinst
To install the driver libraries, execute the following command:
shell> make install
That command installs one of the following sets of libraries:
For MyODBC 3.51:
libmyodbc3.solibmyodbc3-3.51.01.so, where 3.51.01 is the version of the driverlibmyodbc3.a
For thread-safe MyODBC 3.51:
libmyodbc3_r.solibmyodbc3-3_r.51.01.solibmyodbc3_r.a
For MyODBC 2.5.0:
libmyodbc.solibmyodbc-2.50.39.so, where 2.50.39 is the version of the driverlibmyodbc.a
For more information on build process, refer to the
INSTALL file that comes with the source
distribution. Note that if you are trying to use the
make from Sun, you may end up with
errors. On the other hand, GNU gmake
should work fine on all platforms.
To run the basic samples provided in the distribution with the libraries that you built, use the following command:
shell> make test
Before running the tests, create the DSN 'myodbc3' in
odbc.ini and set the environment
variable ODBCINI to the correct
odbc.ini file; and MySQL server is
running. You can find a sample odbc.ini
with the driver distribution.
You can even modify the
samples/run-samples script to pass the
desired DSN, UID, and PASSWORD values as the command-line
arguments to each sample.
To build the driver on Mac OS X (Darwin), make use of the following configure example:
shell>./configure --prefix=/usr/local--with-unixODBC=/usr/local--with-mysql-path=/usr/local/mysql--disable-shared--enable-gui=no--host=powerpc-apple
The command assumes that the unixODBC and
MySQL are installed in the default locations. If not,
configure accordingly.
On Mac OS X, --enable-shared builds
.dylib files by default. You can build
.so files like this:
shell>makeshell>cd drivershell>CC=/usr/bin/gcc \$CC -bundle -flat_namespace -undefined error-o .libs/libmyodbc3-3.51.01.so *.o-L/usr/local/mysql/lib/-L/usr/local/iodbc/lib-liodbcinst -lmysqlclient -lz -lc
To build the thread-safe driver library:
shell>CC=/usr/bin/gcc \$CC -bundle -flat_namespace -undefined error-o .libs/libmyodbc3-3.51.01.so *.o-L/usr/local/mysql/lib/-L/usr/local/iodbc/lib-liodbcinst -lmysqlclienti_r -lz -lc -lpthread
Make sure to change the -liodbcinst to
-lodbcinst in case of using
unixODBC instead of
iODBC and configure the libraries path
accordingly.
In Apple's version of GCC, both cc and gcc are actually symbolic links to gcc3.
Copy this library to the $prefix/lib
directory and symlink to libmyodbc3.so.
You can cross-check the output shared-library properties using this command:
shell> otool -LD .libs/libmyodbc3-3.51.01.so
To build the driver on HP-UX 10.x or 11.x, make use of the following configure example:
If using cc:
shell>CC="cc" \CFLAGS="+z" \LDFLAGS="-Wl,+b:-Wl,+s" \./configure --prefix=/usr/local--with-unixodbc=/usr/local--with-mysql-path=/usr/local/mysql/lib/mysql--enable-shared--enable-thread-safe
If using gcc:
shell>CC="gcc" \LDFLAGS="-Wl,+b:-Wl,+s" \./configure --prefix=/usr/local--with-unixodbc=/usr/local--with-mysql-path=/usr/local/mysql--enable-shared--enable-thread-safe
Once the driver is built, cross-check its attributes using
chatr .libs/libmyodbc3.sl to determine
whether you need to have set the MySQL client library path
using the SHLIB_PATH environment
variable. For static versions, ignore all shared-library
options and run configure with the
--disable-shared option.
To build the driver on AIX, make use of the following configure example:
shell>./configure --prefix=/usr/local--with-unixodbc=/usr/local--with-mysql-path=/usr/local/mysql--disable-shared--enable-thread-safe
NOTE: For more information about how to build and set up the static and shared libraries across the different platforms refer to ' Using static and shared libraries across platforms'.
Caution: You should read this section only if you are interested in helping us test our new code. If you just want to get MySQL Connector/ODBC up and running on your system, you should use a standard release distribution.
To be able to access the MyODBC source tree, you must have Subversion installed. Subversion is freely available from http://subversion.tigris.org/.
To build from the source trees, you need the following tools:
autoconf 2.52 (or newer)
automake 1.4 (or newer)
libtool 1.4 (or newer)
m4
The most recent development source tree is available from our public Subversion trees at http://dev.mysql.com/tech-resources/sources.html.
To checkout out the Connector/ODBC sources, change to the directory where you want the copy of the MyODBC tree to be stored, then use the following command:
shell> svn co http://svn.mysql.com/svnpublic/connector-odbc3
You should now have a copy of the entire MyODBC source tree in
the directory connector-odbc3. To build
from this source tree on Unix or Linux follow these steps:
shell>cd connector-odbc3shell>aclocalshell>autoheadershell>autoconfshell>automake;shell>./configure # Add your favorite options hereshell>make
For more information on how to build, refer to the
INSTALL file located in the same
directory. For more information on options to
configure, see
Section 23.1.2.4.2.1, “Typical configure Options”
When the build is done, run make install to install the MyODBC 3.51 driver on your system.
If you have gotten to the make stage and
the distribution does not compile, please report it to
<myodbc@lists.mysql.com>.
On Windows, make use of Windows Makefiles
WIN-Makefile and
WIN-Makefile_debug in building the
driver. For more information, see
Section 23.1.2.4.1, “Installing MyODBC from a Source Distribution on Windows”.
After the initial checkout operation to get the source tree, you should run svn update periodically update your source according to the latest version.
- 23.1.3.1. Data Source Names
- 23.1.3.2. Configuring a MyODBC DSN on Windows
- 23.1.3.3. Configuring a MyODBC DSN on Mac OS X
- 23.1.3.4. Configuring a MyODBC DSN on Unix
- 23.1.3.5. MyODBC Connection Parameters
- 23.1.3.6. Connecting Without a Predefined DSN
- 23.1.3.7. ODBC Connection Pooling
- 23.1.3.8. Getting an ODBC Trace File
Before you connect to a MySQL database using the MyODBC driver you must configure an ODBC Data Source Name. The DSN associates the various configuration parameters required to communicate with a database to a specific name. You use the DSN in an application to communicate with the database, rather than specifying individual parameters within the application itself. DSN information can be user specific, system specific, or provided in a special file. ODBC data source names are configured in different ways, depending on your platform and ODBC driver.
A Data Source Name associates the configuration parameters for communicating with a specific database. Generally a DSN consists of the following parameters:
- Name
- Hostname
- Database Name
- Login
- Password
In addition, different ODBC drivers, including MyODBC, may accept additional driver-specific options and parameters.
There are three types of DSN:
A System DSN is a global DSN definition that is available to any user and application on a particular system. A System DSN can normally only be configured by a systems administrator, or by a user who has specific permissions that let them create System DSNs.
A User DSN is specific to an individual user, and can be used to store database connectivity information that the user regularly uses.
A File DSN uses a simple file to define the DSN configuration. File DSNs can be shared between users and machines and are therefore more practical when installing or deploying DSN information as part of an application across many machines.
DSN information is stored in different locations depending on your platform and environment.
The ODBC Data Source Administrator within
Windows enables you to create DSNs, check driver installation
and configure ODBC systems such as tracing (used for debugging)
and connection pooling.
Different editions and versions of Windows store the
ODBC Data Source Administrator in different
locations depending on the version of Windows that you are
using.
To open the ODBC Data Source Administrator in
Windows Server 2003:
On the
Startmenu, chooseAdministrative Tools, and then clickData Sources (ODBC).
To open the ODBC Data Source Administrator in
Windows 2000 Server or Windows 2000 Professional:
On the
Startmenu, chooseSettings, and then clickControl Panel.In
Control Panel, clickAdministrative Tools.In
Administrative Tools, clickData Sources (ODBC).
To open the ODBC Data Source Administrator on
Windows XP:
On the
Startmenu, clickControl Panel.In the
Control Panelwhen inCategory ViewclickPerformance and Maintenanceand then clickAdministrative Tools.. If you are viewing theControl PanelinClassic View, clickAdministrative Tools.In
Administrative Tools, clickData Sources (ODBC).
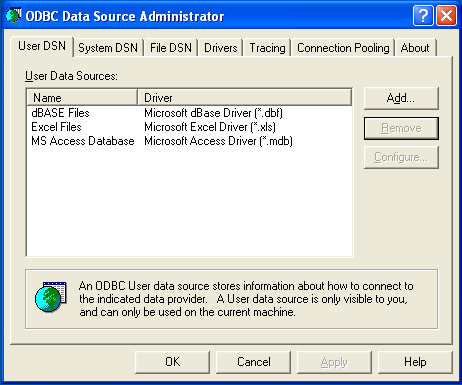
Irrespective of your Windows version, you should be presented
the ODBC Data Source Administrator window:
Within Windows XP, you can add the Administrative
Tools folder to your menu
to make it easier to locate the ODBC Data Source Administrator.
To do this:
Right click on the menu.
Select
Properties.Click .
Select the tab.
Within
Start menu items, within theSystem Administrative Toolssection, selectDisplay on the All Programs menu.
Within both Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP you may want to
permanently add the ODBC Data Source
Administrator to your
menu. To do this, locate the Data Sources
(ODBC) icon using the methods shown, then right-click
on the icon and then choose .
To add and configure a new MyODBC data source on Windows, use
the ODBC Data Source Administrator:
Open the
ODBC Data Source Administrator.To create a System DSN (which will be available to all users) , select the
System DSNtab. To create a User DSN, which will be unique only to the current user, click the button.You will need to select the ODBC driver for this DSN.
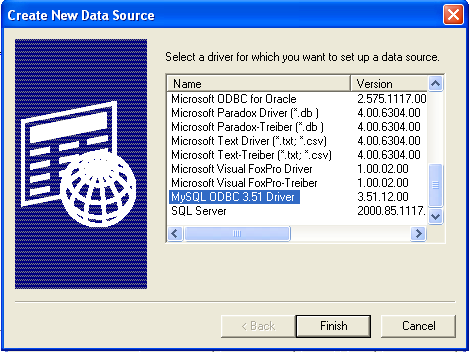
Select
MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver, then clickFinish.You now need to configure the specific fields for the DSN you are creating through the
Add Data Source Namedialog.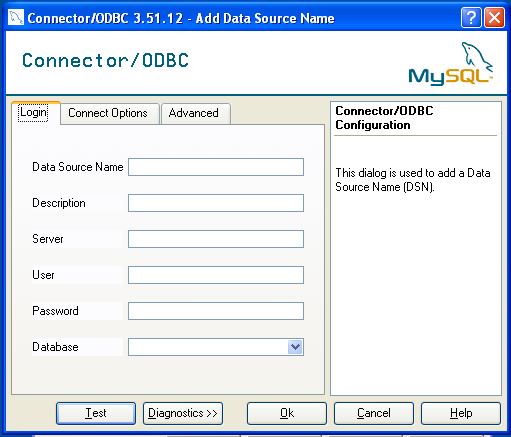
In the
Data Source Namebox, enter the name of the data source you want to access. It can be any valid name that you choose.In the
Descriptionbox, enter some text to help identify the connection.In the
Serverfield, enter the name of the MySQL server host that you want to access. By default, it islocalhost.In the
Userfield, enter the user name to use for this connection.In the
Passwordfield, enter the corresponding password for this connection.The
Databasepopup should automatically populate with the list of databases that the user has permissions to access.Click to save the DSN.
A completed DSN configuration may look like this:
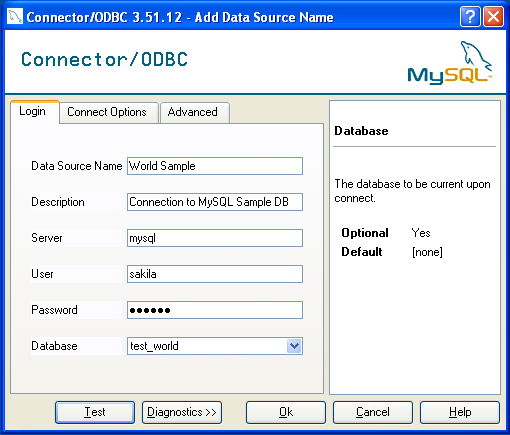
You can verify the connection using the parameters you have
entered by clicking the button. If
the connection could be made successfully, you will be
notified with a Success; connection was
made! dialog.
If the connection failed, you can obtain more information on the test and why it may have failed by clicking the button to show additional error messages.
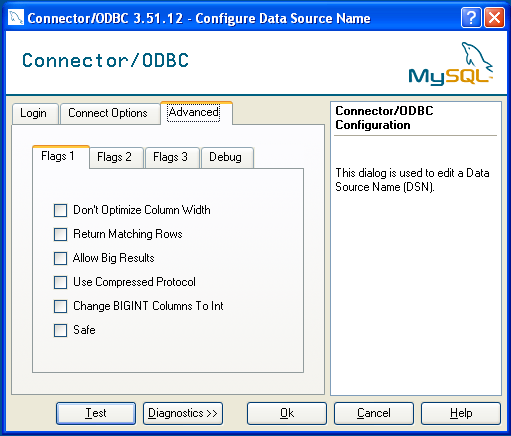
You can configure a number of options for a specific DSN by using either the or tabs in the DSN configuration dialog.
The dialog can be seen below.
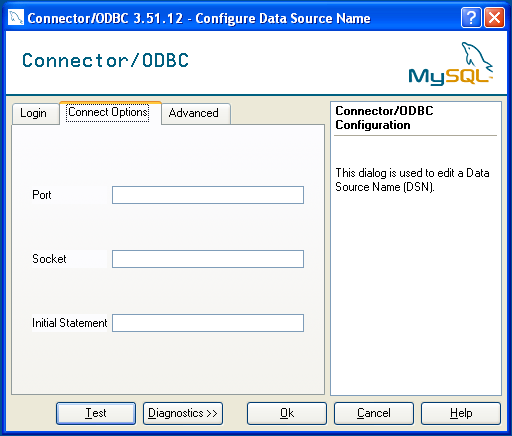
The three options you can configure are:
Portsets the TCP/IP port number to use when communicating with MySQL. Communication with MySQL uses port 3306 by default. If your server is configured to use a different TCP/IP port, you must specify that port number here.Socketsets the name or location of a specific socket or Windows pipe to use when communicating with MySQL.Initial Statementdefines an SQL statement that will be executed when the connection to MySQL is opened. You can use this to set MySQL options for your connection, such as setting the default character set or database to use during your connection.
The tab enables you to configure MyODBC connection parameters. Refer to Section 23.1.3.5, “MyODBC Connection Parameters”, for information about the meaning of these options.
This section answers MyODBC connection-related questions.
While configuring a MyODBC DSN, a
Could Not Load Translator or Setup Libraryerror occursFor more information, refer to MS KnowledgeBase Article(Q260558). Also, make sure you have the latest valid
ctl3d32.dllin your system directory.On Windows, the default
myodbc3.dllis compiled for optimal performance. If you want to debug MyODBC 3.51 (for example, to enable tracing), you should instead usemyodbc3d.dll. To install this file, copymyodbc3d.dllover the installedmyodbc3.dllfile. Make sure to revert back to the release version of the driver DLL once you are done with the debugging because the debug version may cause performance issues. Note that themyodbc3d.dllisn't included in MyODBC 3.51.07 through 3.51.11. If you are using one of these versions, you should copy that DLL from a previous version (for example, 3.51.06).For MyODBC 2.50,
myodbc.dllandmyodbcd.dllare used instead.
To configure a DSN on Mac OS X you should use the ODBC Administrator. If you have Mac OS X 10.2 or earlier, refer to Section 23.1.3.4, “Configuring a MyODBC DSN on Unix”. Select whether you want to create a User DSN or a System DSN. If you want to add a System DSN, you may need to authenticate with the system. You must click the padlock and enter a user and password with administrator privileges.
Open the ODBC Administrator from the
Utilitiesfolder in theApplicationsfolder.
On the User DSN or System DSN panel, click
Select the MyODBC driver and click .
You will be presented with the
Data Source Namedialog. Enter TheData Source Nameand an optionalDescriptionfor the DSN.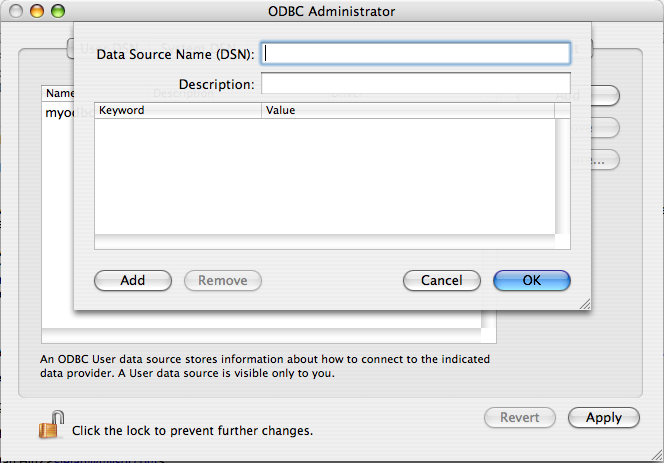
Click to add a new keyword/value pair to the panel. You should configure at least four pairs to specify the
server,username,passwordanddatabaseconnection parameters. See Section 23.1.3.5, “MyODBC Connection Parameters”.Click to add the DSN to the list of configured data source names.
A completed DSN configuration may look like this:
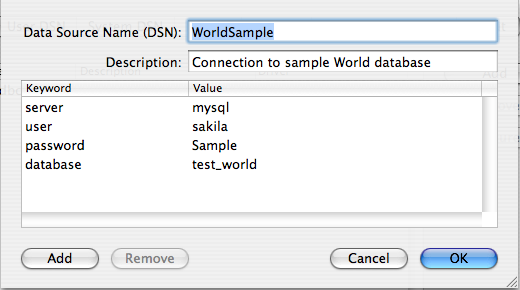
You can configure additional ODBC options to your DSN by adding further keyword/value pairs and setting the corresponding values. See Section 23.1.3.5, “MyODBC Connection Parameters”.
On Unix, you configure DSN entries directly
in the odbc.ini file. Here is a typical
odbc.ini file that configures
myodbc and myodbc3 as the
DSN names for MyODBC 2.50 and MyODBC 3.51, respectively:
; ; odbc.ini configuration for MyODBC and MyODBC 3.51 drivers ; [ODBC Data Sources] myodbc = MyODBC 2.50 Driver DSN myodbc3 = MyODBC 3.51 Driver DSN [myodbc] Driver = /usr/local/lib/libmyodbc.so Description = MyODBC 2.50 Driver DSN SERVER = localhost PORT = USER = root Password = Database = test OPTION = 3 SOCKET = [myodbc3] Driver = /usr/local/lib/libmyodbc3.so Description = MyODBC 3.51 Driver DSN SERVER = localhost PORT = USER = root Password = Database = test OPTION = 3 SOCKET = [Default] Driver = /usr/local/lib/libmyodbc3.so Description = MyODBC 3.51 Driver DSN SERVER = localhost PORT = USER = root Password = Database = test OPTION = 3 SOCKET =
Refer to the Section 23.1.3.5, “MyODBC Connection Parameters”, for the list of connection parameters that can be supplied.
Note: If you are using
unixODBC, you can use the following tools to
set up the DSN:
ODBCConfig GUI tool(HOWTO: ODBCConfig)
odbcinst
In some cases when using unixODBC, you might
get this error:
Data source name not found and no default driver specified
If this happens, make sure the ODBCINI and
ODBCSYSINI environment variables are pointing
to the right odbc.ini file. For example, if
your odbc.ini file is located in
/usr/local/etc, set the environment
variables like this:
export ODBCINI=/usr/local/etc/odbc.ini export ODBCSYSINI=/usr/local/etc
You can specify the parameters in the following tables for
MyODBC when configuring a DSN. Users on Windows can use the
Options and Advanced panels when configuring a DSN to set these
parameters; see the table for information on which options
relate to which fields and checkboxes. On Unix and Mac OS X, use
the parameter name and value as the keyword/value pair in the
DSN configuration. Alternatively, you can set these parameters
within the InConnectionString argument in the
SQLDriverConnect() call.
| Parameter | Default Value | Comment |
user | ODBC (on Windows) | The username used to connect to MySQL. |
server | localhost | The hostname of the MySQL server. |
database | The default database. | |
option | 0 | Options that specify how MyODBC should work. See below. |
port | 3306 | The TCP/IP port to use if server is not
localhost. |
stmt | A statement to execute when connecting to MySQL. | |
password | The password for the user account on
server. | |
socket | The Unix socket file or Windows named pipe to connect to if
server is
localhost. |
The option argument is used to tell MyODBC
that the client isn't 100% ODBC compliant. On Windows, you
normally select options by toggling the checkboxes in the
connection screen, but you can also select them in the
option argument. The following options are
listed in the order in which they appear in the MyODBC connect
screen:
| Value | Windows Checkbox | Description |
| 1 | Don't Optimized Column Width | The client can't handle that MyODBC returns the real width of a column. |
| 2 | Return Matching Rows | The client can't handle that MySQL returns the true value of affected rows. If this flag is set, MySQL returns “found rows” instead. You must have MySQL 3.21.14 or newer to get this to work. |
| 4 | Trace Driver Calls To myodbc.log | Make a debug log in C:\myodbc.log on Windows, or
/tmp/myodbc.log on Unix variants. |
| 8 | Allow Big Results | Don't set any packet limit for results and parameters. |
| 16 | Don't Prompt Upon Connect | Don't prompt for questions even if driver would like to prompt. |
| 32 | Enable Dynamic Cursor | Enable or disable the dynamic cursor support. (Not allowed in MyODBC 2.50.) |
| 64 | Ignore # in Table Name | Ignore use of database name in
db_name.tbl_name.col_name. |
| 128 | User Manager Cursors | Force use of ODBC manager cursors (experimental). |
| 256 | Don't Use Set Locale | Disable the use of extended fetch (experimental). |
| 512 | Pad Char To Full Length | Pad CHAR columns to full column length. |
| 1024 | Return Table Names for SQLDescribeCol | SQLDescribeCol() returns fully qualified column
names. |
| 2048 | Use Compressed Protocol | Use the compressed client/server protocol. |
| 4096 | Ignore Space After Function Names | Tell server to ignore space after function name and before
‘(’ (needed by
PowerBuilder). This makes all function names keywords. |
| 8192 | Force Use of Named Pipes | Connect with named pipes to a mysqld server running on NT. |
| 16384 | Change BIGINT Columns to Int | Change BIGINT columns to INT
columns (some applications can't handle
BIGINT). |
| 32768 | No Catalog (exp) | Return 'user' as Table_qualifier and
Table_owner from
SQLTables (experimental). |
| 65536 | Read Options From my.cnf | Read parameters from the [client] and
[odbc] groups from
my.cnf. |
| 131072 | Safe | Add some extra safety checks (should not be needed but...). |
| 262144 | Disable transaction | Disable transactions. |
| 524288 | Save queries to myodbc.sql | Enable query logging to
c:\myodbc.sql(/tmp/myodbc.sql)
file. (Enabled only in debug mode.) |
| 1048576 | Don't Cache Result (forward only cursors) | Do not cache the results locally in the driver, instead read from server
(mysql_use_result()). This works only
for forward-only cursors. This option is very important
in dealing with large tables when you don't want the
driver to cache the entire result set. |
| 2097152 | Force Use Of Forward Only Cursors | Force the use of Forward-only cursor type. In case of
applications setting the default static/dynamic cursor
type, and one wants the driver to use non-cache result
sets, then this option ensures the forward-only cursor
behavior. |
To select multiple options, add together their values. For
example, setting option to 12 (4+8) gives you
debugging without packet limits.
The following table shows some recommended
option values for various configurations:
| Configuration | Option Value |
| Microsoft Access, Visual Basic | 3 |
| Driver trace generation (Debug mode) | 4 |
| Microsoft Access (with improved DELETE queries) | 35 |
| Large tables with too many rows | 2049 |
| Sybase PowerBuilder | 135168 |
| Query log generation (Debug mode) | 524288 |
| Generate driver trace as well as query log (Debug mode) | 524292 |
| Large tables with no-cache results | 3145731 |
You can connect to the MySQL server using SQLDriverConnect, by
specifying the DRIVER name field. Here are
the connection strings for MyODBC using DSN-Less connections:
For MyODBC 2.50:
ConnectionString = "DRIVER={MySQL};\
SERVER=localhost;\
DATABASE=test;\
USER=venu;\
PASSWORD=venu;\
OPTION=3;"For MyODBC 3.51:
ConnectionString = "DRIVER={MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver};\
SERVER=localhost;\
DATABASE=test;\
USER=venu;\
PASSWORD=venu;\
OPTION=3;"If your programming language converts backslash followed by whitespace to a space, it is preferable to specify the connection string as a single long string, or to use a concatenation of multiple strings that does not add spaces in between. For example:
ConnectionString = "DRIVER={MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver};"
"SERVER=localhost;"
"DATABASE=test;"
"USER=venu;"
"PASSWORD=venu;"
"OPTION=3;"Refer to the Section 23.1.3.5, “MyODBC Connection Parameters”, for the list of connection parameters that can be supplied.
Connection pooling enables the ODBC driver to re-use existing connections to a given database from a pool of connections, instead of opening a new connection each time the database is accessed. By enabling connection pooling you can improve the overall performance of your application by lowering the time taken to open a connection to a database in the connection pool.
For more information about connection pooling: http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;q169470.
If you encounter difficulties or problems with MyODBC, you
should start by making a log file from the ODBC
Manager and MyODBC. This is called
tracing, and is enabled through the ODBC
Manager. The procedure for this differs for Windows, Mac OS X
and Unix.
To enable the trace option on Windows:
The
Tracingtab of the ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog box enables you to configure the way ODBC function calls are traced.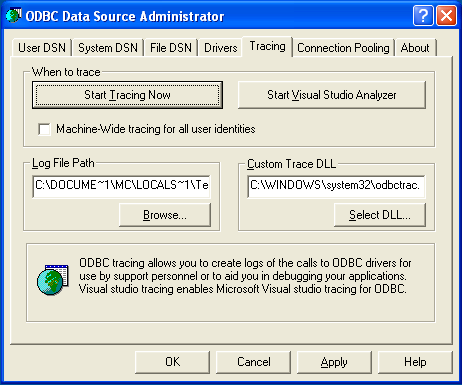
When you activate tracing from the
Tracingtab, theDriver Managerlogs all ODBC function calls for all subsequently run applications.ODBC function calls from applications running before tracing is activated are not logged. ODBC function calls are recorded in a log file you specify.
Tracing ceases only after you click
Stop Tracing Now. Remember that while tracing is on, the log file continues to increase in size and that tracing affects the performance of all your ODBC applications.
To enable the trace option on Mac OS X 10.3 or later you
should use the Tracing tab within
ODBC
Administrator
.
Open the ODBC Administrator.
Select the
Tracingtab.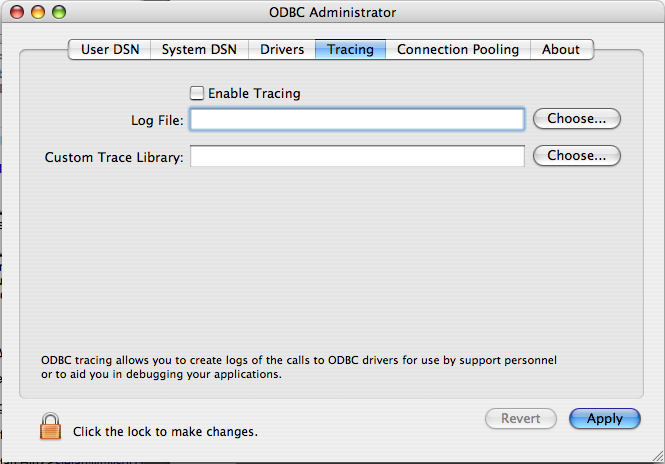
Select the
Enable Tracingcheckbox.Enter the location where you want to save the Tracing log. If you want to append information to an existing log file, click the button.
To enable the trace option on Mac OS X 10.2 (or earlier) or
Unix you must add the trace option to the
ODBC configuration:
On Unix, you need to explicitly set the
Traceoption in theODBC.INIfile.Set the tracing
ONorOFFby usingTraceFileandTraceparameters inodbc.inias shown below:TraceFile = /tmp/odbc.trace Trace = 1
TraceFilespecifies the name and full path of the trace file andTraceis set toONorOFF. You can also use1orYESforONand0orNOforOFF. If you are using ODBCConfig fromunixODBC, then follow the instructions for tracingunixODBCcalls at HOWTO-ODBCConfig.
To generate a MyODBC log, do the following:
Within Windows, enable the
Trace MyODBCoption flag in the MyODBC connect/configure screen. The log is written to fileC:\myodbc.log. If the trace option is not remembered when you are going back to the above screen, it means that you are not using themyodbcd.dlldriver, see xref linkend="myodbc-configuration-dsn-windows-problems"/>.On Mac OS X, Unix, or if you are using DSN-Less connection, then you need to supply
OPTION=4in the connection string or set the corresponding keyword/value pair in the DSN.Start your application and try to get it to fail. Then check the MyODBC trace file to find out what could be wrong.
If you need help determining what is wrong, see Section 23.1.7.1, “MyODBC Community Support”.
Once you have configured a DSN to provide access to a database, how you access and use that connection is dependent on the application or programming language. As ODBC is a standardized interface, any application or language that supports ODBC can use the DSN and connect to the configured database.
Interacting with a MySQL server from an applications using the MyODBC typically involves the following operations:
Configure the MyODBC DSN
Connect to MySQL server
Initialization operations
Execute SQL statements
Retrieve results
Perform Transactions
Disconnect from the server
Most applications use some variation of these steps. The basic application steps are shown in the following diagram:
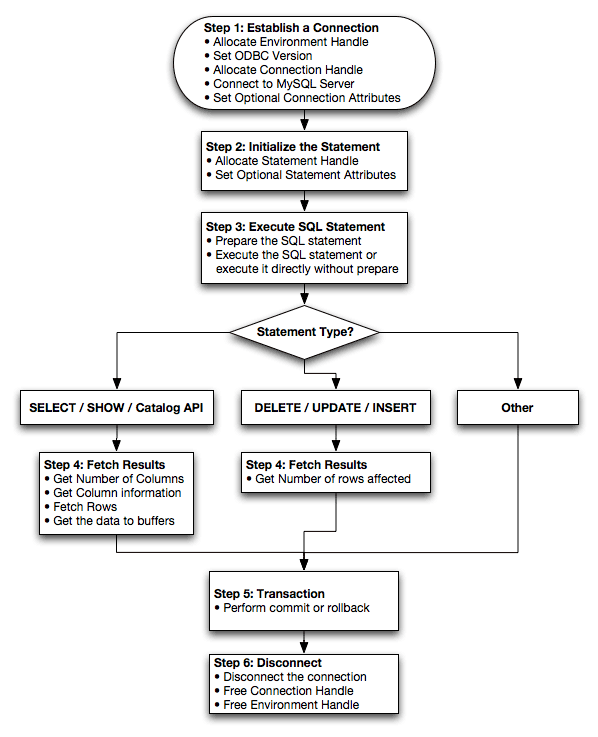
A typical installation situation where you would install MyODBC is when you want to access a database on a Linux or Unix host from a Windows machine.
As an example of the process required to set up access between
two machines, the steps below take you through the basic steps.
These instructions assume that you want to connect to system
ALPHA from system BETA with a username and password of
myuser and mypassword.
On system ALPHA (the MySQL server) follow these steps:
Start the MySQL server.
Use
GRANTto set up an account with a username ofmyuserthat can connect from system BETA using a password ofmyuserto the databasetest:GRANT ALL ON test.* to 'myuser'@'BETA' IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword';
For more information about MySQL privileges, refer to Section 5.9, “MySQL User Account Management”.
On system BETA (the MyODBC client), follow these steps:
Configure a MyODBC DSN using parameters that match the server, database and authentication information that you have just configured on system ALPHA.
Parameter Value Comment DSN remote_test A name to identify the connection. SERVER ALPHA The address of the remote server. DATABASE test The name of the default database. USER myuser The username configured for access to this database. PASSWORD mypassword The password for myuser.Using an ODBC-capable application, such as Microsoft Office, connect to the MySQL server using the DSN you have just created. If the connection fails, use tracing to examine the connection process. See Section 23.1.3.8, “Getting an ODBC Trace File”, for more information.
Once you have configured your MyODBC DSN, you can access your MySQL database through any application that supports the ODBC interface, including programming languages and third-party applications. This section contains guides and help on using MyODBC with various ODBC-compatible tools and applications, including Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel and Adobe/Macromedia ColdFusion.
MyODBC has been tested with the following applications:
| Publisher | Application | Notes |
| Adobe | ColdFusion | Formerly Macromedia ColdFusion |
| Borland | C++ Builder | |
| Builder 4 | ||
| Delphi | ||
| Business Objects | Crystal Reports | |
| Claris | Filemaker Pro | |
| Corel | Paradox | |
| Computer Associates | Visual Objects | Also known as CAVO |
| AllFusion ERwin Data Modeler | ||
| Gupta | Team Developer | Previously known as Centura Team Developer; Gupta SQL/Windows |
| Gensym | G2-ODBC Bridge | |
| Inline | iHTML | |
| Lotus | Notes | Versions 4.5 and 4.6 |
| Microsoft | Access | |
| Excel | ||
| Visio Enterprise | ||
| Visual C++ | ||
| Visual Basic | ||
| ODBC.NET | Using C#, Visual Basic, C++ | |
| FoxPro | ||
| Visual Interdev | ||
| OpenOffice.org | OpenOffice.org | |
| Perl | DBD::ODBC | |
| Pervasive Software | DataJunction | |
| Sambar Technologies | Sambar Server | |
| SPSS | SPSS | |
| SoftVelocity | Clarion | |
| SQLExpress | SQLExpress for Xbase++ | |
| Sun | StarOffice | |
| SunSystems | Vision | |
| Sybase | PowerBuilder | |
| PowerDesigner | ||
| theKompany.com | Data Architect |
If you know of any other applications that work with MyODBC,
please send mail to <myodbc@lists.mysql.com>
about them.
You can use Microsoft Word and Microsoft Excel to access information from a MySQL database using MyODBC. Within Microsoft Word, this facility is most useful when importing data for mailmerge, or for tables and data to be included in reports. Within Microsoft Excel, you can execute queries on your MySQL server and import the data directly into an Excel Worksheet, presenting the data as a series of rows and columns.
With both applications, data is accessed and imported into the application using Microsoft Query , which enables you to execute a query though an ODBC source. You use Microsoft Query to build the SQL statement to be executed, selecting the tables, fields, selection criteria and sort order. For example, to insert information from a table in the World test database into an Excel spreadsheet, using the DSN samples shown in Section 23.1.3, “MyODBC Configuration”:
Create a new Worksheet.
From the
Datamenu, chooseImport External Data, and then selectNew Database Query.Microsoft Query will start. First, you need to choose the data source, by selecting an existing Data Source Name.
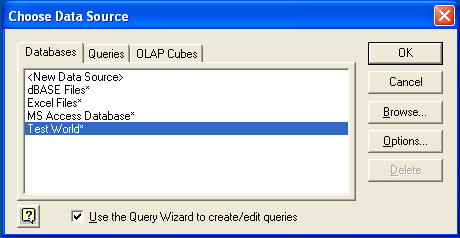
Within the
Query Wizard, you must choose the columns that you want to import. The list of tables available to the user configured through the DSN is shown on the left, the columns that will be added to your query are shown on the right. The columns you choose are equivalent to those in the first section of aSELECTquery. Click to continue.
You can filter rows from the query (the equivalent of a
WHEREclause) using theFilter Datadialog. Click to continue.
Select an (optional) sort order for the data. This is equivalent to using a
ORDER BYclause in your SQL query. You can select up to three fields for sorting the information returned by the query. Click to continue.
Select the destination for your query. You can select to return the data Microsoft Excel, where you can choose a worksheet and cell where the data will be inserted; you can continue to view the query and results within Microsoft Query, where you can edit the SQL query and further filter and sort the information returned; or you can create an OLAP Cube from the query, which can then be used directly within Microsoft Excel. Click .
The same process can be used to import data into a Word document, where the data will be inserted as a table. This can be used for mail merge purposes (where the field data is read from a Word table), or where you want to include data and reports within a report or other document.
You can use MySQL database with Microsoft Access using MyODBC. The MySQL database can be used as an import source, an export source, or as a linked table for direct use within an Access application, so you can use Access as the front-end interface to a MySQL database.
To export a table of data from an Access database to MySQL, follow these instructions:
When you open an Access database or an Access project, a Database window appears. It displays shortcuts for creating new database objects and opening existing objects.
Click the name of the
tableorqueryyou want to export, and then in theFilemenu, selectExport.In the
Export Object Typedialog box, in theObject nameToSave As Typebox, selectODBC Databases ()as shown here: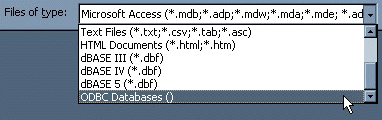
In the
Exportdialog box, enter a name for the file (or use the suggested name), and then selectOK.The Select Data Source dialog box is displayed; it lists the defined data sources for any ODBC drivers installed on your computer. Click either the File Data Source or Machine Data Source tab, and then double-click the MyODBC or MyODBC 3.51 data source that you want to export to. To define a new data source for MyODBC, please Section 23.1.3.2, “Configuring a MyODBC DSN on Windows”.
Microsoft Access connects to the MySQL Server through this data source and exports new tables and or data.
To import or link a table or tables from MySQL to Access, follow these instructions:
Open a database, or switch to the Database window for the open database.
To import tables, on the
Filemenu, point toGet External Data, and then clickImport. To link tables, on the File menu, point toGet External Data, and then clickLink Tables.In the
Import(orLink) dialog box, in the Files Of Type box, selectODBC Databases (). The Select Data Source dialog box lists the defined data sources The Select Data Source dialog box is displayed; it lists the defined data source names.If the ODBC data source that you selected requires you to log on, enter your login ID and password (additional information might also be required), and then click
OK.Microsoft Access connects to the MySQL server through
ODBC data sourceand displays the list of tables that you canimportorlink.Click each table that you want to
importorlink, and then clickOK. If you're linking a table and it doesn't have an index that uniquely identifies each record, Microsoft Access displays a list of the fields in the linked table. Click a field or a combination of fields that uniquely identifies each record, and then clickOK.
Use the following procedure to view or to refresh links when the structure or location of a linked table has changed. The Linked Table Manager lists the paths to all currently linked tables.
To view or refresh links:
Open the database that contains links to tables.
On the
Toolsmenu, point toAdd-ins(Database Utilitiesin Access 2000 or newer), and then clickLinked Table Manager.Select the check box for the tables whose links you want to refresh.
Click OK to refresh the links.
Microsoft Access confirms a successful refresh or, if the
table wasn't found, displays the Select New
Location of <table name> dialog box in which
you can specify its the table's new location. If several
selected tables have moved to the new location that you
specify, the Linked Table Manager searches that location for
all selected tables, and updates all links in one step.
To change the path for a set of linked tables:
Open the database that contains links to tables.
On the
Toolsmenu, point toAdd-ins(Database Utilitiesin Access 2000 or newer), and then clickLinked Table Manager.Select the
Always Prompt For A New Locationcheck box.Select the check box for the tables whose links you want to change, and then click
OK.In the
Select New Location of<table name> dialog box, specify the new location, clickOpen, and then clickOK.
With a suitable ODBC Manager and the my MyODBC driver installed, any programming language or environment that can support ODBC should be able to connect to a MySQL database through MyODBC.
This includes, but is certainly not limited to, Microsoft support languages (including Visual Basic, C# and interfaces such as ODBC.NET), Perl (through the DBI module, and the DBD::ODBC driver).
This section contains simple examples of the use of MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver with ADO, DAO and RDO.
The following ADO (ActiveX Data Objects) example creates a
table my_ado and demonstrates the use of
rs.addNew, rs.delete,
and rs.update.
Private Sub myodbc_ado_Click()
Dim conn As ADODB.Connection
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
Dim fld As ADODB.Field
Dim sql As String
'connect to MySQL server using MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver
Set conn = New ADODB.Connection
conn.ConnectionString = "DRIVER={MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver};"_
& "SERVER=localhost;"_
& " DATABASE=test;"_
& "UID=venu;PWD=venu; OPTION=3"
conn.Open
'create table
conn.Execute "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS my_ado"
conn.Execute "CREATE TABLE my_ado(id int not null primary key, name varchar(20)," _
& "txt text, dt date, tm time, ts timestamp)"
'direct insert
conn.Execute "INSERT INTO my_ado(id,name,txt) values(1,100,'venu')"
conn.Execute "INSERT INTO my_ado(id,name,txt) values(2,200,'MySQL')"
conn.Execute "INSERT INTO my_ado(id,name,txt) values(3,300,'Delete')"
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
rs.CursorLocation = adUseServer
'fetch the initial table ..
rs.Open "SELECT * FROM my_ado", conn
Debug.Print rs.RecordCount
rs.MoveFirst
Debug.Print String(50, "-") & "Initial my_ado Result Set " & String(50, "-")
For Each fld In rs.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name,
Next
Debug.Print
Do Until rs.EOF
For Each fld In rs.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Value,
Next
rs.MoveNext
Debug.Print
Loop
rs.Close
'rs insert
rs.Open "select * from my_ado", conn, adOpenDynamic, adLockOptimistic
rs.AddNew
rs!Name = "Monty"
rs!txt = "Insert row"
rs.Update
rs.Close
'rs update
rs.Open "SELECT * FROM my_ado"
rs!Name = "update"
rs!txt = "updated-row"
rs.Update
rs.Close
'rs update second time..
rs.Open "SELECT * FROM my_ado"
rs!Name = "update"
rs!txt = "updated-second-time"
rs.Update
rs.Close
'rs delete
rs.Open "SELECT * FROM my_ado"
rs.MoveNext
rs.MoveNext
rs.Delete
rs.Close
'fetch the updated table ..
rs.Open "SELECT * FROM my_ado", conn
Debug.Print rs.RecordCount
rs.MoveFirst
Debug.Print String(50, "-") & "Updated my_ado Result Set " & String(50, "-")
For Each fld In rs.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Name,
Next
Debug.Print
Do Until rs.EOF
For Each fld In rs.Fields
Debug.Print fld.Value,
Next
rs.MoveNext
Debug.Print
Loop
rs.Close
conn.Close
End Sub
The following DAO (Data Access Objects) example creates a
table my_dao and demonstrates the use of
rs.addNew, rs.update,
and result set scrolling.
Private Sub myodbc_dao_Click()
Dim ws As Workspace
Dim conn As Connection
Dim queryDef As queryDef
Dim str As String
'connect to MySQL using MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver
Set ws = DBEngine.CreateWorkspace("", "venu", "venu", dbUseODBC)
str = "odbc;DRIVER={MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver};"_
& "SERVER=localhost;"_
& " DATABASE=test;"_
& "UID=venu;PWD=venu; OPTION=3"
Set conn = ws.OpenConnection("test", dbDriverNoPrompt, False, str)
'Create table my_dao
Set queryDef = conn.CreateQueryDef("", "drop table if exists my_dao")
queryDef.Execute
Set queryDef = conn.CreateQueryDef("", "create table my_dao(Id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, " _
& "Ts TIMESTAMP(14) NOT NULL, Name varchar(20), Id2 INT)")
queryDef.Execute
'Insert new records using rs.addNew
Set rs = conn.OpenRecordset("my_dao")
Dim i As Integer
For i = 10 To 15
rs.AddNew
rs!Name = "insert record" & i
rs!Id2 = i
rs.Update
Next i
rs.Close
'rs update..
Set rs = conn.OpenRecordset("my_dao")
rs.Edit
rs!Name = "updated-string"
rs.Update
rs.Close
'fetch the table back...
Set rs = conn.OpenRecordset("my_dao", dbOpenDynamic)
str = "Results:"
rs.MoveFirst
While Not rs.EOF
str = " " & rs!Id & " , " & rs!Name & ", " & rs!Ts & ", " & rs!Id2
Debug.Print "DATA:" & str
rs.MoveNext
Wend
'rs Scrolling
rs.MoveFirst
str = " FIRST ROW: " & rs!Id & " , " & rs!Name & ", " & rs!Ts & ", " & rs!Id2
Debug.Print str
rs.MoveLast
str = " LAST ROW: " & rs!Id & " , " & rs!Name & ", " & rs!Ts & ", " & rs!Id2
Debug.Print str
rs.MovePrevious
str = " LAST-1 ROW: " & rs!Id & " , " & rs!Name & ", " & rs!Ts & ", " & rs!Id2
Debug.Print str
'free all resources
rs.Close
queryDef.Close
conn.Close
ws.Close
End Sub
The following RDO (Remote Data Objects) example creates a
table my_rdo and demonstrates the use of
rs.addNew and
rs.update.
Dim rs As rdoResultset
Dim cn As New rdoConnection
Dim cl As rdoColumn
Dim SQL As String
'cn.Connect = "DSN=test;"
cn.Connect = "DRIVER={MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver};"_
& "SERVER=localhost;"_
& " DATABASE=test;"_
& "UID=venu;PWD=venu; OPTION=3"
cn.CursorDriver = rdUseOdbc
cn.EstablishConnection rdDriverPrompt
'drop table my_rdo
SQL = "drop table if exists my_rdo"
cn.Execute SQL, rdExecDirect
'create table my_rdo
SQL = "create table my_rdo(id int, name varchar(20))"
cn.Execute SQL, rdExecDirect
'insert - direct
SQL = "insert into my_rdo values (100,'venu')"
cn.Execute SQL, rdExecDirect
SQL = "insert into my_rdo values (200,'MySQL')"
cn.Execute SQL, rdExecDirect
'rs insert
SQL = "select * from my_rdo"
Set rs = cn.OpenResultset(SQL, rdOpenStatic, rdConcurRowVer, rdExecDirect)
rs.AddNew
rs!id = 300
rs!Name = "Insert1"
rs.Update
rs.Close
'rs insert
SQL = "select * from my_rdo"
Set rs = cn.OpenResultset(SQL, rdOpenStatic, rdConcurRowVer, rdExecDirect)
rs.AddNew
rs!id = 400
rs!Name = "Insert 2"
rs.Update
rs.Close
'rs update
SQL = "select * from my_rdo"
Set rs = cn.OpenResultset(SQL, rdOpenStatic, rdConcurRowVer, rdExecDirect)
rs.Edit
rs!id = 999
rs!Name = "updated"
rs.Update
rs.Close
'fetch back...
SQL = "select * from my_rdo"
Set rs = cn.OpenResultset(SQL, rdOpenStatic, rdConcurRowVer, rdExecDirect)
Do Until rs.EOF
For Each cl In rs.rdoColumns
Debug.Print cl.Value,
Next
rs.MoveNext
Debug.Print
Loop
Debug.Print "Row count="; rs.RowCount
'close
rs.Close
cn.Close
End SubThis section contains simple examples that demonstrate the use of MyODBC drivers with ODBC.NET.
The following sample creates a table
my_odbc_net and demonstrates its use in
C#.
/**
* @sample : mycon.cs
* @purpose : Demo sample for ODBC.NET using MyODBC
* @author : Venu, <myodbc@lists.mysql.com>
*
* (C) Copyright MySQL AB, 1995-2006
*
**/
/* build command
*
* csc /t:exe
* /out:mycon.exe mycon.cs
* /r:Microsoft.Data.Odbc.dll
*/
using Console = System.Console;
using Microsoft.Data.Odbc;
namespace myodbc3
{
class mycon
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
//Connection string for MyODBC 2.50
/*string MyConString = "DRIVER={MySQL};" +
"SERVER=localhost;" +
"DATABASE=test;" +
"UID=venu;" +
"PASSWORD=venu;" +
"OPTION=3";
*/
//Connection string for MyODBC 3.51
string MyConString = "DRIVER={MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver};" +
"SERVER=localhost;" +
"DATABASE=test;" +
"UID=venu;" +
"PASSWORD=venu;" +
"OPTION=3";
//Connect to MySQL using MyODBC
OdbcConnection MyConnection = new OdbcConnection(MyConString);
MyConnection.Open();
Console.WriteLine("\n !!! success, connected successfully !!!\n");
//Display connection information
Console.WriteLine("Connection Information:");
Console.WriteLine("\tConnection String:" +
MyConnection.ConnectionString);
Console.WriteLine("\tConnection Timeout:" +
MyConnection.ConnectionTimeout);
Console.WriteLine("\tDatabase:" +
MyConnection.Database);
Console.WriteLine("\tDataSource:" +
MyConnection.DataSource);
Console.WriteLine("\tDriver:" +
MyConnection.Driver);
Console.WriteLine("\tServerVersion:" +
MyConnection.ServerVersion);
//Create a sample table
OdbcCommand MyCommand =
new OdbcCommand("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS my_odbc_net",
MyConnection);
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
MyCommand.CommandText =
"CREATE TABLE my_odbc_net(id int, name varchar(20), idb bigint)";
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
//Insert
MyCommand.CommandText =
"INSERT INTO my_odbc_net VALUES(10,'venu', 300)";
Console.WriteLine("INSERT, Total rows affected:" +
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery());;
//Insert
MyCommand.CommandText =
"INSERT INTO my_odbc_net VALUES(20,'mysql',400)";
Console.WriteLine("INSERT, Total rows affected:" +
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery());
//Insert
MyCommand.CommandText =
"INSERT INTO my_odbc_net VALUES(20,'mysql',500)";
Console.WriteLine("INSERT, Total rows affected:" +
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery());
//Update
MyCommand.CommandText =
"UPDATE my_odbc_net SET id=999 WHERE id=20";
Console.WriteLine("Update, Total rows affected:" +
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery());
//COUNT(*)
MyCommand.CommandText =
"SELECT COUNT(*) as TRows FROM my_odbc_net";
Console.WriteLine("Total Rows:" +
MyCommand.ExecuteScalar());
//Fetch
MyCommand.CommandText = "SELECT * FROM my_odbc_net";
OdbcDataReader MyDataReader;
MyDataReader = MyCommand.ExecuteReader();
while (MyDataReader.Read())
{
if(string.Compare(MyConnection.Driver,"myodbc3.dll") == 0) {
//Supported only by MyODBC 3.51
Console.WriteLine("Data:" + MyDataReader.GetInt32(0) + " " +
MyDataReader.GetString(1) + " " +
MyDataReader.GetInt64(2));
}
else {
//BIGINTs not supported by MyODBC
Console.WriteLine("Data:" + MyDataReader.GetInt32(0) + " " +
MyDataReader.GetString(1) + " " +
MyDataReader.GetInt32(2));
}
}
//Close all resources
MyDataReader.Close();
MyConnection.Close();
}
catch (OdbcException MyOdbcException) //Catch any ODBC exception ..
{
for (int i=0; i < MyOdbcException.Errors.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write("ERROR #" + i + "\n" +
"Message: " +
MyOdbcException.Errors[i].Message + "\n" +
"Native: " +
MyOdbcException.Errors[i].NativeError.ToString() + "\n" +
"Source: " +
MyOdbcException.Errors[i].Source + "\n" +
"SQL: " +
MyOdbcException.Errors[i].SQLState + "\n");
}
}
}
}
}
The following sample creates a table
my_vb_net and demonstrates the use in VB.
' @sample : myvb.vb
' @purpose : Demo sample for ODBC.NET using MyODBC
' @author : Venu, <myodbc@lists.mysql.com>
'
' (C) Copyright MySQL AB, 1995-2006
'
'
'
' build command
'
' vbc /target:exe
' /out:myvb.exe
' /r:Microsoft.Data.Odbc.dll
' /r:System.dll
' /r:System.Data.dll
'
Imports Microsoft.Data.Odbc
Imports System
Module myvb
Sub Main()
Try
'MyODBC 3.51 connection string
Dim MyConString As String = "DRIVER={MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver};" & _
"SERVER=localhost;" & _
"DATABASE=test;" & _
"UID=venu;" & _
"PASSWORD=venu;" & _
"OPTION=3;"
'Connection
Dim MyConnection As New OdbcConnection(MyConString)
MyConnection.Open()
Console.WriteLine("Connection State::" & MyConnection.State.ToString)
'Drop
Console.WriteLine("Dropping table")
Dim MyCommand As New OdbcCommand()
MyCommand.Connection = MyConnection
MyCommand.CommandText = "DROP TABLE IF EXISTS my_vb_net"
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery()
'Create
Console.WriteLine("Creating....")
MyCommand.CommandText = "CREATE TABLE my_vb_net(id int, name varchar(30))"
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery()
'Insert
MyCommand.CommandText = "INSERT INTO my_vb_net VALUES(10,'venu')"
Console.WriteLine("INSERT, Total rows affected:" & _
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery())
'Insert
MyCommand.CommandText = "INSERT INTO my_vb_net VALUES(20,'mysql')"
Console.WriteLine("INSERT, Total rows affected:" & _
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery())
'Insert
MyCommand.CommandText = "INSERT INTO my_vb_net VALUES(20,'mysql')"
Console.WriteLine("INSERT, Total rows affected:" & _
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery())
'Insert
MyCommand.CommandText = "INSERT INTO my_vb_net(id) VALUES(30)"
Console.WriteLine("INSERT, Total rows affected:" & _
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery())
'Update
MyCommand.CommandText = "UPDATE my_vb_net SET id=999 WHERE id=20"
Console.WriteLine("Update, Total rows affected:" & _
MyCommand.ExecuteNonQuery())
'COUNT(*)
MyCommand.CommandText = "SELECT COUNT(*) as TRows FROM my_vb_net"
Console.WriteLine("Total Rows:" & MyCommand.ExecuteScalar())
'Select
Console.WriteLine("Select * FROM my_vb_net")
MyCommand.CommandText = "SELECT * FROM my_vb_net"
Dim MyDataReader As OdbcDataReader
MyDataReader = MyCommand.ExecuteReader
While MyDataReader.Read
If MyDataReader("name") Is DBNull.Value Then
Console.WriteLine("id = " & _
CStr(MyDataReader("id")) & " name = " & _
"NULL")
Else
Console.WriteLine("id = " & _
CStr(MyDataReader("id")) & " name = " & _
CStr(MyDataReader("name")))
End If
End While
'Catch ODBC Exception
Catch MyOdbcException As OdbcException
Dim i As Integer
Console.WriteLine(MyOdbcException.ToString)
'Catch program exception
Catch MyException As Exception
Console.WriteLine(MyException.ToString)
End Try
End SubThis section provides reference material for the MyODBC API, showing supported functions and methods, supported MySQL column types and the corresponding native type in MyODBC, and the error codes returned by MyODBC when a fault occurs.
This section summarizes ODBC routines, categorized by functionality.
For the complete ODBC API reference, please refer to the ODBC Programer's Reference at http://msdn.microsoft.com/library/en-us/odbc/htm/odbcabout_this_manual.asp.
An application can call SQLGetInfo function
to obtain conformance information about MyODBC. To obtain
information about support for a specific function in the driver,
an application can call SQLGetFunctions.
Note: For backward compatibility, the MyODBC 3.51 driver supports all deprecated functions.
The following tables list MyODBC API calls grouped by task:
Connecting to a data source:
| MyODBC | ||||
| Function name | 2.50 | 3.51 | Standard | Purpose |
SQLAllocHandle | No | Yes | ISO 92 | Obtains an environment, connection, statement, or descriptor handle. |
SQLConnect | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Connects to a specific driver by data source name, user ID, and password. |
SQLDriverConnect | Yes | Yes | ODBC | Connects to a specific driver by connection string or requests that the Driver Manager and driver display connection dialog boxes for the user. |
SQLAllocEnv | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Obtains an environment handle allocated from driver. |
SQLAllocConnect | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Obtains a connection handle |
Obtaining information about a driver and data source:
| MyODBC | ||||
| Function name | 2.50 | 3.51 | Standard | Purpose |
SQLDataSources | No | No | ISO 92 | Returns the list of available data sources, handled by the Driver Manager |
SQLDrivers | No | No | ODBC | Returns the list of installed drivers and their attributes, handles by Driver Manager |
SQLGetInfo | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns information about a specific driver and data source. |
SQLGetFunctions | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns supported driver functions. |
SQLGetTypeInfo | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns information about supported data types. |
Setting and retrieving driver attributes:
| MyODBC | ||||
| Function name | 2.50 | 3.51 | Standard | Purpose |
SQLSetConnectAttr | No | Yes | ISO 92 | Sets a connection attribute. |
SQLGetConnectAttr | No | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns the value of a connection attribute. |
SQLSetConnectOption | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Sets a connection option |
SQLGetConnectOption | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Returns the value of a connection option |
SQLSetEnvAttr | No | Yes | ISO 92 | Sets an environment attribute. |
SQLGetEnvAttr | No | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns the value of an environment attribute. |
SQLSetStmtAttr | No | Yes | ISO 92 | Sets a statement attribute. |
SQLGetStmtAttr | No | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns the value of a statement attribute. |
SQLSetStmtOption | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Sets a statement option |
SQLGetStmtOption | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Returns the value of a statement option |
Preparing SQL requests:
| MyODBC | ||||
| Function name | 2.50 | 3.51 | Standard | Purpose |
SQLAllocStmt | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Allocates a statement handle |
SQLPrepare | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Prepares an SQL statement for later execution. |
SQLBindParameter | Yes | Yes | ODBC | Assigns storage for a parameter in an SQL statement. |
SQLGetCursorName | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns the cursor name associated with a statement handle. |
SQLSetCursorName | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Specifies a cursor name. |
SQLSetScrollOptions | Yes | Yes | ODBC | Sets options that control cursor behavior. |
Submitting requests:
| MyODBC | ||||
| Function name | 2.50 | 3.51 | Standard | Purpose |
SQLExecute | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Executes a prepared statement. |
SQLExecDirect | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Executes a statement |
SQLNativeSql | Yes | Yes | ODBC | Returns the text of an SQL statement as translated by the driver. |
SQLDescribeParam | Yes | Yes | ODBC | Returns the description for a specific parameter in a statement. |
SQLNumParams | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns the number of parameters in a statement. |
SQLParamData | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Used in conjunction with SQLPutData to supply
parameter data at execution time. (Useful for long data
values.) |
SQLPutData | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Sends part or all of a data value for a parameter. (Useful for long data values.) |
Retrieving results and information about results:
| MyODBC | ||||
| Function name | 2.50 | 3.51 | Standard | Purpose |
SQLRowCount | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns the number of rows affected by an insert, update, or delete request. |
SQLNumResultCols | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns the number of columns in the result set. |
SQLDescribeCol | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Describes a column in the result set. |
SQLColAttribute | No | Yes | ISO 92 | Describes attributes of a column in the result set. |
SQLColAttributes | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Describes attributes of a column in the result set. |
SQLFetch | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns multiple result rows. |
SQLFetchScroll | No | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns scrollable result rows. |
SQLExtendedFetch | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Returns scrollable result rows. |
SQLSetPos | Yes | Yes | ODBC | Positions a cursor within a fetched block of data and allows an application to refresh data in the rowset or to update or delete data in the result set. |
SQLBulkOperations | No | Yes | ODBC | Performs bulk insertions and bulk bookmark operations, including update, delete, and fetch by bookmark. |
Retrieving error or diagnostic information:
| MyODBC | ||||
| Function name | 2.50 | 3.51 | Standard | Purpose |
SQLError | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Returns additional error or status information |
SQLGetDiagField | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns additional diagnostic information (a single field of the diagnostic data structure). |
SQLGetDiagRec | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns additional diagnostic information (multiple fields of the diagnostic data structure). |
Obtaining information about the data source's system tables (catalog functions) item:
| MyODBC | ||||
| Function name | 2.50 | 3.51 | Standard | Purpose |
SQLColumnPrivileges | Yes | Yes | ODBC | Returns a list of columns and associated privileges for one or more tables. |
SQLColumns | Yes | Yes | X/Open | Returns the list of column names in specified tables. |
SQLForeignKeys | Yes | Yes | ODBC | Returns a list of column names that make up foreign keys, if they exist for a specified table. |
SQLPrimaryKeys | Yes | Yes | ODBC | Returns the list of column names that make up the primary key for a table. |
SQLSpecialColumns | Yes | Yes | X/Open | Returns information about the optimal set of columns that uniquely identifies a row in a specified table, or the columns that are automatically updated when any value in the row is updated by a transaction. |
SQLStatistics | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Returns statistics about a single table and the list of indexes associated with the table. |
SQLTablePrivileges | Yes | Yes | ODBC | Returns a list of tables and the privileges associated with each table. |
SQLTables | Yes | Yes | X/Open | Returns the list of table names stored in a specific data source. |
Performing transactions:
| MyODBC | ||||
| Function name | 2.50 | 3.51 | Standard | Purpose |
SQLTransact | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Commits or rolls back a transaction |
SQLEndTran | No | Yes | ISO 92 | Commits or rolls back a transaction. |
Terminating a statement:
| MyODBC | ||||
| Function name | 2.50 | 3.51 | Standard | Purpose |
SQLFreeStmt | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Ends statement processing, discards pending results, and, optionally, frees all resources associated with the statement handle. |
SQLCloseCursor | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Closes a cursor that has been opened on a statement handle. |
SQLCancel | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Cancels an SQL statement. |
Terminating a connection:
| MyODBC | ||||
| Function name | 2.50 | 3.51 | Standard | Purpose |
SQLDisconnect | Yes | Yes | ISO 92 | Closes the connection. |
SQLFreeHandle | No | Yes | ISO 92 | Releases an environment, connection, statement, or descriptor handle. |
SQLFreeConnect | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Releases connection handle |
SQLFreeEnv | Yes | Yes | Deprecated | Releases an environment handle |
The following table illustrates how driver maps the server data types to default SQL and C data types:
| Native Value | SQL Type | C Type |
bit | SQL_BIT | SQL_C_BIT |
tinyint | SQL_TINYINT | SQL_C_STINYINT |
tinyint unsigned | SQL_TINYINT | SQL_C_UTINYINT |
bigint | SQL_BIGINT | SQL_C_SBIGINT |
bigint unsigned | SQL_BIGINT | SQL_C_UBIGINT |
long varbinary | SQL_LONGVARBINARY | SQL_C_BINARY |
blob | SQL_LONGVARBINARY | SQL_C_BINARY |
longblob | SQL_LONGVARBINARY | SQL_C_BINARY |
tinyblob | SQL_LONGVARBINARY | SQL_C_BINARY |
mediumblob | SQL_LONGVARBINARY | SQL_C_BINARY |
long varchar | SQL_LONGVARCHAR | SQL_C_CHAR |
text | SQL_LONGVARCHAR | SQL_C_CHAR |
mediumtext | SQL_LONGVARCHAR | SQL_C_CHAR |
char | SQL_CHAR | SQL_C_CHAR |
numeric | SQL_NUMERIC | SQL_C_CHAR |
decimal | SQL_DECIMAL | SQL_C_CHAR |
integer | SQL_INTEGER | SQL_C_SLONG |
integer unsigned | SQL_INTEGER | SQL_C_ULONG |
int | SQL_INTEGER | SQL_C_SLONG |
int unsigned | SQL_INTEGER | SQL_C_ULONG |
mediumint | SQL_INTEGER | SQL_C_SLONG |
mediumint unsigned | SQL_INTEGER | SQL_C_ULONG |
smallint | SQL_SMALLINT | SQL_C_SSHORT |
smallint unsigned | SQL_SMALLINT | SQL_C_USHORT |
real | SQL_FLOAT | SQL_C_DOUBLE |
double | SQL_FLOAT | SQL_C_DOUBLE |
float | SQL_REAL | SQL_C_FLOAT |
double precision | SQL_DOUBLE | SQL_C_DOUBLE |
date | SQL_DATE | SQL_C_DATE |
time | SQL_TIME | SQL_C_TIME |
year | SQL_SMALLINT | SQL_C_SHORT |
datetime | SQL_TIMESTAMP | SQL_C_TIMESTAMP |
timestamp | SQL_TIMESTAMP | SQL_C_TIMESTAMP |
text | SQL_VARCHAR | SQL_C_CHAR |
varchar | SQL_VARCHAR | SQL_C_CHAR |
enum | SQL_VARCHAR | SQL_C_CHAR |
set | SQL_VARCHAR | SQL_C_CHAR |
bit | SQL_CHAR | SQL_C_CHAR |
bool | SQL_CHAR | SQL_C_CHAR |
The following tables lists the error codes returned by the driver apart from the server errors.
| Native Code | SQLSTATE 2 | SQLSTATE 3 | Error Message |
| 500 | 01000 | 01000 | General warning |
| 501 | 01004 | 01004 | String data, right truncated |
| 502 | 01S02 | 01S02 | Option value changed |
| 503 | 01S03 | 01S03 | No rows updated/deleted |
| 504 | 01S04 | 01S04 | More than one row updated/deleted |
| 505 | 01S06 | 01S06 | Attempt to fetch before the result set returned the first row set |
| 506 | 07001 | 07002 | SQLBindParameter not used for all parameters |
| 507 | 07005 | 07005 | Prepared statement not a cursor-specification |
| 508 | 07009 | 07009 | Invalid descriptor index |
| 509 | 08002 | 08002 | Connection name in use |
| 510 | 08003 | 08003 | Connection does not exist |
| 511 | 24000 | 24000 | Invalid cursor state |
| 512 | 25000 | 25000 | Invalid transaction state |
| 513 | 25S01 | 25S01 | Transaction state unknown |
| 514 | 34000 | 34000 | Invalid cursor name |
| 515 | S1000 | HY000 | General driver defined error |
| 516 | S1001 | HY001 | Memory allocation error |
| 517 | S1002 | HY002 | Invalid column number |
| 518 | S1003 | HY003 | Invalid application buffer type |
| 519 | S1004 | HY004 | Invalid SQL data type |
| 520 | S1009 | HY009 | Invalid use of null pointer |
| 521 | S1010 | HY010 | Function sequence error |
| 522 | S1011 | HY011 | Attribute can not be set now |
| 523 | S1012 | HY012 | Invalid transaction operation code |
| 524 | S1013 | HY013 | Memory management error |
| 525 | S1015 | HY015 | No cursor name available |
| 526 | S1024 | HY024 | Invalid attribute value |
| 527 | S1090 | HY090 | Invalid string or buffer length |
| 528 | S1091 | HY091 | Invalid descriptor field identifier |
| 529 | S1092 | HY092 | Invalid attribute/option identifier |
| 530 | S1093 | HY093 | Invalid parameter number |
| 531 | S1095 | HY095 | Function type out of range |
| 532 | S1106 | HY106 | Fetch type out of range |
| 533 | S1117 | HY117 | Row value out of range |
| 534 | S1109 | HY109 | Invalid cursor position |
| 535 | S1C00 | HYC00 | Optional feature not implemented |
| 0 | 21S01 | 21S01 | Column count does not match value count |
| 0 | 23000 | 23000 | Integrity constraint violation |
| 0 | 42000 | 42000 | Syntax error or access violation |
| 0 | 42S02 | 42S02 | Base table or view not found |
| 0 | 42S12 | 42S12 | Index not found |
| 0 | 42S21 | 42S21 | Column already exists |
| 0 | 42S22 | 42S22 | Column not found |
| 0 | 08S01 | 08S01 | Communication link failure |
Here are some common notes and tips for using MyODBC within different environments, applications and tools. The notes provided here are based on the experiences of MyODBC developers and users.
This section provides help with common queries and areas of functionality in MySQL and how to use them with MyODBC.
Obtaining the value of column that uses
AUTO_INCREMENT after an
INSERT statement can be achieved in a
number of different ways. To obtain the value immediately
after an INSERT, use a
SELECT query with the
LAST_INSERT_ID() function.
For example, using MyODBC you would execute two separate
statements, the INSERT statement and the
SELECT query to obtain the auto-increment
value.
INSERT INTO tbl (auto,text) VALUES(NULL,'text'); SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();
If you do not require the value within your application, but
do require the value as part of another
INSERT, the entire process can be handled
by executing the following statements:
INSERT INTO tbl (auto,text) VALUES(NULL,'text'); INSERT INTO tbl2 (id,text) VALUES(LAST_INSERT_ID(),'text');
Certain ODBC applications (including Delphi and Access) may have trouble obtaining the auto-increment value using the previous examples. In this case, try the following statement as an alternative:
SELECT * FROM tbl WHERE auto IS NULL;
See Section 22.2.13.3, “How to Get the Unique ID for the Last Inserted Row”.
Support for the dynamic cursor is provided
in MyODBC 3.51, but dynamic cursors are not enabled by
default. You can enable this function within Windows by
selecting the Enable Dynamic Cursor
checkbox within the ODBC data Source Administrator.
On other platforms, you can enable the dynamic cursor by
adding 32 to the OPTION
value when creating the DSN.
The MyODBC driver has been optimized to provide very fast performance. If you experience problems with the performance of MyODBC, or notice a large amount of disk activity for simple queries, there are a number of aspects you should check:
Ensure that
ODBC Tracingis not enabled. With tracing enabled, a lot of information is recorded in the tracing file by the ODBC Manager. You can check, and disable, tracing within Windows using the panel of the ODBC Data Source Administrator. Within Mac OS X, check the panel of ODBC Administrator. See Section 23.1.3.8, “Getting an ODBC Trace File”.Make sure you are using the standard version of the driver, and not the debug version. The debug version includes additional checks and reporting measures.
Disable the MyODBC driver trace and query logs. These options are enabled for each DSN, so make sure to examine only the DSN that you are using in your application. Within Windows, you can disable the MyODBC and query logs by modifying the DSN configuration. Within Mac OS X and Unix, ensure that the driver trace (option value 4) and query logging (option value 524288) are not enabled.
For more information on how to set the query timeout on Microsoft Windows when executing queries through an ODBC connection, read the Microsoft knowledgebase document at http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb%3Ben-us%3B153756.
- 23.1.6.2.1. Using MyODBC with Microsoft Applications
- 23.1.6.2.2. Using MyODBC with Borland Applications
- 23.1.6.2.3. Using MyODBC with ColdFusion
- 23.1.6.2.4. Using MyODBC with OpenOffice
- 23.1.6.2.5. Using MyODBC with Sambar Server
- 23.1.6.2.6. Using MyODBC with Pervasive Software DataJunction
- 23.1.6.2.7. Using MyODBC with SunSystems Vision
Most programs should work with MyODBC, but for each of those listed here, there are specific notes and tips to improve or enhance the way you work with MyODBC and these applications.
With all applications you should ensure that you are using the latest MyODBC drivers, ODBC Manager and any supporting libraries and interfaces used by your application. For example, on Windows, using the latest version of Microsoft Data Access Components (MDAC) will improve the compatibility with ODBC in general, and with the MyODBC driver.
- 23.1.6.2.1.1. Microsoft Access
- 23.1.6.2.1.2. Microsoft Excel and Column Types
- 23.1.6.2.1.3. Microsoft Visual Basic
- 23.1.6.2.1.4. Microsoft Visual InterDev
- 23.1.6.2.1.5. Visual Objects
- 23.1.6.2.1.6. Microsoft ADO
- 23.1.6.2.1.7. Using MyODBC with Active Server Pages (ASP)
- 23.1.6.2.1.8. Using MyODBC with Visual Basic (ADO, DAO and RDO) and ASP
The majority of Microsoft applications have been tested with MyODBC, including Microsoft Office, Microsoft Access and the various programming languages supported within ASP and Microsoft Visual Studio.
If you have problem with MyODBC and your program also works with OLEDB, you should try the OLEDB driver.
To improve the integration between Microsoft Access and MySQL through MyODBC:
For all versions of Access, you should enable the MyODBC
Return matching rowsoption. For Access 2.0, you should additionally enable theSimulate ODBC 1.0option.You should have a
TIMESTAMPcolumn in all tables that you want to be able to update. For maximum portability, don't use a length specification in the column declaration (which is unsupported within MySQL in versions earlier than 4.1).You should have a primary key in each MySQL table you want to use with Access. If not, new or updated rows may show up as
#DELETED#.Use only
DOUBLEfloat fields. Access fails when comparing with single-precision floats. The symptom usually is that new or updated rows may show up as#DELETED#or that you can't find or update rows.If you are using MyODBC to link to a table that has a
BIGINTcolumn, the results are displayed as#DELETED#. The work around solution is:Have one more dummy column with
TIMESTAMPas the data type.Select the
Change BIGINT columns to INToption in the connection dialog in ODBC DSN Administrator.Delete the table link from Access and re-create it.
Old records may still display as
#DELETED#, but newly added/updated records are displayed properly.If you still get the error
Another user has changed your dataafter adding aTIMESTAMPcolumn, the following trick may help you:Don't use a
tabledata sheet view. Instead, create a form with the fields you want, and use thatformdata sheet view. You should set theDefaultValueproperty for theTIMESTAMPcolumn toNOW(). It may be a good idea to hide theTIMESTAMPcolumn from view so your users are not confused.In some cases, Access may generate SQL statements that MySQL can't understand. You can fix this by selecting
"Query|SQLSpecific|Pass-Through"from the Access menu.On Windows NT, Access reports
BLOBcolumns asOLE OBJECTS. If you want to haveMEMOcolumns instead, you should changeBLOBcolumns toTEXTwithALTER TABLE.Access can't always handle the MySQL
DATEcolumn properly. If you have a problem with these, change the columns toDATETIME.If you have in Access a column defined as
BYTE, Access tries to export this asTINYINTinstead ofTINYINT UNSIGNED. This gives you problems if you have values larger than 127 in the column.If you have very large (long) tables in Access, it might take a very long time to open them. Or you might run low on virtual memory and eventually get an
ODBC Query Failederror and the table cannot open. To deal with this, select the following options:Return Matching Rows (2)
Allow BIG Results (8).
These add up to a value of 10 (
OPTION=10).
Some external articles and tips that may be useful when using Access, ODBC and MyODBC:
Optimizing Access ODBC Applications
For a list of tools that can be used with Access and ODBC data sources, refer to converters section for list of available tools.
If you have problems importing data into Microsoft Excel, particularly numerical, date, and time values, this is probably because of a bug in Excel, where the column type of the source data is used to determine the data type when that data is inserted into a cell within the worksheet. The result is that Excel incorrectly identifies the content and this affects both the display format and the data when it is used within calculations.
To address this issue, use the CONCAT()
function in your queries. The use of
CONCAT() forces Excel to treat the value
as a string, which Excel will then parse and usually
correctly identify the embedded information.
However, even with this option, some data may be incorrectly
formatted, even though the source data remains unchanged.
Use the Format Cells option within Excel
to change the format of the displayed information.
To be able to update a table, you must define a primary key for the table.
Visual Basic with ADO can't handle big integers. This means
that some queries like SHOW PROCESSLIST
do not work properly. The fix is to use
OPTION=16384 in the ODBC connect string
or to select the Change BIGINT columns to
INT option in the MyODBC connect screen. You may
also want to select the Return matching
rows option.
If you have a BIGINT in your result, you
may get the error [Microsoft][ODBC Driver Manager]
Driver does not support this parameter. Try
selecting the Change BIGINT columns to
INT option in the MyODBC connect screen.
When you are coding with the ADO API and MyODBC, you need to
pay attention to some default properties that aren't
supported by the MySQL server. For example, using the
CursorLocation Property as
adUseServer returns a result of –1
for the RecordCount Property. To have the
right value, you need to set this property to
adUseClient, as shown in the VB code
here:
Dim myconn As New ADODB.Connection Dim myrs As New Recordset Dim mySQL As String Dim myrows As Long myconn.Open "DSN=MyODBCsample" mySQL = "SELECT * from user" myrs.Source = mySQL Set myrs.ActiveConnection = myconn myrs.CursorLocation = adUseClient myrs.Open myrows = myrs.RecordCount myrs.Close myconn.Close
Another workaround is to use a SELECT
COUNT(*) statement for a similar query to get the
correct row count.
To find the number of rows affected by a specific SQL
statement in ADO, use the RecordsAffected
property in the ADO execute method. For more information on
the usage of execute method, refer to
http://msdn.microsoft.com/library/default.asp?url=/library/en-us/ado270/htm/mdmthcnnexecute.asp.
For information, see ActiveX Data Objects(ADO) Frequently Asked Questions.
You should select the Return matching
rows option in the DSN.
For more information about how to access MySQL via ASP using MyODBC, refer to the following articles:
A Frequently Asked Questions list for ASP can be found at http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=/Support/ActiveServer/faq/data/adofaq.asp.
Some articles that may help with Visual Basic and ASP:
MySQL BLOB columns and Visual Basic 6 by Mike Hillyer (
<mike@openwin.org>).How to map Visual basic data type to MySQL types by Mike Hillyer (
<mike@openwin.org>).
With all Borland applications where the Borland Database Engine (BDE) is used, follow these steps to improve compatibility:
Update to BDE 3.2 or newer.
Enable the
Don't optimize column widthsoption in the DSN.Enabled the
Return matching rowsoption in the DSN.
When you start a query, you can use the
Active property or the
Open method. Note that
Active starts by automatically issuing a
SELECT * FROM ... query. That may not be
a good thing if your tables are large.
Also, here is some potentially useful Delphi code that sets
up both an ODBC entry and a BDE entry for MyODBC. The BDE
entry requires a BDE Alias Editor that is free at a Delphi
Super Page near you. (Thanks to Bryan Brunton
<bryan@flesherfab.com> for this):
fReg:= TRegistry.Create;
fReg.OpenKey('\Software\ODBC\ODBC.INI\DocumentsFab', True);
fReg.WriteString('Database', 'Documents');
fReg.WriteString('Description', ' ');
fReg.WriteString('Driver', 'C:\WINNT\System32\myodbc.dll');
fReg.WriteString('Flag', '1');
fReg.WriteString('Password', '');
fReg.WriteString('Port', ' ');
fReg.WriteString('Server', 'xmark');
fReg.WriteString('User', 'winuser');
fReg.OpenKey('\Software\ODBC\ODBC.INI\ODBC Data Sources', True);
fReg.WriteString('DocumentsFab', 'MySQL');
fReg.CloseKey;
fReg.Free;
Memo1.Lines.Add('DATABASE NAME=');
Memo1.Lines.Add('USER NAME=');
Memo1.Lines.Add('ODBC DSN=DocumentsFab');
Memo1.Lines.Add('OPEN MODE=READ/WRITE');
Memo1.Lines.Add('BATCH COUNT=200');
Memo1.Lines.Add('LANGDRIVER=');
Memo1.Lines.Add('MAX ROWS=-1');
Memo1.Lines.Add('SCHEMA CACHE DIR=');
Memo1.Lines.Add('SCHEMA CACHE SIZE=8');
Memo1.Lines.Add('SCHEMA CACHE TIME=-1');
Memo1.Lines.Add('SQLPASSTHRU MODE=SHARED AUTOCOMMIT');
Memo1.Lines.Add('SQLQRYMODE=');
Memo1.Lines.Add('ENABLE SCHEMA CACHE=FALSE');
Memo1.Lines.Add('ENABLE BCD=FALSE');
Memo1.Lines.Add('ROWSET SIZE=20');
Memo1.Lines.Add('BLOBS TO CACHE=64');
Memo1.Lines.Add('BLOB SIZE=32');
AliasEditor.Add('DocumentsFab','MySQL',Memo1.Lines);
The following information is taken from the ColdFusion documentation:
Use the following information to configure ColdFusion Server
for Linux to use the unixODBC driver with
MyODBC for MySQL data sources. Allaire has verified that
MyODBC 2.50.26 works with MySQL 3.22.27 and ColdFusion for
Linux. (Any newer version should also work.) You can download
MyODBC at
http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/odbc/.
ColdFusion version 4.5.1 allows you to us the ColdFusion
Administrator to add the MySQL data source. However, the
driver is not included with ColdFusion version 4.5.1. Before
the MySQL driver appears in the ODBC data sources drop-down
list, you must build and copy the MyODBC driver to
/opt/coldfusion/lib/libmyodbc.so.
The Contrib directory contains the program
mydsn-
which allows you to build and remove the DSN registry file for
the MyODBC driver on ColdFusion applications.
xxx.zip
For more information and guides on using ColdFusion and MyODBC, see the following external sites:
Refer to MySQL ColdFusion unixODBC MyODBC and Solaris - how to succeed
ColdFusion (on Solaris and NT with service pack 5), How-to: MySQL and ColdFusion.
Troubleshooting Data Sources and Database Connectivity for Unix Platforms.
Open Office (http://www.openoffice.org) How-to: MySQL + OpenOffice. How-to: OpenOffice + MyODBC + unixODBC.
Sambar Server (http://www.sambarserver.info) How-to: MyODBC + SambarServer + MySQL.
The following section details some common errors and their suggested fix or alternative solution. If you are still experiencing problems, use the MyODBC mailing list; see Section 23.1.7.1, “MyODBC Community Support”.
Many problems can be resolved by upgrading your MyODBC drivers to the latest available release. On Windows, you should also make sure that you have the latest versions of the Microsoft Data Access Components (MDAC) installed.
24.1.6.3.1:
Question:
Are MyODBC 2.50 applications compatible with MyODBC 3.51?
Answer:
Applications based on MyODBC 2.50 should work fine with MyODBC 3.51 and later versions. If you find something is not working with the latest version of MyODBC which previously worked under an earlier version, please file a bug report. See Section 23.1.7.2, “How to Report MyODBC Problems or Bugs”.
24.1.6.3.2:
Question:
The following error is reported when using transactions:
Transactions are not enabled
Answer:
This error indicates that you are trying to use
transactions with a MySQL table that does not support
transactions. Transactions are supported within MySQL when
using the InnoDB and
BDB database engines.
You should check the following before continuing:
Verify that your MySQL server supports a transactional database engine. Use
SHOW ENGINESto obtain a list of the available engine types.Verify that the tables you are updating use a transaction database engine.
Ensure that you have not enabled the
disable transactionsoption in your DSN.
24.1.6.3.3:
Question:
The following error is reported when I submit a query:
Cursor not found
Answer:
This occurs because the application is using the old MyODBC 2.50 version, and it did not set the cursor name explicitly through SQLSetCursorName. The fix is to upgrade to MyODBC 3.51 version.
24.1.6.3.4:
Question:
Access reports records as #DELETED#
when inserting or updating records in linked tables.
Answer:
If the inserted or updated records are shown as
#DELETED# in the access, then:
If you are using Access 2000, you should get and install the newest (version 2.6 or higher) Microsoft MDAC (
Microsoft Data Access Components) from http://www.microsoft.com/data/. This fixes a bug in Access that when you export data to MySQL, the table and column names aren't specified. Another way to work around this bug is to upgrade to MyODBC 2.50.33 or higher and MySQL 3.23.x or higher, which together provide a workaround for the problem.You should also get and apply the Microsoft Jet 4.0 Service Pack 5 (SP5) which can be found at http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;q239114. This fixes some cases where columns are marked as
#DELETED#in Access.Note: If you are using MySQL 3.22, you must apply the MDAC patch and use MyODBC 2.50.32 or 2.50.34 and up to work around this problem.
For all versions of Access, you should enable the MyODBC
Return matching rowsoption. For Access 2.0, you should additionally enable theSimulate ODBC 1.0option.You should have a timestamp in all tables that you want to be able to update..
You should have a primary key in the table. If not, new or updated rows may show up as
#DELETED#.Use only
DOUBLEfloat fields. Access fails when comparing with single-precision floats. The symptom usually is that new or updated rows may show up as#DELETED#or that you can't find or update rows.If you are using MyODBC to link to a table that has a
BIGINTcolumn, the results are displayed as#DELETED. The work around solution is:Have one more dummy column with
TIMESTAMPas the data type.Select the
Change BIGINT columns to INToption in the connection dialog in ODBC DSN Administrator.Delete the table link from Access and re-create it.
Old records still display as
#DELETED#, but newly added/updated records are displayed properly.
24.1.6.3.5:
Question:
How do I handle Write Conflicts or Row Location errors?
Answer:
If you see the following errors, select the
Return Matching Rows option in the DSN
configuration dialog, or specify
OPTION=2, as the connection parameter:
Write Conflict. Another user has changed your data. Row cannot be located for updating. Some values may have been changed since it was last read.
24.1.6.3.6:
Question:
Exporting data from Access 97 to MySQL reports a
Syntax Error.
Answer:
This error is specific to Access 97 and versions of MyODBC earlier than 3.51.02. Update to the latest version of the MyODBC driver to resolve this problem.
24.1.6.3.7:
Question:
Exporting data from Microsoft DTS to MySQL reports a
Syntax Error.
Answer:
This error occurs only with MySQL tables using the
TEXT or VARCHAR data
types. You can fix this error by upgrading your MyODBC
driver to version 3.51.02 or higher.
24.1.6.3.8:
Question:
Using ODBC.NET with MyODBC, while fetching empty string (0 length), it starts giving the SQL_NO_DATA exception.
Answer:
You can get the patch that addresses this problem from http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;q319243.
24.1.6.3.9:
Question:
Using SELECT COUNT(*) FROM
within
Visual Basic and ASP returns an error.
tbl_name
Answer:
This error occurs because the COUNT(*)
expression is returning a BIGINT, and
ADO can't make sense of a number this big. Select the
Change BIGINT columns to INT option
(option value 16384).
24.1.6.3.10:
Question:
Using the AppendChunk() or
GetChunk() ADO methods, the
Multiple-step operation generated errors. Check
each status value error is returned.
Answer:
The GetChunk() and
AppendChunk() methods from ADO doesn't
work as expected when the cursor location is specified as
adUseServer. On the other hand, you can
overcome this error by using
adUseClient.
A simple example can be found from http://www.dwam.net/iishelp/ado/docs/adomth02_4.htm
24.1.6.3.11:
Question:
Access Returns Another user had modified the
record that you have modified while editing
records on a Linked Table.
Answer:
In most cases, this can be solved by doing one of the following things:
Add a primary key for the table if one doesn't exist.
Add a timestamp column if one doesn't exist.
Only use double-precision float fields. Some programs may fail when they compare single-precision floats.
If these strategies don't help, you should start by making a log file from the ODBC manager (the log you get when requesting logs from ODBCADMIN) and a MyODBC log to help you figure out why things go wrong. For instructions, see Section 23.1.3.8, “Getting an ODBC Trace File”.
There are many different places where you can get support for using MyODBC. You should always try the MyODBC Mailing List or MyODBC Forum. See Section 23.1.7.1, “MyODBC Community Support”, for help before reporting a specific bug or issue to MySQL.
MySQL AB provides assistance to the user community by means of
its mailing lists. For MyODBC-related issues, you can get help
from experienced users by using the
<myodbc@lists.mysql.com> mailing list. Archives are
available online at
http://lists.mysql.com/myodbc.
For information about subscribing to MySQL mailing lists or to browse list archives, visit http://lists.mysql.com/. See Section 1.7.1, “MySQL Mailing Lists”.
Community support from experienced users is also available through the MyODBC Forum. You may also find help from other users in the other MySQL Forums, located at http://forums.mysql.com. See Section 1.7.2, “MySQL Community Support at the MySQL Forums”.
If you encounter difficulties or problems with MyODBC, you
should start by making a log file from the ODBC
Manager (the log you get when requesting logs from
ODBC ADMIN) and MyODBC. The procedure for
doing this is described in
Section 23.1.3.8, “Getting an ODBC Trace File”.
Check the MyODBC trace file to find out what could be wrong. You
should be able to determine what statements were issued by
searching for the string >mysql_real_query
in the myodbc.log file.
You should also try issuing the statements from the
mysql client program or from
admndemo. This helps you determine whether
the error is in MyODBC or MySQL.
If you find out something is wrong, please only send the
relevant rows (maximum 40 rows) to the myodbc
mailing list. See Section 1.7.1, “MySQL Mailing Lists”. Please never
send the whole MyODBC or ODBC log file!
You should ideally include the following information with the email:
Operating system and version
MyODBC version
ODBC Driver Manager type and version
MySQL server version
ODBC trace from Driver Manager
MyODBC log file from MyODBC driver
Simple reproducible sample
Remember that the more information you can supply to us, the more likely it is that we can fix the problem!
Also, before posting the bug, check the MyODBC mailing list archive at http://lists.mysql.com/myodbc.
If you are unable to find out what's wrong, the last option is
to create an archive in tar or Zip format
that contains a MyODBC trace file, the ODBC log file, and a
README file that explains the problem. You
can send this to ftp://ftp.mysql.com/pub/mysql/upload/. Only MySQL
engineers have access to the files you upload, and we are very
discreet with the data.
If you can create a program that also demonstrates the problem, please include it in the archive as well.
If the program works with another SQL server, you should include an ODBC log file where you perform exactly the same SQL statements so that we can compare the results between the two systems.
Remember that the more information you can supply to us, the more likely it is that we can fix the problem.
You can send a patch or suggest a better solution for any
existing code or problems by sending a mail message to
<myodbc@lists.mysql.com>.
MySQL Connector/NET enables developers to easily create .NET applications that require secure, high-performance data connectivity with MySQL. It implements the required ADO.NET interfaces and integrates into ADO.NET aware tools. Developers can build applications using their choice of .NET languages. MySQL Connector/NET is a fully managed ADO.NET driver written in 100% pure C#.
MySQL Connector/NET includes full support for:
MySQL 5.0 features (such as stored procedures)
MySQL 4.1 features (server-side prepared statements, Unicode, and shared memory access, and so forth)
Large-packet support for sending and receiving rows and BLOBs up to 2 gigabytes in size.
Protocol compression which allows for compressing the data stream between the client and server.
Support for connecting using TCP/IP sockets, named pipes, or shared memory on Windows.
Support for connecting using TCP/IP sockets or Unix sockets on Unix.
Support for the Open Source Mono framework developed by Novell.
Fully managed, does not utilize the MySQL client library.
The developers of MySQL Connector/NET greatly value the input of our users in the software development process. If you find MySQL Connector/NET lacking some feature important to you, or if you discover a bug and need to file a bug report, please use the instructions in Section 1.8, “How to Report Bugs or Problems”.
Additional resources
Community support for MySQL Connector/NET can be found through the forums at http://forums.mysql.com.
Community support for MySQL Connector/NET can also be found through the mailing lists at http://lists.mysql.com.
Paid support is available from MySQL AB. Additional information is available at http://www.mysql.com/support/.
This document is intended as a user's guide to MySQL Connector/NET and
not as a syntax reference. If you need detailed syntax information
you should read the Documentation.chm file
included with the MySQL Connector/NET distribution.
MySQL Connector/NET runs on any platform that supports the .NET framework. The .NET framework is primarily supported on recent versions of Microsoft Windows, and is supported on Linux through the Open Source Mono framework developed by Novell (see http://www.mono-project.com).
MySQL Connector/NET is installed through the use of a Windows
Installer (.msi) installation package, which
can be used to install MySQL Connector/NET on all Windows operating
systems. The MSI package in contained within a ZIP archive named
mysql-connector-net-,
where version.zipversion indicates the
MySQL Connector/NET version.
MySQL Connector/NET is available for download from http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/net/1.0.html.
The Windows Installer engine was updated with the release of Windows XP; those using an older version can reference this Microsoft Knowledge Base article for information on upgrading to the latest version.
To install MySQL Connector/NET, right-click on the MSI file and select
. The installation will begin
automatically after the installer prompts you for your
installation preferences. The Typical
installation is recommended for most users.
If you are having problems running the installer, you can download
a ZIP file without an installer as an alternative. That file is
called
mysql-connector-net-.
Using a ZIP program, unpack it to a directory of your choice.
version-noinstall.zip
Unless you choose otherwise, MySQL Connector/NET is installed in
C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Connector Net
, where
X.X.XX.X.X is replaced with the version of
MySQL Connector/NET you are installing. New installations do not
overwrite existing versions of MySQL Connector/NET.
MySQL Connector/NET comprises several classes that are used to connect to the database, execute queries and statements, and manage query results.
The following are the major classes of MySQL Connector/NET:
MySqlCommand: Represents an SQL statement to execute against a MySQL database.MySqlCommandBuilder: Automatically generates single-table commands used to reconcile changes made to a DataSet with the associated MySQL database.MySqlConnection: Represents an open connection to a MySQL Server database.MySqlDataAdapter: Represents a set of data commands and a database connection that are used to fill a dataset and update a MySQL database.MySqlDataReader: Provides a means of reading a forward-only stream of rows from a MySQL database.MySqlException: The exception that is thrown when MySQL returns an error.MySqlHelper: Helper class that makes it easier to work with the provider.MySqlTransaction: Represents an SQL transaction to be made in a MySQL database.
Each of these objects will be described in the upcoming sections.
These sections are intended to be an overview of the major classes
of MySQL Connector/NET, and not a syntax reference. If you need more
detailed information you should read the
Documentation.chm file included with the
MySQL Connector/NET distribution.
The MySqlCommand class represents an SQL
statement to execute against a MySQL database.
Note: Prior versions of the provider used the '@' symbol to mark parameters in SQL. This is incompatible with MySQL user variables, so the provider now uses the '?' symbol to locate parameters in SQL. To support older code, you can set 'old syntax=yes' in your connection string. If you do this, please be aware that an exception will not be thrown if you fail to define a parameter that you intended to use in your SQL.
The following properties are available:
CommandText: Gets or sets the SQL statement to execute at the data source.CommandTimeout: Gets or sets the wait time before terminating the attempt to execute a command and generating an error.CommandType: Gets or sets a value indicating how the CommandText property is to be interpreted. Possible types areStoredProcedure,TableDirect, andText.Connection: Gets or sets the MySqlConnection used by this instance of the MySqlCommand.IsPrepared: Is true if this command has been prepared, false otherwise.Parameters: Gets the MySqlParameterCollection.Transaction: Gets or sets the MySqlTransaction within which the MySqlCommand executes.UpdatedRowSource: Gets or sets how command results are applied to the DataRow when used by the Update method of the DbDataAdapter.
The following methods are available:
Cancel: Attempts to cancel the execution of a MySqlCommand. This operation is not supported.Clone: Creates a clone of this MySqlCommand object. CommandText, Connection, and Transaction properties are included as well as the entire parameter list.CreateParameter: Creates a new instance of a MySqlParameter object.Dispose: Disposes of this instance of MySqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery: Executes an SQL statement against the connection and returns the number of rows affected.ExecuteReader: Sends the CommandText to the Connection and builds a MySqlDataReader.ExecuteScalar: Executes the query, and returns the first column of the first row in the result set returned by the query. Extra columns or rows are ignored.Prepare: Creates a prepared version of the command on an instance of MySQL Server.
The following example creates a MySqlCommand and a MySqlConnection. The MySqlConnection is opened and set as the Connection for the MySqlCommand. The example then calls ExecuteNonQuery, and closes the connection. To accomplish this, the ExecuteNonQuery is passed a connection string and a query string that is an SQL INSERT statement.
The following example show how to use the MySqlCommand class with VB.NET:
Public Sub InsertRow(myConnectionString As String)
' If the connection string is null, use a default.
If myConnectionString = "" Then
myConnectionString = "Database=Test;Data Source=localhost;User Id=username;Password=pass"
End If
Dim myConnection As New MySqlConnection(myConnectionString)
Dim myInsertQuery As String = "INSERT INTO Orders (id, customerId, amount) Values(1001, 23, 30.66)"
Dim myCommand As New MySqlCommand(myInsertQuery)
myCommand.Connection = myConnection
myConnection.Open()
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery()
myCommand.Connection.Close()
End Sub
The following example show how to use the MySqlCommand class with C#:
public void InsertRow(string myConnectionString)
{
// If the connection string is null, use a default.
if(myConnectionString == "")
{
myConnectionString = "Database=Test;Data Source=localhost;User Id=username;Password=pass";
}
MySqlConnection myConnection = new MySqlConnection(myConnectionString);
string myInsertQuery = "INSERT INTO Orders (id, customerId, amount) Values(1001, 23, 30.66)";
MySqlCommand myCommand = new MySqlCommand(myInsertQuery);
myCommand.Connection = myConnection;
myConnection.Open();
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
myCommand.Connection.Close();
}
The MySqlDataAdapter does not automatically generate the SQL statements required to reconcile changes made to a DataSet with the associated instance of MySQL. However, you can create a MySqlCommandBuilder object to automatically generate SQL statements for single-table updates if you set the SelectCommand property of the MySqlDataAdapter. Then, any additional SQL statements that you do not set are generated by the MySqlCommandBuilder.
The MySqlCommandBuilder registers itself as a listener for OnRowUpdating events whenever you set the DataAdapter property. You can only associate one MySqlDataAdapter or MySqlCommandBuilder object with each other at one time.
To generate INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements, the MySqlCommandBuilder uses the SelectCommand property to retrieve a required set of metadata automatically. If you change the SelectCommand after the metadata has is retrieved (for example, after the first update), you should call the RefreshSchema method to update the metadata.
The SelectCommand must also return at least one primary key or unique column. If none are present, an InvalidOperation exception is generated, and the commands are not generated.
The MySqlCommandBuilder also uses the Connection, CommandTimeout, and Transaction properties referenced by the SelectCommand. The user should call RefreshSchema if any of these properties are modified, or if the SelectCommand itself is replaced. Otherwise the InsertCommand, UpdateCommand, and DeleteCommand properties retain their previous values.
If you call Dispose, the MySqlCommandBuilder is disassociated from the MySqlDataAdapter, and the generated commands are no longer used.
The following properties are available:
DataAdapter: The MySqlCommandBuilder registers itself as a listener for RowUpdating events that are generated by the MySqlDataAdapter specified in this property. When you create a new instance MySqlCommandBuilder, any existing MySqlCommandBuilder associated with this MySqlDataAdapter is released.QuotePrefix,QuoteSuffix: Database objects in MySQL can contain special characters such as spaces that would make normal SQL strings impossible to correctly parse. Use of the QuotePrefix and the QuoteSuffix properties allows the MySqlCommandBuilder to build SQL commands that handle this situation.
The following methods are available:
DeriveParameters: Retrieves parameter information from the stored procedure specified in the MySqlCommand and populates the Parameters collection of the specified MySqlCommand object. This method is not currently supported because stored procedures are not available in MySql.GetDeleteCommand: Gets the automatically generated MySqlCommand object required to perform deletions on the database.GetInsertCommand: Gets the automatically generated MySqlCommand object required to perform insertions on the database.GetUpdateCommand: Gets the automatically generated MySqlCommand object required to perform updates on the database.RefreshSchema: Refreshes the database schema information used to generate INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements.
The following example uses the MySqlCommand, along MySqlDataAdapter and MySqlConnection, to select rows from a data source. The example is passed an initialized DataSet, a connection string, a query string that is an SQL SELECT statement, and a string that is the name of the database table. The example then creates a MySqlCommandBuilder.
The following example shows how to use the MySqlCommandBuilder class with VB.NET:
Public Shared Function SelectRows(myConnection As String, mySelectQuery As String, myTableName As String) As DataSet
Dim myConn As New MySqlConnection(myConnection)
Dim myDataAdapter As New MySqlDataAdapter()
myDataAdapter.SelectCommand = New MySqlCommand(mySelectQuery, myConn)
Dim cb As SqlCommandBuilder = New MySqlCommandBuilder(myDataAdapter)
myConn.Open()
Dim ds As DataSet = New DataSet
myDataAdapter.Fill(ds, myTableName)
' Code to modify data in DataSet here
' Without the MySqlCommandBuilder this line would fail.
myDataAdapter.Update(ds, myTableName)
myConn.Close()
End Function 'SelectRows
The following example shows how to use the MySqlCommandBuilder class with C#:
public static DataSet SelectRows(string myConnection, string mySelectQuery, string myTableName)
{
MySqlConnection myConn = new MySqlConnection(myConnection);
MySqlDataAdapter myDataAdapter = new MySqlDataAdapter();
myDataAdapter.SelectCommand = new MySqlCommand(mySelectQuery, myConn);
MySqlCommandBuilder cb = new MySqlCommandBuilder(myDataAdapter);
myConn.Open();
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
myDataAdapter.Fill(ds, myTableName);
//code to modify data in DataSet here
//Without the MySqlCommandBuilder this line would fail
myDataAdapter.Update(ds, myTableName);
myConn.Close();
return ds;
}
A MySqlConnection object represents a session to a MySQL Server data source. When you create an instance of MySqlConnection, all properties are set to their initial values. For a list of these values, see the MySqlConnection constructor.
If the MySqlConnection goes out of scope, it is not closed. Therefore, you must explicitly close the connection by calling Close or Dispose.
The following properties are available:
ConnectionString: Gets or sets the string used to connect to a MySQL Server database.ConnectionTimeout: Gets the time to wait while trying to establish a connection before terminating the attempt and generating an error.Database: Gets the name of the current database or the database to be used after a connection is opened.DataSource: Gets the name of the MySQL server to which to connect.ServerThread: Returns the id of the server thread this connection is executing on.ServerVersion: Gets a string containing the version of the MySQL server to which the client is connected.State: Gets the current state of the connection.UseConnection: Indicates if this connection should use compression when communicating with the server.
The following methods are available:
BeginTransaction: Begins a database transaction.ChangeDatabase: Changes the current database for an open MySqlConnection.Close: Closes the connection to the database. This is the preferred method of closing any open connection.CreateCommand: Creates and returns a MySqlCommand object associated with the MySqlConnection.Dispose: Releases the resources used by the MySqlConnection.Open: Opens a database connection with the property settings specified by the ConnectionString.Ping: Pings the MySQL server.
The following example creates a MySqlCommand and a MySqlConnection. The MySqlConnection is opened and set as the Connection for the MySqlCommand. The example then calls ExecuteNonQuery, and closes the connection. To accomplish this, the ExecuteNonQuery is passed a connection string and a query string that is an SQL INSERT statement.
The following example shows how to use the MySqlConnection class with VB.NET:
Public Sub InsertRow(myConnectionString As String)
' If the connection string is null, use a default.
If myConnectionString = "" Then
myConnectionString = "Database=Test;Data Source=localhost;User Id=username;Password=pass"
End If
Dim myConnection As New MySqlConnection(myConnectionString)
Dim myInsertQuery As String = "INSERT INTO Orders (id, customerId, amount) Values(1001, 23, 30.66)"
Dim myCommand As New MySqlCommand(myInsertQuery)
myCommand.Connection = myConnection
myConnection.Open()
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery()
myCommand.Connection.Close()
End Sub
The following example shows how to use the MySqlConnection class with C#:
public void InsertRow(string myConnectionString)
{
// If the connection string is null, use a default.
if(myConnectionString == "")
{
myConnectionString = "Database=Test;Data Source=localhost;User Id=username;Password=pass";
}
MySqlConnection myConnection = new MySqlConnection(myConnectionString);
string myInsertQuery = "INSERT INTO Orders (id, customerId, amount) Values(1001, 23, 30.66)";
MySqlCommand myCommand = new MySqlCommand(myInsertQuery);
myCommand.Connection = myConnection;
myConnection.Open();
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
myCommand.Connection.Close();
}
The MySQLDataAdapter serves as a bridge between a DataSet and MySQL for retrieving and saving data. The MySQLDataAdapter provides this bridge by mapping Fill, which changes the data in the DataSet to match the data in the data source, and Update, which changes the data in the data source to match the data in the DataSet, using the appropriate SQL statements against the data source.
When the MySQLDataAdapter fills a DataSet, it will create the necessary tables and columns for the returned data if they do not already exist. However, primary key information will not be included in the implicitly created schema unless the MissingSchemaAction property is set to AddWithKey. You may also have the MySQLDataAdapter create the schema of the DataSet, including primary key information, before filling it with data using FillSchema.
MySQLDataAdapter is used in conjunction with MySqlConnection and MySqlCommand to increase performance when connecting to a MySQL database.
The MySQLDataAdapter also includes the SelectCommand, InsertCommand, DeleteCommand, UpdateCommand, and TableMappings properties to facilitate the loading and updating of data.
The following properties are available:
AcceptChangesDuringFill: Gets or sets a value indicating whether AcceptChanges is called on a DataRow after it is added to the DataTable during any of the Fill operations.ContinueUpdateOnError: Gets or sets a value that specifies whether to generate an exception when an error is encountered during a row update.DeleteCommand: Gets or sets an SQL statement or stored procedure used to delete records from the data set.InsertCommand: Gets or sets an SQL statement or stored procedure used to insert records into the data set.MissingMappingAction: Determines the action to take when incoming data does not have a matching table or column.MissingSchemaAction: Determines the action to take when existing DataSet schema does not match incoming data.SelectCommand: Gets or sets an SQL statement or stored procedure used to select records in the data source.TableMappings: Gets a collection that provides the master mapping between a source table and a DataTable.UpdateCommand: Gets or sets an SQL statement or stored procedure used to updated records in the data source.
The following methods are available:
Fill: Adds or refreshes rows in the DataSet to match those in the data source using the DataSet name, and creates a DataTable named "Table".FillSchema: Adds a DataTable named "Table" to the specified DataSet and configures the schema to match that in the data source based on the specified SchemaType.GetFillParameters: Gets the parameters set by the user when executing an SQL SELECT statement.Update: Calls the respective INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements for each inserted, updated, or deleted row in the specified DataSet.
The following example creates a MySqlCommand and a MySqlConnection. The MySqlConnection is opened and set as the Connection for the MySqlCommand. The example then calls ExecuteNonQuery, and closes the connection. To accomplish this, the ExecuteNonQuery is passed a connection string and a query string that is an SQL INSERT statement.
The following example shows how to use the MySqlDataAdapter class with VB.NET:
Public Function SelectRows(dataSet As DataSet, connection As String, query As String) As DataSet
Dim conn As New MySqlConnection(connection)
Dim adapter As New MySqlDataAdapter()
adapter.SelectCommand = new MySqlCommand(query, conn)
adapter.Fill(dataset)
Return dataset
End Function
The following example shows how to use the MySqlDataAdapter class with C#:
public DataSet SelectRows(DataSet dataset,string connection,string query)
{
MySqlConnection conn = new MySqlConnection(connection);
MySqlDataAdapter adapter = new MySqlDataAdapter();
adapter.SelectCommand = new MySqlCommand(query, conn);
adapter.Fill(dataset);
return dataset;
}
The MySqlDataReader class provides a means of reading a forward-only stream of rows from a MySQL database.
To create a MySQLDataReader, you must call the ExecuteReader method of the MySqlCommand object, rather than directly using a constructor.
While the MySqlDataReader is in use, the associated MySqlConnection is busy serving the MySqlDataReader, and no other operations can be performed on the MySqlConnection other than closing it. This is the case until the Close method of the MySqlDataReader is called.
IsClosed and RecordsAffected are the only properties that you can call after the MySqlDataReader is closed. Though the RecordsAffected property may be accessed at any time while the MySqlDataReader exists, always call Close before returning the value of RecordsAffected to ensure an accurate return value.
For optimal performance, MySqlDataReader avoids creating unnecessary objects or making unnecessary copies of data. As a result, multiple calls to methods such as GetValue return a reference to the same object. Use caution if you are modifying the underlying value of the objects returned by methods such as GetValue.
The following properties are available:
Depth: Gets a value indicating the depth of nesting for the current row. This method is not supported currently and always returns 0.FieldCount: Gets the number of columns in the current row.HasRows: Gets a value indicating whether the MySqlDataReader contains one or more rows.IsClosed: Gets a value indicating whether the data reader is closed.Item: Gets the value of a column in its native format. In C#, this property is the indexer for the MySqlDataReader class.RecordsAffected: Gets the number of rows changed, inserted, or deleted by execution of the SQL statement.
The following methods are available:
Close: Closes the MySqlDataReader object.GetBoolean: Gets the value of the specified column as a Boolean.GetByte: Gets the value of the specified column as a byte.GetBytes: Reads a stream of bytes from the specified column offset into the buffer an array starting at the given buffer offset.GetChar: Gets the value of the specified column as a single character.GetChars: Reads a stream of characters from the specified column offset into the buffer as an array starting at the given buffer offset.GetDataTypeName: Gets the name of the source data type.GetDateTime: Gets the value of the specified column as a DateTime object.GetDecimal: Gets the value of the specified column as a Decimal object.GetDouble: Gets the value of the specified column as a double-precision floating point number.GetFieldType: Gets the Type that is the data type of the object.GetFloat: Gets the value of the specified column as a single-precision floating point number.GetGuid: Gets the value of the specified column as a GUID.GetInt16: Gets the value of the specified column as a 16-bit signed integer.GetInt32: Gets the value of the specified column as a 32-bit signed integer.GetInt64: Gets the value of the specified column as a 64-bit signed integer.GetMySqlDateTime: Gets the value of the specified column as a MySqlDateTime object.GetName: Gets the name of the specified column.GetOrdinal: Gets the column ordinal, given the name of the column.GetSchemaTable: Returns a DataTable that describes the column metadata of the MySqlDataReader.GetString: Gets the value of the specified column as a String object.GetTimeSpan: Gets the value of the specified column as a TimeSpan object.GetUInt16: Gets the value of the specified column as a 16-bit unsigned integer.GetUInt32: Gets the value of the specified column as a 32-bit unsigned integer.GetUInt64: Gets the value of the specified column as a 64-bit unsigned integer.GetValue: Gets the value of the specified column in its native format.GetValues: Gets all attribute columns in the collection for the current row.IsDBNull: Gets a value indicating whether the column contains non-existent or missing values.NextResult: Advances the data reader to the next result, when reading the results of batch SQL statements.Read: Advances the MySqlDataReader to the next record.
The following example creates a MySqlConnection, a MySqlCommand, and a MySqlDataReader. The example reads through the data, writing it out to the console. Finally, the example closes the MySqlDataReader, then the MySqlConnection
The following example shows how to use the MySqlDataReader class with VB.NET:
Public Sub ReadMyData(myConnString As String)
Dim mySelectQuery As String = "SELECT OrderID, CustomerID FROM Orders"
Dim myConnection As New MySqlConnection(myConnString)
Dim myCommand As New MySqlCommand(mySelectQuery, myConnection)
myConnection.Open()
Dim myReader As MySqlDataReader
myReader = myCommand.ExecuteReader()
' Always call Read before accessing data.
While myReader.Read()
Console.WriteLine((myReader.GetInt32(0) & ", " & myReader.GetString(1)))
End While
' always call Close when done reading.
myReader.Close()
' Close the connection when done with it.
myConnection.Close()
End Sub 'ReadMyData
The following example shows how to use the MySqlDataReader class with C#:
public void ReadMyData(string myConnString) {
string mySelectQuery = "SELECT OrderID, CustomerID FROM Orders";
MySqlConnection myConnection = new MySqlConnection(myConnString);
MySqlCommand myCommand = new MySqlCommand(mySelectQuery,myConnection);
myConnection.Open();
MySqlDataReader myReader;
myReader = myCommand.ExecuteReader();
// Always call Read before accessing data.
while (myReader.Read()) {
Console.WriteLine(myReader.GetInt32(0) + ", " + myReader.GetString(1));
}
// always call Close when done reading.
myReader.Close();
// Close the connection when done with it.
myConnection.Close();
}
This class is created whenever the MySql Data Provider encounters an error generated from the server.
Any open connections are not automatically closed when an exception is thrown. If the client application determines that the exception is fatal, it should close any open MySqlDataReader objects or MySqlConnection objects.
The following properties are available:
HelpLink: Gets or sets a link to the help file associated with this exception.InnerException: Gets the Exception instance that caused the current exception.IsFatal: True if this exception was fatal and cause the closing of the connection, false otherwise.Message: Gets a message that describes the current exception.Number: Gets a number that identifies the type of error.Source: Gets or sets the name of the application or the object that causes the error.StackTrace: Gets a string representation of the frames on the call stack at the time the current exception was thrown.TargetSite: Gets the method that throws the current exception.
The following example generates a MySqlException due to a missing server, and then displays the exception.
This example demonstrates how to use the MySqlException class with VB.NET:
Public Sub ShowException()
Dim mySelectQuery As String = "SELECT column1 FROM table1"
Dim myConnection As New MySqlConnection ("Data Source=localhost;Database=Sample;")
Dim myCommand As New MySqlCommand(mySelectQuery, myConnection)
Try
myCommand.Connection.Open()
Catch e As MySqlException
MessageBox.Show( e.Message )
End Try
End Sub
This example demonstrates how to use the MySqlException class with C#:
public void ShowException()
{
string mySelectQuery = "SELECT column1 FROM table1";
MySqlConnection myConnection =
new MySqlConnection("Data Source=localhost;Database=Sample;");
MySqlCommand myCommand = new MySqlCommand(mySelectQuery,myConnection);
try
{
myCommand.Connection.Open();
}
catch (MySqlException e)
{
MessageBox.Show( e.Message );
}
}
Helper class that makes it easier to work with the provider. Developers can use the methods of this class to automatically perform common tasks.
The following methods are available:
ExecuteDataRow: Executes a single SQL command and returns the first row of the resultset. A new MySqlConnection object is created, opened, and closed during this method.ExecuteDataset: Executes a single SQL command and returns the resultset in a DataSet. A new MySqlConnection object is created, opened, and closed during this method.ExecuteNonQuery: Executes a single command against a MySQL database. The MySqlConnection is assumed to be open when the method is called and remains open after the method completes.ExecuteReader: Overloaded. Executes a single command against a MySQL database.ExecuteScalar: Execute a single command against a MySQL database.UpdateDataSet: Updates the given table with data from the given DataSet.
Represents an SQL transaction to be made in a MySQL database.
The following properties are available:
Connection: Gets the MySqlConnection object associated with the transaction, or a null reference (Nothing in Visual Basic) if the transaction is no longer valid.IsolationLevel: Specifies the IsolationLevel for this transaction.
The following methods are available:
Commit: Commits the database transaction.Rollback: Rolls back a transaction from a pending state.
The following example creates a MySqlConnection and a MySqlTransaction. It also demonstrates how to use the BeginTransaction, Commit, and Rollback methods.
The following example shows how to use the MySqlTransaction class with VB.NET:
Public Sub RunTransaction(myConnString As String)
Dim myConnection As New MySqlConnection(myConnString)
myConnection.Open()
Dim myCommand As MySqlCommand = myConnection.CreateCommand()
Dim myTrans As MySqlTransaction
' Start a local transaction
myTrans = myConnection.BeginTransaction()
' Must assign both transaction object and connection
' to Command object for a pending local transaction
myCommand.Connection = myConnection
myCommand.Transaction = myTrans
Try
myCommand.CommandText = "Insert into Region (RegionID, RegionDescription) VALUES (100, 'Description')"
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery()
myCommand.CommandText = "Insert into Region (RegionID, RegionDescription) VALUES (101, 'Description')"
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery()
myTrans.Commit()
Console.WriteLine("Both records are written to database.")
Catch e As Exception
Try
myTrans.Rollback()
Catch ex As MySqlException
If Not myTrans.Connection Is Nothing Then
Console.WriteLine("An exception of type " & ex.GetType().ToString() & _
" was encountered while attempting to roll back the transaction.")
End If
End Try
Console.WriteLine("An exception of type " & e.GetType().ToString() & _
"was encountered while inserting the data.")
Console.WriteLine("Neither record was written to database.")
Finally
myConnection.Close()
End Try
End Sub 'RunTransaction
The following example shows how to use the MySqlTransaction class with C#:
public void RunTransaction(string myConnString)
{
MySqlConnection myConnection = new MySqlConnection(myConnString);
myConnection.Open();
MySqlCommand myCommand = myConnection.CreateCommand();
MySqlTransaction myTrans;
// Start a local transaction
myTrans = myConnection.BeginTransaction();
// Must assign both transaction object and connection
// to Command object for a pending local transaction
myCommand.Connection = myConnection;
myCommand.Transaction = myTrans;
try
{
myCommand.CommandText = "Insert into Region (RegionID, RegionDescription) VALUES (100, 'Description')";
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
myCommand.CommandText = "Insert into Region (RegionID, RegionDescription) VALUES (101, 'Description')";
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
myTrans.Commit();
Console.WriteLine("Both records are written to database.");
}
catch(Exception e)
{
try
{
myTrans.Rollback();
}
catch (MySqlException ex)
{
if (myTrans.Connection != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("An exception of type " + ex.GetType() +
" was encountered while attempting to roll back the transaction.");
}
}
Console.WriteLine("An exception of type " + e.GetType() +
" was encountered while inserting the data.");
Console.WriteLine("Neither record was written to database.");
}
finally
{
myConnection.Close();
}
}
- 23.2.4.1. Introduction
- 23.2.4.2. Connecting to MySQL Using MySQL Connector/NET
- 23.2.4.3. Using the MySQL Connector/NET with Prepared Statements
- 23.2.4.4. Accessing Stored Procedures with MySQL Connector/NET
- 23.2.4.5. Handling BLOB Data With Connector/NET
- 23.2.4.6. Using MySQL Connector/NET with Crystal Reports
- 23.2.4.7. Handling Date and Time Information in MySQL Connector/NET
In this section we will cover some of the more common use cases for Connector/NET, including BLOB handling, date handling, and using Connector/NET with common tools such as Crystal Reports.
All interaction between a .NET application and the MySQL
server is routed through a MySqlConnection
object. Before your application can interact with the server,
a MySqlConnection object must be instanced,
configured, and opened.
Even when using the MySqlHelper class, a
MySqlConnection object is created by the
helper class.
In this section, we will describe how to connect to MySQL
using the MySqlConnection object.
The MySqlConnection object is configured
using a connection string. A connection string contains sever
key/value pairs, separated by semicolons. Each key/value pair
is joined with an equals sign.
The following is a sample connection string:
Server=127.0.0.1;Uid=root;Pwd=12345;Database=test;
In this example, the MySqlConnection object
is configured to connect to a MySQL server at
127.0.0.1, with a username of
root and a password of
12345. The default database for all
statements will be the test database.
The following options are typically used (a full list of options is available in the API documentation):
Server: The name or network address of the instance of MySQL to which to connect. The default islocalhost. Aliases includehost,Data Source,DataSource,Address,AddrandNetwork Address.Uid: The MySQL user account to use when connecting. Aliases includeUser Id,UsernameandUser name.Pwd: The password for the MySQL account being used. AliasPasswordcan also be used.Database: The default database that all statements are applied to. Default ismysql. AliasInitial Catalogcan also be used.Port: The port MySQL is using to listen for connections. Default is3306. Specify-1for this value to use a named-pipe connection.
Once you have created a connection string it can be used to open a connection to the MySQL server.
The following code is used to create a
MySqlConnection object, assign the
connection string, and open the connection.
[VB]
Dim conn As New MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection
Dim myConnectionString as String
myConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;" _
& "uid=root;" _
& "pwd=12345;" _
& "database=test;"
Try
conn.ConnectionString = myConnectionString
conn.Open()
Catch ex As MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message)
End Try
[C#]
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection conn;
string myConnectionString;
myConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;uid=root;" +
"pwd=12345;database=test;";
try
{
conn = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection();
conn.ConnectionString = myConnectionString;
conn.Open();
}
catch (MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
You can also pass the connection string to the constructor of
the MySqlConnection class:
[VB]
Dim myConnectionString as String
myConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;" _
& "uid=root;" _
& "pwd=12345;" _
& "database=test;"
Try
Dim conn As New MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection(myConnectionString)
conn.Open()
Catch ex As MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message)
End Try
[C#]
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection conn;
string myConnectionString;
myConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;uid=root;" +
"pwd=12345;database=test;";
try
{
conn = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection(myConnectionString);
conn.Open();
}
catch (MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
Once the connection is open it can be used by the other MySQL Connector/NET classes to communicate with the MySQL server.
Because connecting to an external server is unpredictable, it
is important to add error handling to your .NET application.
When there is an error connecting, the
MySqlConnection class will return a
MySqlException object. This object has two
properties that are of interest when handling errors:
Message: A message that describes the current exception.Number: The MySQL error number.
When handling errors, you can your application's response based on the error number. The two most common error numbers when connecting are as follows:
0: Cannot connect to server.1045: Invalid username and/or password.
The following code shows how to adapt the application's response based on the actual error:
[VB]
Dim myConnectionString as String
myConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;" _
& "uid=root;" _
& "pwd=12345;" _
& "database=test;"
Try
Dim conn As New MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection(myConnectionString)
conn.Open()
Catch ex As MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException
Select Case ex.Number
Case 0
MessageBox.Show("Cannot connect to server. Contact administrator")
Case 1045
MessageBox.Show("Invalid username/password, please try again")
End Select
End Try
[C#]
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection conn;
string myConnectionString;
myConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;uid=root;" +
"pwd=12345;database=test;";
try
{
conn = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection(myConnectionString);
conn.Open();
}
catch (MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException ex)
{
switch (ex.Number)
{
case 0:
MessageBox.Show("Cannot connect to server. Contact administrator");
case 1045:
MessageBox.Show("Invalid username/password, please try again");
}
}
Important Note that if you
are using multilanguage databases you must specify the
character set in the connection string. If you do not specify
the character set, the connection defaults to the
latin1 charset. You can specify the
character set as part of the connection string, for example:
MySqlConnection myConnection = new MySqlConnection("server=127.0.0.1;uid=root;" +
"pwd=12345;database=test;Charset=latin1;");
As of MySQL 4.1, it is possible to use prepared statements with MySQL Connector/NET. Use of prepared statements can provide significant performance improvements on queries that are executed more than once.
Prepared execution is faster than direct execution for statements executed more than once, primarily because the query is parsed only once. In the case of direct execution, the query is parsed every time it is executed. Prepared execution also can provide a reduction of network traffic because for each execution of the prepared statement, it is necessary only to send the data for the parameters.
Another advantage of prepared statements is that it uses a binary protocol that makes data transfer between client and server more efficient.
To prepare a statement, create a command object and set the
.CommandText property to your query.
After entering your statement, call the
.Prepare method of the
MySqlCommand object. After the statement is
prepared, add parameters for each of the dynamic elements in
the query.
After you enter your query and enter parameters, execute the
statement using the .ExecuteNonQuery(),
.ExecuteScalar(), or
.ExecuteReader methods.
For subsequent executions, you need only modify the values of
the parameters and call the execute method again, there is no
need to set the .CommandText property or
redefine the parameters.
[VB]
Dim conn As New MySqlConnection
Dim cmd As New MySqlCommand
conn.ConnectionString = strConnection
Try
conn.Open()
cmd.Connection = conn
cmd.CommandText = "INSERT INTO myTable VALUES(NULL, ?number, ?text)"
cmd.Prepare()
cmd.Parameters.Add("?number", 1)
cmd.Parameters.Add("?text", "One")
For i = 1 To 1000
cmd.Parameters("?number").Value = i
cmd.Parameters("?text").Value = "A string value"
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery()
Next
Catch ex As MySqlException
MessageBox.Show("Error " & ex.Number & " has occurred: " & ex.Message, "Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error)
End Try
[C#]
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection conn;
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand cmd;
conn = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection();
cmd = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand();
conn.ConnectionString = strConnection;
try
{
conn.Open();
cmd.Connection = conn;
cmd.CommandText = "INSERT INTO myTable VALUES(NULL, ?number, ?text)";
cmd.Prepare();
cmd.Parameters.Add("?number", 1);
cmd.Parameters.Add("?text", "One");
for (int i=1; i <= 1000; i++)
{
cmd.Parameters["?number"].Value = i;
cmd.Parameters["?text"].Value = "A string value";
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
catch (MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException ex)
{
MessageBox.Show("Error " + ex.Number + " has occurred: " + ex.Message,
"Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
With the release of MySQL version 5 the MySQL server now supports stored procedures with the SQL 2003 stored procedure syntax.
A stored procedure is a set of SQL statements that can be stored in the server. Once this has been done, clients don't need to keep reissuing the individual statements but can refer to the stored procedure instead.
Stored procedures can be particularly useful in situations such as the following:
When multiple client applications are written in different languages or work on different platforms, but need to perform the same database operations.
When security is paramount. Banks, for example, use stored procedures for all common operations. This provides a consistent and secure environment, and procedures can ensure that each operation is properly logged. In such a setup, applications and users would not get any access to the database tables directly, but can only execute specific stored procedures.
MySQL Connector/NET supports the calling of stored procedures
through the MySqlCommand object. Data can
be passed in and our of a MySQL stored procedure through use
of the MySqlCommand.Parameters collection.
This section will not provide in-depth information on creating Stored Procedures. For such information, please refer to http://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql/en/stored-procedures.html.
A sample application demonstrating how to use stored
procedures with MySQL Connector/NET can be found in the
Samples directory of your MySQL Connector/NET
installation.
Stored procedures in MySQL can be created using a variety of
tools. First, stored procedures can be created using the
mysql command-line client. Second, stored
procedures can be created using the MySQL Query
Browser GUI client. Finally, stored procedures can
be created using the .ExecuteNonQuery
method of the MySqlCommand object:
[VB]
Dim conn As New MySqlConnection
Dim cmd As New MySqlCommand
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;" _
& "uid=root;" _
& "pwd=12345;" _
& "database=test"
Try
conn.Open()
cmd.Connection = conn
cmd.CommandText = "CREATE PROCEDURE add_emp(" _
& "IN fname VARCHAR(20), IN lname VARCHAR(20), IN bday DATETIME, OUT empno INT) " _
& "BEGIN INSERT INTO emp(first_name, last_name, birthdate) " _
& "VALUES(fname, lname, DATE(bday)); SET empno = LAST_INSERT_ID(); END"
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery()
Catch ex As MySqlException
MessageBox.Show("Error " & ex.Number & " has occurred: " & ex.Message, "Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error)
End Try
[C#]
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection conn;
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand cmd;
conn = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection();
cmd = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand();
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;uid=root;" +
"pwd=12345;database=test;";
try
{
conn.Open();
cmd.Connection = conn;
cmd.CommandText = "CREATE PROCEDURE add_emp(" +
"IN fname VARCHAR(20), IN lname VARCHAR(20), IN bday DATETIME, OUT empno INT) " +
"BEGIN INSERT INTO emp(first_name, last_name, birthdate) " +
"VALUES(fname, lname, DATE(bday)); SET empno = LAST_INSERT_ID(); END";
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
catch (MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException ex)
{
MessageBox.Show("Error " + ex.Number + " has occurred: " + ex.Message,
"Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
It should be noted that, unlike the command-line and GUI clients, you are not required to specify a special delimiter when creating stored procedures in MySQL Connector/NET.
To call a stored procedure using MySQL Connector/NET, create a
MySqlCommand object and pass the stored
procedure name as the .CommandText
property. Set the .CommandType property to
CommandType.StoredProcedure.
After the stored procedure is named, create one
MySqlCommand parameter for every parameter
in the stored procedure. IN parameters are
defined with the parameter name and the object containing the
value, OUT parameters are defined with the
parameter name and the datatype that is expected to be
returned. All parameters need the parameter direction defined.
After defining parameters, call the stored procedure by using
the MySqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery() method:
[VB]
Dim conn As New MySqlConnection
Dim cmd As New MySqlCommand
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;" _
& "uid=root;" _
& "pwd=12345;" _
& "database=test"
Try
conn.Open()
cmd.Connection = conn
cmd.CommandText = "add_emp"
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure
cmd.Parameters.Add("?lname", 'Jones')
cmd.Parameters("?lname").Direction = ParameterDirection.Input
cmd.Parameters.Add("?fname", 'Tom')
cmd.Parameters("?fname").Direction = ParameterDirection.Input
cmd.Parameters.Add("?bday", #12/13/1977 2:17:36 PM#)
cmd.Parameters("?bday").Direction = ParameterDirection.Input
cmd.Parameters.Add("?empno", MySqlDbType.Int32)
cmd.Parameters("?empno").Direction = ParameterDirection.Output
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery()
MessageBox.Show(cmd.Parameters("?empno").Value)
Catch ex As MySqlException
MessageBox.Show("Error " & ex.Number & " has occurred: " & ex.Message, "Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error)
End Try
[C#]
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection conn;
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand cmd;
conn = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection();
cmd = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand();
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;uid=root;" +
"pwd=12345;database=test;";
try
{
conn.Open();
cmd.Connection = conn;
cmd.CommandText = "add_emp";
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.Add("?lname", "Jones");
cmd.Parameters["?lname"].Direction = ParameterDirection.Input;
cmd.Parameters.Add("?fname", "Tom");
cmd.Parameters["?fname"].Direction = ParameterDirection.Input;
cmd.Parameters.Add("?bday", DateTime.Parse("12/13/1977 2:17:36 PM"));
cmd.Parameters["?bday"].Direction = ParameterDirection.Input;
cmd.Parameters.Add("?empno", MySqlDbType.Int32);
cmd.Parameters["?empno"].Direction = ParameterDirection.Output;
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show(cmd.Parameters["?empno"].Value);
}
catch (MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException ex)
{
MessageBox.Show("Error " + ex.Number + " has occurred: " + ex.Message,
"Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
Once the stored procedure is called, the values of output
parameters can be retrieved by using the
.Value property of the
MySqlConnector.Parameters collection.
One common use for MySQL is the storage of binary data in
BLOB columns. MySQL supports four different
BLOB datatypes: TINYBLOB,
BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, and
LONGBLOB.
Data stored in a BLOB column can be accessed using Connector/NET and manipulated using client-side code. There are no special requirements for using Connector/NET with BLOB data.
Simple code examples will be presented within this section,
and a full sample application can be found in the
Samples directory of the MySQL Connector/NET
installation.
The first step is using MySQL with BLOB data is to configure the server. Let's start by creating a table to be accessed. In my file tables, I usually have four columns: an AUTO_INCREMENT column of appropriate size (UNSIGNED SMALLINT) to serve as a primary key to identify the file, a VARCHAR column that stores the filename, an UNSIGNED MEDIUMINT column that stores the size of the file, and a MEDIUMBLOB column that stores the file itself. For this example, I will use the following table definition:
CREATE TABLE file( file_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, file_name VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL, file_size MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, file MEDIUMBLOB NOT NULL);
After creating a table, you may need to modify the max_allowed_packet system variable. This variable determines how large of a packet (i.e. a single row) can be sent to the MySQL server. By default, the server will only accept a maximum size of 1 meg from our client application. If you do not intend to exceed 1 meg, this should be fine. If you do intend to exceed 1 meg in your file transfers, this number has to be increased.
The max_allowed_packet option can be modified using MySQL
Administrator's Startup Variables screen. Adjust the Maximum
allowed option in the Memory section of the Networking tab to
an appropriate setting. After adjusting the value, click the
button and restart the
server using the Service Control screen of
MySQL Administrator. You can also adjust this value directly
in the my.cnf file (add a line that reads
max_allowed_packet=xxM), or use the SET
max_allowed_packet=xxM; syntax from within MySQL.
Try to be conservative when setting max_allowed_packet, as transfers of BLOB data can take some time to complete. Try to set a value that will be adequate for your intended use and increase the value if necessary.
To write a file to a database we need to convert the file to a
byte array, then use the byte array as a parameter to an
INSERT query.
The following code opens a file using a FileStream object,
reads it into a byte array, and inserts it into the
file table:
[VB]
Dim conn As New MySqlConnection
Dim cmd As New MySqlCommand
Dim SQL As String
Dim FileSize As UInt32
Dim rawData() As Byte
Dim fs As FileStream
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;" _
& "uid=root;" _
& "pwd=12345;" _
& "database=test"
Try
fs = New FileStream("c:\image.png", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read)
FileSize = fs.Length
rawData = New Byte(FileSize) {}
fs.Read(rawData, 0, FileSize)
fs.Close()
conn.Open()
SQL = "INSERT INTO file VALUES(NULL, ?FileName, ?FileSize, ?File)"
cmd.Connection = conn
cmd.CommandText = SQL
cmd.Parameters.Add("?FileName", strFileName)
cmd.Parameters.Add("?FileSize", FileSize)
cmd.Parameters.Add("?File", rawData)
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery()
MessageBox.Show("File Inserted into database successfully!", _
"Success!", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Asterisk)
conn.Close()
Catch ex As Exception
MessageBox.Show("There was an error: " & ex.Message, "Error", _
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error)
End Try
[C#]
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection conn;
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand cmd;
conn = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection();
cmd = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand();
string SQL;
UInt32 FileSize;
byte[] rawData;
FileStream fs;
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;uid=root;" +
"pwd=12345;database=test;";
try
{
fs = new FileStream(@"c:\image.png", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
FileSize = fs.Length;
rawData = new byte[FileSize];
fs.Read(rawData, 0, FileSize);
fs.Close();
conn.Open();
SQL = "INSERT INTO file VALUES(NULL, ?FileName, ?FileSize, ?File)";
cmd.Connection = conn;
cmd.CommandText = SQL;
cmd.Parameters.Add("?FileName", strFileName);
cmd.Parameters.Add("?FileSize", FileSize);
cmd.Parameters.Add("?File", rawData);
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("File Inserted into database successfully!",
"Success!", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Asterisk);
conn.Close();
}
catch (MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException ex)
{
MessageBox.Show("Error " + ex.Number + " has occurred: " + ex.Message,
"Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
The Read method of the
FileStream object is used to load the file
into a byte array which is sized according to the
Length property of the FileStream object.
After assigning the byte array as a parameter of the
MySqlCommand object, the
ExecuteNonQuery method is called and the
BLOB is inserted into the file table.
Once a file is loaded into the file table,
we can use the MySqlDataReader class to
retrieve it.
The following code retrieves a row from the
file table, then loads the data into a
FileStream object to be written to disk:
[VB]
Dim conn As New MySqlConnection
Dim cmd As New MySqlCommand
Dim myData As MySqlDataReader
Dim SQL As String
Dim rawData() As Byte
Dim FileSize As UInt32
Dim fs As FileStream
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;" _
& "uid=root;" _
& "pwd=12345;" _
& "database=test"
SQL = "SELECT file_name, file_size, file FROM file"
Try
conn.Open()
cmd.Connection = conn
cmd.CommandText = SQL
myData = cmd.ExecuteReader
If Not myData.HasRows Then Throw New Exception("There are no BLOBs to save")
myData.Read()
FileSize = myData.GetUInt32(myData.GetOrdinal("file_size"))
rawData = New Byte(FileSize) {}
myData.GetBytes(myData.GetOrdinal("file"), 0, rawData, 0, FileSize)
fs = New FileStream("C:\newfile.png", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write)
fs.Write(rawData, 0, FileSize)
fs.Close()
MessageBox.Show("File successfully written to disk!", "Success!", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Asterisk)
myData.Close()
conn.Close()
Catch ex As Exception
MessageBox.Show("There was an error: " & ex.Message, "Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error)
End Try
[C#]
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection conn;
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand cmd;
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlDataReader myData;
conn = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection();
cmd = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand();
string SQL;
UInt32 FileSize;
byte[] rawData;
FileStream fs;
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;uid=root;" +
"pwd=12345;database=test;";
SQL = "SELECT file_name, file_size, file FROM file";
try
{
conn.Open();
cmd.Connection = conn;
cmd.CommandText = SQL;
myData = cmd.ExecuteReader();
if (! myData.HasRows)
throw new Exception("There are no BLOBs to save");
myData.Read();
FileSize = myData.GetUInt32(myData.GetOrdinal("file_size"));
rawData = new byte[FileSize];
myData.GetBytes(myData.GetOrdinal("file"), 0, rawData, 0, FileSize);
fs = new FileStream(@"C:\newfile.png", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write);
fs.Write(rawData, 0, FileSize);
fs.Close();
MessageBox.Show("File successfully written to disk!",
"Success!", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Asterisk);
myData.Close();
conn.Close();
}
catch (MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException ex)
{
MessageBox.Show("Error " + ex.Number + " has occurred: " + ex.Message,
"Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
After connecting, the contents of the file
table are loaded into a MySqlDataReader
object. The GetBytes method of the
MySqlDataReader is used to load the BLOB into a byte array,
which is then written to disk using a FileStream object.
The GetOrdinal method of the
MySqlDataReader can be used to determine the integer index of
a named column. Use of the GetOrdinal method prevents errors
if the column order of the SELECT query is changed.
Crystal Reports is a common tool used by Windows application developers to perform reporting and document generation. In this section we will show how to use Crystal Reports XI with MySQL and Connector/NET.
Complete sample applications are available in the CrystalDemo subdirectory of the Samples directory of your MySQL Connector/NET installation.
When creating a report in Crystal Reports there are two options for accessing the MySQL data while designing your report.
The first option is to use Connector/ODBC as an ADO data source when designing your report. You will be able to browse your database and choose tables and fields using drag and drop to build your report. The disadvantage of this approach is that additional work must be performed within your application to produce a dataset that matches the one expected by your report.
The second option is to create a dataset in VB.NET and save it as XML. This XML file can then be used to design a report. This works quite well when displaying the report in your application, but is less versatile at design time because you must choose all relevant columns when creating the dataset. If you forget a column you must re-create the dataset before the column can be added to the report.
The following code can be used to create a dataset from a query and write it to disk:
[VB]
Dim myData As New DataSet
Dim conn As New MySqlConnection
Dim cmd As New MySqlCommand
Dim myAdapter As New MySqlDataAdapter
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;" _
& "uid=root;" _
& "pwd=12345;" _
& "database=world"
Try
conn.Open()
cmd.CommandText = "SELECT city.name AS cityName, city.population AS CityPopulation, " _
& "country.name, country.population, country.continent " _
& "FROM country, city ORDER BY country.continent, country.name"
cmd.Connection = conn
myAdapter.SelectCommand = cmd
myAdapter.Fill(myData)
myData.WriteXml("C:\dataset.xml", XmlWriteMode.WriteSchema)
Catch ex As Exception
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Report could not be created", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error)
End Try
[C#]
DataSet myData = new DataSet();
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection conn;
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand cmd;
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlDataAdapter myAdapter;
conn = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection();
cmd = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand();
myAdapter = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlDataAdapter();
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;uid=root;" +
"pwd=12345;database=test;";
try
{
cmd.CommandText = "SELECT city.name AS cityName, city.population AS CityPopulation, " +
"country.name, country.population, country.continent " +
"FROM country, city ORDER BY country.continent, country.name";
cmd.Connection = conn;
myAdapter.SelectCommand = cmd;
myAdapter.Fill(myData);
myData.WriteXml(@"C:\dataset.xml", XmlWriteMode.WriteSchema);
}
catch (MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Report could not be created",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
The resulting XML file can be used as an ADO.NET XML datasource when designing your report.
If you choose to design your reports using Connector/ODBC, it can be downloaded from dev.mysql.com.
For most purposes the Standard Report wizard should help with the initial creation of a report. To start the wizard, open Crystal Reports and choose the New > Standard Report option from the File menu.
The wizard will first prompt you for a data source. If you are using Connector/ODBC as your data source, use the OLEDB provider for ODBC option from the OLE DB (ADO) tree instead of the ODBC (RDO) tree when choosing a data source. If using a saved dataset, choose the ADO.NET (XML) option and browse to your saved dataset.
The remainder of the report creation process is done automatically by the wizard.
After the report is created, choose the Report Options... entry of the File menu. Un-check the Save Data With Report option. This prevents saved data from interfering with the loading of data within our application.
To display a report we first populate a dataset with the data needed for the report, then load the report and bind it to the dataset. Finally we pass the report to the crViewer control for display to the user.
The following references are needed in a project that displays a report:
CrytalDecisions.CrystalReports.Engine
CrystalDecisions.ReportSource
CrystalDecisions.Shared
CrystalDecisions.Windows.Forms
The following code assumes that you created your report using
a dataset saved using the code shown in
Section 23.2.4.6.2, “Creating a Data Source”, and have
a crViewer control on your form named
myViewer.
[VB]
Imports CrystalDecisions.CrystalReports.Engine
Imports System.Data
Imports MySql.Data.MySqlClient
Dim myReport As New ReportDocument
Dim myData As New DataSet
Dim conn As New MySqlConnection
Dim cmd As New MySqlCommand
Dim myAdapter As New MySqlDataAdapter
conn.ConnectionString = _
"server=127.0.0.1;" _
& "uid=root;" _
& "pwd=12345;" _
& "database=test"
Try
conn.Open()
cmd.CommandText = "SELECT city.name AS cityName, city.population AS CityPopulation, " _
& "country.name, country.population, country.continent " _
& "FROM country, city ORDER BY country.continent, country.name"
cmd.Connection = conn
myAdapter.SelectCommand = cmd
myAdapter.Fill(myData)
myReport.Load(".\world_report.rpt")
myReport.SetDataSource(myData)
myViewer.ReportSource = myReport
Catch ex As Exception
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Report could not be created", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error)
End Try
[C#]
using CrystalDecisions.CrystalReports.Engine;
using System.Data;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;
ReportDocument myReport = new ReportDocument();
DataSet myData = new DataSet();
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection conn;
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand cmd;
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlDataAdapter myAdapter;
conn = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection();
cmd = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand();
myAdapter = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlDataAdapter();
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;uid=root;" +
"pwd=12345;database=test;";
try
{
cmd.CommandText = "SELECT city.name AS cityName, city.population AS CityPopulation, " +
"country.name, country.population, country.continent " +
"FROM country, city ORDER BY country.continent, country.name";
cmd.Connection = conn;
myAdapter.SelectCommand = cmd;
myAdapter.Fill(myData);
myReport.Load(@".\world_report.rpt");
myReport.SetDataSource(myData);
myViewer.ReportSource = myReport;
}
catch (MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Report could not be created",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
A new dataset it generated using the same query used to generate the previously saved dataset. Once the dataset is filled, a ReportDocument is used to load the report file and bind it to the dataset. The ReportDocument is the passed as the ReportSource of the crViewer.
This same approach is taken when a report is created from a single table using Connector/ODBC. The dataset replaces the table used in the report and the report is displayed properly.
When a report is created from multiple tables using Connector/ODBC, a dataset with multiple tables must be created in our application. This allows each table in the report data source to be replaced with a report in the dataset.
We populate a dataset with multiple tables by providing multiple SELECT statements in our MySqlCommand object. These SELECT statements are based on the SQL query shown in Crystal Reports in the Database menu's Show SQL Query option. Assume the following query:
SELECT `country`.`Name`, `country`.`Continent`, `country`.`Population`, `city`.`Name`, `city`.`Population` FROM `world`.`country` `country` LEFT OUTER JOIN `world`.`city` `city` ON `country`.`Code`=`city`.`CountryCode` ORDER BY `country`.`Continent`, `country`.`Name`, `city`.`Name`
This query is converted to two SELECT queries and displayed with the following code:
[VB]
Imports CrystalDecisions.CrystalReports.Engine
Imports System.Data
Imports MySql.Data.MySqlClient
Dim myReport As New ReportDocument
Dim myData As New DataSet
Dim conn As New MySqlConnection
Dim cmd As New MySqlCommand
Dim myAdapter As New MySqlDataAdapter
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;" _
& "uid=root;" _
& "pwd=12345;" _
& "database=world"
Try
conn.Open()
cmd.CommandText = "SELECT name, population, countrycode FROM city ORDER BY countrycode, name; " _
& "SELECT name, population, code, continent FROM country ORDER BY continent, name"
cmd.Connection = conn
myAdapter.SelectCommand = cmd
myAdapter.Fill(myData)
myReport.Load(".\world_report.rpt")
myReport.Database.Tables(0).SetDataSource(myData.Tables(0))
myReport.Database.Tables(1).SetDataSource(myData.Tables(1))
myViewer.ReportSource = myReport
Catch ex As Exception
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Report could not be created", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error)
End Try
[C#]
using CrystalDecisions.CrystalReports.Engine;
using System.Data;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;
ReportDocument myReport = new ReportDocument();
DataSet myData = new DataSet();
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection conn;
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand cmd;
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlDataAdapter myAdapter;
conn = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlConnection();
cmd = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlCommand();
myAdapter = new MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlDataAdapter();
conn.ConnectionString = "server=127.0.0.1;uid=root;" +
"pwd=12345;database=test;";
try
{
cmd.CommandText = "SELECT name, population, countrycode FROM city ORDER " +
"BY countrycode, name; SELECT name, population, code, continent FROM " +
"country ORDER BY continent, name";
cmd.Connection = conn;
myAdapter.SelectCommand = cmd;
myAdapter.Fill(myData);
myReport.Load(@".\world_report.rpt");
myReport.Database.Tables(0).SetDataSource(myData.Tables(0));
myReport.Database.Tables(1).SetDataSource(myData.Tables(1));
myViewer.ReportSource = myReport;
}
catch (MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlException ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Report could not be created",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
It is important to order the SELECT queries in alphabetical order, as this is the order the report will expect its source tables to be in. One SetDataSource statement is needed for each table in the report.
This approach can cause performance problems because Crystal Reports must bind the tables together on the client-side, which will be slower than using a pre-saved dataset.
MySQL and the .NET languages handle date and time information
differently, with MySQL allowing dates that cannot be
represented by a .NET data type, such as '0000-00-00
00:00:00'. These differences can cause problems if
not properly handled.
In this section we will demonstrate how to properly handle date and time information when using MySQL Connector/NET.
The differences in date handling can cause problems for
developers who use invalid dates. Invalid MySQL dates cannot
be loaded into native .NET DateTime
objects, including NULL dates.
Because of this issue, .NET DataSet objects
cannot be populated by the Fill method of
the MySqlDataAdapter class as invalid dates
will cause a
System.ArgumentOutOfRangeException
exception to occur.
The best solution to the date problem is to restrict users from entering invalid dates. This can be done on either the client or the server side.
Restricting invalid dates on the client side is as simple as
always using the .NET DateTime class to
handle dates. The DateTime class will only
allow valid dates, ensuring that the values in your database
are also valid. The disadvantage of this is that it is not
useful in a mixed environment where .NET and non .NET code are
used to manipulate the database, as each application must
perform its own date validation.
Users of MySQL 5.0.2 and higher can use the new
traditional SQL mode to restrict invalid
date values. For information on using the
traditional SQL mode, see
Section 5.2.5, “The Server SQL Mode”.
Although it is strongly recommended that you avoid the use of
invalid dates within your .NET application, it is possible to
use invalid dates by means of the
MySqlDateTime datatype.
The MySqlDateTime datatype supports the
same date values that are supported by the MySQL server. The
default behavior of MySQL Connector/NET is to return a .NET
DateTime object for valid date values, and return an error for
invalid dates. This default can be modified to cause
MySQL Connector/NET to return MySqlDateTime
objects for invalid dates.
To instruct MySQL Connector/NET to return a
MySqlDateTime object for invalid dates, add
the following line to your connection string:
Allow Zero Datetime=True
Please note that the use of the
MySqlDateTime class can still be
problematic. The following are some known issues:
Data binding for invalid dates can still cause errors (zero dates like 0000-00-00 do not seem to have this problem).
The
ToStringmethod return a date formatted in the standard MySQL format (for example,2005-02-23 08:50:25). This differs from theToStringbehavior of the .NET DateTime class.The
MySqlDateTimeclass supports NULL dates, while the .NET DateTime class does not. This can cause errors when trying to convert a MySQLDateTime to a DateTime if you do not check for NULL first.
Because of the known issues, the best recommendation is still to use only valid dates in your application.
The .NET DateTime datatype cannot handle
NULL values. As such, when assigning values
from a query to a DateTime variable, you
must first check whether the value is in fact
NULL.
When using a MySqlDataReader, use the
.IsDBNull method to check whether a value
is NULL before making the assignment:
[VB]
If Not myReader.IsDBNull(myReader.GetOrdinal("mytime")) Then
myTime = myReader.GetDateTime(myReader.GetOrdinal("mytime"))
Else
myTime = DateTime.MinValue
End If
[C#]
if (! myReader.IsDBNull(myReader.GetOrdinal("mytime")))
myTime = myReader.GetDateTime(myReader.GetOrdinal("mytime"));
else
myTime = DateTime.MinValue;
NULL values will work in a dataset and can
be bound to form controls without special handling.
- 23.2.5.1. Version 1.0.8
- 23.2.5.2. Version 1.0.7
- 23.2.5.3. Version 1.0.6
- 23.2.5.4. Version 1.0.5
- 23.2.5.5. Version 1.0.4 1-20-05
- 23.2.5.6. Version 1.0.3-gamma 12-10-04
- 23.2.5.7. Version 1.0.2-gamma 04-11-15
- 23.2.5.8. Version 1.0.1-beta2 04-10-27
- 23.2.5.9. Version 1.0.0 04-09-01
- 23.2.5.10. Version 0.9.0 04-08-30
- 23.2.5.11. Version 0.76
- 23.2.5.12. Version 0.75
- 23.2.5.13. Version 0.74
- 23.2.5.14. Version 0.71
- 23.2.5.15. Version 0.70
- 23.2.5.16. Version 0.68
- 23.2.5.17. Version 0.65
- 23.2.5.18. Version 0.60
- 23.2.5.19. Version 0.50
An exception would be raised when using an output parameter to a
System.Stringvalue. (Bug#17814)The DiscoverParameters function would fail when a stored procedure used a
NUMERICparameter type. (Bug#19515)When running a query that included a date comparison, a DateReader error would be raised. (Bug#19481)
Parameter substitution in queries where the order of parameters and table fields did not match would substitute incorrect values. (Bug#19261)
When working with multiple threads, character set initialization would generate errors. (Bug#17106)
When using an unsigned 64-bit integer in a stored procedure, the unsigned bit would be lost stored. (Bug#16934)
The connection string parser did not allow single or double quotes in the password. (Bug#16659)
The CommandBuilder ignored Unsigned flag at Parameter creation. (Bug#17375)
CHAR type added to MySqlDbType. (Bug#17749)
Unsigned data types were not properly supported. (Bug#16788)
The parameter collection object's
Add()method added parameters to the list without first checking to see whether they already existed. Now it updates the value of the existing parameter object if it exists. (Bug#13927)A
#42000Query was emptyexception occurred when executing a query built withMySqlCommandBuilder, if the query string ended with a semicolon. (Bug#14631)Implemented the
MySqlCommandBuilder.DeriveParametersmethod that is used to discover the parameters for a stored procedure. (Bug#13632)Added support for the
cp932character set. (Bug#13806)Calling a stored procedure where a parameter contained special characters (such as
'@') would produce an exception. Note thatANSI_QUOTEShad to be enabled to make this possible. (Bug#13753)A statement that contained multiple references to the same parameter could not be prepared. (Bug#13541)
The
Ping()method did not update theStateproperty of theConnectionobject. (Bug#13658)
The
nantbuild sequence had problems. (Bug#12978)Serializing a parameter failed if the first value passed in was
NULL. (Bug#13276)Field names that contained the following characters caused errors:
()%<>/(Bug#13036)The MySQL Connector/NET 1.0.5 installer would not install alongside MySQL Connector/NET 1.0.4. (Bug#12835)
MySQL Connector/NET 1.0.5 could not connect on Mono. (Bug#13345)
With multiple hosts in the connection string, MySQL Connector/NET would not connect to the last host in the list. (Bug#12628)
MySQL Connector/NET interpreted the new decimal data type as a byte array. (Bug#11294)
The
cp1250character set was not supported. (Bug#11621)Connection could fail when .NET thread pool had no available worker threads. (Bug#10637)
Decimal parameters caused syntax errors. (Bug#11550, Bug#10486, Bug#10152)
A call to a stored procedure caused an exception if the stored procedure had no parameters. (Bug#11542)
Certain malformed queries would trigger a
Connection must be valid and openerror message. (Bug#11490)The
MySqlCommandBuilderclass could not handle queries that referenced tables in a database other than the default database. (Bug#8382)MySQL Connector/NET could not work properly with certain regional settings. (WL#8228)
Trying to use a stored procedure when
Connection.Databasewas not populated generated an exception. (Bug#11450)Trying to read a
TIMESTAMPcolumn generated an exception. (Bug#7951)Parameters were not recognized when they were separated by linefeeds. (Bug#9722)
Calling
MySqlConnection.clonewhen a connection string had not yet been set on the original connection would generate an error. (Bug#10281)Added support to call a stored function from MySQL Connector/NET. (Bug#10644)
MySQL Connector/NET could not connect to MySQL 4.1.14. (Bug#12771)
The
ConnectionStringproperty could not be set when aMySqlConnectionobject was added with the designer. (Bug#12551, Bug#8724)
Bug#7243 calling prepare causing exception [fixed]
Fixed another small problem with prepared statements
Bug#7258 MySqlCommand.Connection returns an IDbConnection [fixed]
Bug#7345 MySqlAdapter.Fill method throws Error message : Non-negative number required [fixed]
Bug#7478 Clone method bug in MySqlCommand [fixed]
Bug#7612 MySqlDataReader.GetString(index) returns non-Null value when field is Null [fixed]
Bug#7755 MySqlReader.GetInt32 throws exception if column is unsigned [fixed]
Bug#7704 GetBytes is working no more [fixed]
Bug#7724 Quote character \222 not quoted in EscapeString [fixed]
Fixed problem that causes named pipes to not work with some blob functionality
Fixed problem with shared memory connections
Bug#7436 Problem with Multiple resultsets... [fixed]
Added or filled out several more topics in the API reference documentation
Made MySQL the default named pipe name
Now SHOW COLLATION is used upon connection to retrieve the full list of charset ids
Fixed Invalid character set index: 200 (Bug#6547)
Installer now includes options to install into GAC and create Start Menu items
Bug#6863 - Int64 Support in MySqlCommand Parameters [fixed]
Connections now do not have to give a database on the connection string
Bug#6770 - MySqlDataReader.GetChar(int i) throws IndexOutOfRange Exception [fixed]
Fixed problem where multiple resultsets having different numbers of columns would cause a problem
Bug#6983 Exception stack trace lost when re-throwing exceptions [fixed]
Fixed major problem with detecting null values when using prepared statements
Bug#6902 Errors in parsing stored procedure parameters [fixed]
Bug#6668 Integer "out" parameter from stored procedure returned as string [fixed]
Bug#7032 MySqlDateTime in Datatables sorting by Text, not Date. [fixed]
Bug#7133 Invalid query string when using inout parameters [fixed]
Bug#6831 Test suite fails with MySQL 4.0 because of case sensitivity of table names [fixed]
Bug#7132 Inserting DateTime causes System.InvalidCastException to be thrown [fixed]
Bug#6879 InvalidCast when using DATE_ADD-function [fixed]
Bug#6634 An Open Connection has been Closed by the Host System [fixed]
Added ServerThread property to MySqlConnection to expose server thread id
Added Ping method to MySqlConnection
Changed the name of the test suite to MySql.Data.Tests.dll
Fixed problem with MySqlBinary where string values could not be used to update extended text columns
Fixed Installation directory ignored using custom installation (Bug#6329)
Fixed problem where setting command text leaves the command in a prepared state
Fixed double type handling in MySqlParameter(string parameterName, object value) (Bug#6428)
Fixed Zero date "0000-00-00" is returned wrong when filling Dataset (Bug#6429)
Fixed problem where calling stored procedures might cause an "Illegal mix of collations" problem.
Added charset connection string option
Fixed #HY000 Illegal mix of collations (latin1_swedish_ci,IMPLICIT) and (utf8_general_ (Bug#6322)
Added the TableEditor CS and VB sample
Fixed Charset-map for UCS-2 (Bug#6541)
Updated the installer to include the new samples
Fixed Long inserts take very long time (Bu #5453)
Fixed Objects not being disposed (Bug#6649)
Provider is now using character set specified by server as default
Fixed Bug#5602 Possible bug in MySqlParameter(string, object) constructor
Fixed Bug#5458 Calling GetChars on a longtext column throws an exception
Fixed Bug#5474 cannot run a stored procedure populating mysqlcommand.parameters
Fixed Bug#5469 Setting DbType throws NullReferenceException
Fixed problem where connector was not issuing a CMD_QUIT before closing the socket
Fixed Bug#5392 MySqlCommand sees "?" as parameters in string literals
Fixed problem with ConnectionInternal where a key might be added more than once
CP1252 is now used for Latin1 only when the server is 4.1.2 and later
Fixed Bug#5388 DataReader reports all rows as NULL if one row is NULL
Virtualized driver subsystem so future releases could easily support client or embedded server support
Field buffers being reused to decrease memory allocations and increase speed
Fixed problem where using old syntax while using the interfaces caused problems
Using PacketWriter instead of Packet for writing to streams
Refactored compression code into CompressedStream to clean up NativeDriver
Added test case for resetting the command text on a prepared command
Fixed problem where MySqlParameterCollection.Add() would throw unclear exception when given a null value (Bug#5621)
Fixed construtor initialize problems in MySqlCommand() (Bug#5613)
Fixed Parsing the ';' char (Bug#5876)
Fixed missing Reference in DbType setter (Bug#5897)
Fixed System.OverflowException when using YEAR datatype (Bug#6036)
Added Aggregate function test (wasn't really a bug)
Fixed serializing of floating point parameters (double, numeric, single, decimal) (Bug#5900)
IsNullable error (Bug#5796)
Fixed problem where connection lifetime on the connect string was not being respected
Fixed problem where Min Pool Size was not being respected
Fixed MySqlDataReader and 'show tables from ...' behavior (Bug#5256)
Implemented SequentialAccess
Fixed MySqlDateTime sets IsZero property on all subseq.records after first zero found (Bug#6006)
Fixed Can't display Chinese correctly (Bug#5288)
Fixed Russian character support as well
Fixed Method TokenizeSql() uses only a limited set of valid characters for parameters (Bug#6217)
Fixed NET Connector source missing resx files (Bug#6216)
Fixed DBNull Values causing problems with retrieving/updating queries. (Bug#5798)
Fixed Yet Another "object reference not set to an instance of an object" (Bug#5496)
Fixed problem in PacketReader where it could try to allocate the wrong buffer size in EnsureCapacity
Fixed GetBoolean returns wrong values (Bug#6227)
Fixed IndexOutOfBounds when reading BLOB with DataReader with GetString(index) (Bug#6230)
Fixed BUG# 3889 Thai encoding not correctly supported
Updated many of the test cases
Fixed problem with using compression
Bumped version number to 1.0.0 for beta 1 release
Added COPYING.rtf file for use in installer
Removed all of the XML comment warnings (I'll clean them up better later)
Removed some last references to ByteFX
Added test fixture for prepared statements
All type classes now implement a SerializeBinary method for sending their data to a PacketWriter
Added PacketWriter class that will enable future low-memory large object handling
Fixed many small bugs in running prepared statements and stored procedures
Changed command so that an exception will not be throw in executing a stored procedure with parameters in old syntax mode
SingleRow behavior now working right even with limit
GetBytes now only works on binary columns
Logger now truncates long sql commands so blob columns don't blow out our log
host and database now have a default value of "" unless otherwise set
FIXED BUG# 5214 Connection Timeout seems to be ignored
Added test case for bug# 5051: GetSchema not working correctly
Fixed problem where GetSchema would return false for IsUnique when the column is key
MySqlDataReader GetXXX methods now using the field level MySqlValue object and not performing conversions
FIXED BUG# 5097: DataReader returning NULL for time column
Added test case for LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE
Added replacetext custom nant task
Added CommandBuilderTest fixture
Added Last One Wins feature to CommandBuilder
Fixed persist security info case problem
Fixed GetBool so that 1, true, "true", and "yes" all count as trueWL# 2024 Make parameter mark configurable
Added the "old syntax" connection string parameter to allow use of @ parameter marker
Fixed Bug#4658 MySqlCommandBuilder
Fixed Bug#4864 ByteFX.MySqlClient caches passwords if 'Persist Security Info' is false
Updated license banner in all source files to include FLOSS exception
Added new .Types namespace and implementations for most current MySql types
Added MySqlField41 as a subclass of MySqlField
Changed many classes to now use the new .Types types
Changed type enum int to Int32, short to Int16, and bigint to Int64
Added dummy types UInt16, UInt32, and UInt64 to allow an unsigned parameter to be made
Connections are now reset when they are pulled from the connection pool
Refactored auth code in driver so it can be used for both auth and reset
Added UserReset test in PoolingTests.cs
Connections are now reset using COM_CHANGE_USER when pulled from the pool
Implemented SingleResultSet behavior
Implemented support of unicode
Added char set mappings for utf-8 and ucs-2
fixed Bug#4520 time fields overflow using bytefx .net mysql driver
Modified time test in data type test fixture to check for time spans where hours > 24
Fixed Bug#4505 Wrong string with backslash escaping in ByteFx.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlParameter
Added code to Parameter test case TestQuoting to test for backslashes
Fixed Bug#4486 mysqlcommandbuilder fails with multi-word column names
Fixed bug in TokenizeSql where underscore would terminate character capture in parameter name
Added test case for spaces in column names
Fixed bug# 4324 - MySqlDataReader.GetBytes don't works correctly
Added GetBytes() test case to DataReader test fixture
Now reading all server variables in InternalConnection.Configure into Hashtable
Now using string[] for index map in CharSetMap
Added CRInSQL test case for carriage returns in SQL
setting maxPacketSize to default value in Driver.ctor
Fixed Bug#4442 - Setting MySqlDbType on a parameter doesn't set generic type
Removed obsolete data types Long and LongLong
Fixed bug# 4071 - Overflow exception thrown when using "use pipe" on connection string
Changed "use pipe" keyword to "pipe name" or just "pipe"
Allow reading multiple resultsets from a single query
Added flags attribute to ServerStatusFlags enum
Changed name of ServerStatus enum to ServerStatusFlags
Fixed Bug#4386 - Inserted data row doesn't update properly
Fixed Bug#4074 - Error processing show create table
Change Packet.ReadLenInteger to ReadPackedLong and added packet.ReadPackedInteger that alwasy reads integers packed with 2,3,4
Added syntax.cs test fixture to test various SQL syntax bugs
Fixed bug# 4149 Improper handling of time values. Now time value of 00:00:00 is not treated as null.
Moved all test suite files into TestSuite folder
Fixed bug where null column would move the result packet pointer backward
Added new nant build script
Fixed Bug#3917 - clear tablename so it will be regen'ed properly during the next GenerateSchema.
Fixed Bug#3915 - GetValues was always returning zero and was also always trying to copy all fields rather than respecting the size of the array passed in.
Implemented shared memory access protocol
Implemented prepared statements for MySQL 4.1
Implemented stored procedures for MySQL 5.0
Renamed MySqlInternalConnection to InternalConnection
SQL is now parsed as chars, fixes problems with other languages
Added logging and allow batch connection string options
Fixed Bug#3888 - RowUpdating event not set when setting the DataAdapter property
Fixed bug in char set mapping
Implemented 4.1 authentication
Improved open/auth code in driver
Improved how connection bits are set during connection
Database name is now passed to server during initial handshake
Changed namespace for client to MySql.Data.MySqlClient
Changed assembly name of client to MySql.Data.dll
Changed license text in all source files to GPL
Added the MySqlClient.build Nant file
Removed the mono batch files
Moved some of the unused files into notused folder so nant build file can use wildcards
Implemented shared memory accesss
Major revamp in code structure
Prepared statements now working for MySql 4.1.1 and later
Finished implementing auth for 4.0, 4.1.0, and 4.1.1
Changed namespace from MySQL.Data.MySQLClient back to MySql.Data.MySqlClient
Fixed bug in CharSetMapping where it was trying to use text names as ints
Changed namespace to MySQL.Data.MySQLClient
Integrated auth changes from UC2004
Fixed bug where calling any of the GetXXX methods on a datareader before or after reading data would not throw the appropriate exception (thanks Luca Morelli <morelli.luca@iol.it>)
Added TimeSpan code in parameter.cs to properly serialize a timespan object to mysql time format (thanks Gianluca Colombo <g.colombo@alfi.it>)
Added TimeStamp to parameter serialization code. Prevented DataAdatper updates from working right (thanks MIchael King)
Fixed a misspelling in MySqlHelper.cs (thanks Patrick Kristiansen)
Driver now using charset number given in handshake to create encoding
Changed command editor to point to MySqlClient.Design
Fixed bug in Version.isAtLeast
Changed DBConnectionString to support changes done to MySqlConnectionString
Removed SqlCommandEditor and DataAdapterPreviewDialog
Using new long return values in many places
Integrated new CompressedStream class
Changed ConnectionString and added attributes to allow it to be used in MySqlClient.Design
Changed packet.cs to support newer lengths in ReadLenInteger
changed other classes to use new properties and fields of MySqlConnectionString
ConnectionInternal is now using PING to see whether the server is alive
Moved toolbox bitmaps into resource/
Changed field.cs to allow values to come directly from row buffer
Changed to use the new driver.Send syntax
Using a new packet queueing system
started work handling the "broken" compression packet handling
Fixed bug in StreamCreator where failure to connect to a host would continue to loop infinitly (thanks Kevin Casella)
Improved connectstring handling
Moved designers into Pro product
Removed some old commented out code from command.cs
Fixed a problem with compression
Fixed connection object where an exception throw prior to the connection opening would not leave the connection in the connecting state (thanks Chris Cline )
Added GUID support
Fixed sequence out of order bug (thanks Mark Reay)
Enum values now supported as parameter values (thanks Philipp Sumi)
Year datatype now supported
fixed compression
Fixed bug where a parameter with a TimeSpan as the value would not serialize properly
Fixed bug where default ctor would not set default connection string values
Added some XML comments to some members
Work to fix/improve compression handling
Improved ConnectionString handling so that it better matches the standard set by SqlClient.
A MySqlException is now thrown if a username is not included in the connection string
Localhost is now used as the default if not specified on the connection string
An exception is now thrown if an attempt is made to set the connection string while the connection is open
Small changes to ConnectionString docs
Removed MultiHostStream and MySqlStream. Replaced it with Common/StreamCreator
Added support for Use Pipe connection string value
Added Platform class for easier access to platform utility functions
Fixed small pooling bug where new connection was not getting created after IsAlive fails
Added Platform.cs and StreamCreator.cs
Fixed Field.cs to properly handle 4.1 style timestamps
Changed Common.Version to Common.DBVersion to avoid name conflict
Fixed field.cs so that text columns return the right field type (thanks beni27@gmx.net)
Added MySqlError class to provide some reference for error codes (thanks Geert Veenstra)
Added Unix socket support (thanks Mohammad DAMT [md@mt.web.id])
only calling Thread.Sleep when no data is available
improved escaping of quote characters in parameter data
removed misleading comments from parameter.cs
fixed pooling bug
same pooling bug fixed again!! ;-)
Fixed ConnectionSTring editor dialog (thanks marco p (pomarc))
UserId now supported in connection strings (thanks Jeff Neeley)
Attempting to create a parameter that is not input throws an exception (thanks Ryan Gregg)
Added much documentation
checked in new MultiHostStream capability. Big thanks to Dan Guisinger for this. he originally submitted the code and idea of supporting multiple machines on the connect string.
Added alot of documentation. Still alot to do.
Fixed speed issue with 0.73
changed to Thread.Sleep(0) in MySqlDataStream to help optimize the case where it doesn't need to wait (thanks Todd German)
Prepopulating the idlepools to MinPoolSize
Fixed MySqlPool deadlock condition as well as stupid bug where CreateNewPooledConnection was not ever adding new connections to the pool. Also fixed MySqlStream.ReadBytes and ReadByte to not use TicksPerSecond which does not appear to always be right. (thanks Matthew J. Peddlesden)
Fix for precision and scale (thanks Matthew J. Peddlesden)
Added Thread.Sleep(1) to stream reading methods to be more cpu friendly (thanks Sean McGinnis)
Fixed problem where ExecuteReader would sometime return null (thanks Lloyd Dupont )
Fixed major bug with null field handling (thanks Naucki)
enclosed queries for max_allowed_packet and characterset inside try catch (and set defaults)
fixed problem where socket was not getting closed properly (thanks Steve!)
Fixed problem where ExecuteNonQuery was not always returning the right value
Fixed InternalConnection to not use @@session.max_allowed_packet but use @@max_allowed_packet. (Thanks Miguel)
Added many new XML doc lines
Fixed sql parsing to not send empty queries (thanks Rory)
Fixed problem where the reader was not unpeeking the packet on close
Fixed problem where user variables were not being handled (thanks Sami Vaaraniemi)
Fixed loop checking in the MySqlPool (thanks Steve M. Brown)
Fixed ParameterCollection.Add method to match SqlClient (thanks Joshua Mouch)
Fixed ConnectionSTring parsing to handle no and yes for boolean and not lowercase values (thanks Naucki)
Added InternalConnection class, changes to pooling
Implemented Persist Security Info
Added security.cs and version.cs to project
Fixed DateTime handling in Parameter.cs (thanks Burkhard Perkens-Golomb)
Fixed parameter serialization where some types would throw a cast exception
Fixed DataReader to convert all returned values to prevent casting errors (thanks Keith Murray)
Added code to Command.ExecuteReader to return null if the initial SQL command throws an exception (thanks Burkhard Perkens-Golomb)
Fixed ExecuteScalar bug introduced with restructure
Restructure to allow for LOCAL DATA INFILE and better sequencing of packets
Fixed several bugs related to restructure.
Early work done to support more secure passwords in Mysql 4.1. Old passwords in 4.1 not supported yet
Parameters appearing after system parameters are now handled correctly (Adam M. (adammil))
strings can now be assigned directly to blob fields (Adam M.)
Fixed float parameters (thanks Pent)
Improved Parameter ctor and ParameterCollection.Add methods to better match SqlClient (thx Joshua Mouch )
Corrected Connection.CreateCommand to return a MySqlCommand type
Fixed connection string designer dialog box problem (thanks Abraham Guyt)
Fixed problem with sending commands not always reading the response packet (thanks Joshua Mouch )
Fixed parameter serialization where some blobs types were not being handled (thanks Sean McGinnis )
Removed spurious MessageBox.show from DataReader code (thanks Joshua Mouch )
Fixed a nasty bug in the split sql code (thanks everyone! :-) )
Fixed bug in MySqlStream where too much data could attempt to be read (thanks Peter Belbin)
Implemented HasRows (thanks Nash Pherson)
Fixed bug where tables with more than 252 columns cause an exception ( thanks Joshua Kessler )
Fixed bug where SQL statements ending in ; would cause a problem ( thanks Shane Krueger )
Fixed bug in driver where error messages were getting truncated by 1 character (thanks Shane Krueger)
Made MySqlException serializable (thanks Mathias Hasselmann)
Updated some of the character code pages to be more accurate
Fixed problem where readers could be opened on connections that had readers open
Release of 0.70
Moved test to separate assembly MySqlClientTests
Fixed stupid problem in driver with sequence out of order (Thanks Peter Belbin)
Added some pipe tests
Increased default max pool size to 50
Compiles with Mono 0-24
Fixed connection and data reader dispose problems
Added String datatype handling to parameter serialization
Fixed sequence problem in driver that occurred after thrown exception (thanks Burkhard Perkens-Golomb)
Added support for CommandBehavior.SingleRow to DataReader
Fixed command sql processing so quotes are better handled (thanks Theo Spears)
Fixed parsing of double, single, and decimal values to account for non-English separators. You still have to use the right syntax if you using hard coded sql, but if you use parameters the code will convert floating point types to use '.' appropriately internal both into the server and out. [ Thanks anonymous ]
Added MySqlStream class to simplify timeOuts and driver coding.
Fixed DataReader so that it is closed properly when the associated connection is closed. [thanks smishra]
Made client more SqlClient compliant so that DataReaders have to be closed before the connection can be used to run another command
Improved DBNull.Value handling in the fields
Added several unit tests
Fixed MySqlException so that the base class is actually called :-o
Improved driver coding
Fixed bug where NextResult was returning false on the last resultset
Added more tests for MySQL
Improved casting problems by equating unsigned 32bit values to Int64 and usigned 16bit values to Int32, and so forth.
Added new ctor for MySqlParameter for (name, type, size, srccol)
Fixed bug in MySqlDataReader where it didn't check for null fieldlist before returning field count
Started adding MySqlClient unit tests (added MySqlClient/Tests folder and some test cases)
Fixed some things in Connection String handling
Moved INIT_DB to MySqlPool. I may move it again, this is in preparation of the conference.
Fixed bug inside CommandBuilder that prevented inserts from happening properly
Reworked some of the internals so that all three execute methods of Command worked properly
FIxed many small bugs found during benchmarking
The first cut of CoonectionPooling is working. "min pool size" and "max pool size" are respected.
Work to enable multiple resultsets to be returned
Character sets are handled much more intelligently now. The driver queries MySQL at startup for the default character set. That character set is then used for conversions if that code page can be loaded. If not, then the default code page for the current OS is used.
Added code to save the inferred type in the name,value ctor of Parameter
Also, inferred type if value of null parameter is changed using Value property
Converted all files to use proper Camel case. MySQL is now MySql in all files. PgSQL is now PgSql
Added attribute to PgSql code to prevent designer from trying to show
Added MySQLDbType property to Parameter object and added proper conversion code to convert from DbType to MySQLDbType)
Removed unused ObjectToString method from MySQLParameter.cs
Fixed Add(..) method in ParameterCollection so that it doesn't use Add(name, value) instead.
Fixed IndexOf and Contains in ParameterCollection to be aware that parameter names are now stored without @
Fixed Command.ConvertSQLToBytes so it only allows characters that can be in MySQL variable names
Fixed DataReader and Field so that blob fields read their data from Field.cs and GetBytes works right
Added simple query builder editor to CommandText property of MySQLCommand
Fixed CommandBuilder and Parameter serialization to account for Parameters not storing @ in their names
Removed MySQLFieldType enum from Field.cs. Now using MySQLDbType enum
Added Designer attribute to several classes to prevent designer view when using VS.Net
Fixed Initial catalog typo in ConnectionString designer
Removed 3 parameter ctor for MySQLParameter that conflicted with (name, type, value)
changed MySQLParameter so paramName is now stored without leading @ (this fixed null inserts when using designer)
Changed TypeConverter for MySQLParameter to use the ctor with all properties
Fixed sequence issue in driver
Added DbParametersEditor to make parameter editing more like SqlClient
Fixed Command class so that parameters can be edited using the designer
Update connection string designer to support Use Compression flag
Fixed string encoding so that European characters like ä will work correctly
Creating base classes to aid in building new data providers
Added support for UID key in connection string
Field, parameter, command now using DBNull.Value instead of null
CommandBuilder using DBNull.Value
CommandBuilder now builds insert command correctly when an auto_insert field is not present
Field now uses typeof keyword to return System.Types (performance)
MySQLCommandBuilder now implemented
Transaction support now implemented (not all table types support this)
GetSchemaTable fixed to not use xsd (for Mono)
Driver is now Mono-compatible!!
TIME data type now supported
More work to improve Timestamp data type handling
Changed signatures of all classes to match corresponding SqlClient classes
Protocol compression using SharpZipLib (www.icsharpcode.net)
Named pipes on Windows now working properly
Work done to improve Timestamp data type handling
Implemented IEnumerable on DataReader so DataGrid would work
MySQL provides connectivity for client applications developed in the Java programming language via a JDBC driver, which is called MySQL Connector/J.
MySQL Connector/J is a JDBC-3.0 “Type 4” driver, which means that is pure Java, implements version 3.0 of the JDBC specification, and communicates directly with the MySQL server using the MySQL protocol.
This document is arranged for a beginning JDBC developer. If you are already experienced with using JDBC, you might consider starting with the Section 23.3.2, “Installing Connector/J”.
Although JDBC is useful by itself, we would hope that if you are not familiar with JDBC that after reading the first few sections of this manual, that you would avoid using “naked” JDBC for all but the most trivial problems and consider using one of the popular persistence frameworks such as Hibernate, Spring's JDBC templates or Ibatis SQL Maps to do the majority of repetitive work and heavier lifting that is sometimes required with JDBC.
This section is not designed to be a complete JDBC tutorial. If you need more information about using JDBC you might be interested in the following online tutorials that are more in-depth than the information presented here:
JDBC Basics — A tutorial from Sun covering beginner topics in JDBC
JDBC Short Course — A more in-depth tutorial from Sun and JGuru
This section provides some general JDBC background.
When you are using JDBC outside of an application server, the
DriverManager class manages the establishment
of Connections.
The DriverManager needs to be told which JDBC
drivers it should try to make Connections with. The easiest way
to do this is to use Class.forName() on the
class that implements the java.sql.Driver
interface. With MySQL Connector/J, the name of this class is
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver. With this method, you
could use an external configuration file to supply the driver
class name and driver parameters to use when connecting to a
database.
The following section of Java code shows how you might register
MySQL Connector/J from the main() method of
your application:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
// Notice, do not import com.mysql.jdbc.*
// or you will have problems!
public class LoadDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// The newInstance() call is a work around for some
// broken Java implementations
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver").newInstance();
} catch (Exception ex) {
// handle the error
}
}
After the driver has been registered with the
DriverManager, you can obtain a
Connection instance that is connected to a
particular database by calling
DriverManager.getConnection():
Example 23.1. Obtaining a Connection From the DriverManager
This example shows how you can obtain a
Connection instance from the
DriverManager. There are a few different
signatures for the getConnection()
method. You should see the API documentation that comes with
your JDK for more specific information on how to use them.
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
... try {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost/test?user=monty&password=greatsqldb");
// Do something with the Connection
....
} catch (SQLException ex) {
// handle any errors
System.out.println("SQLException: " + ex.getMessage());
System.out.println("SQLState: " + ex.getSQLState());
System.out.println("VendorError: " + ex.getErrorCode());
}
Once a Connection is established, it
can be used to create Statement and
PreparedStatement objects, as well as
retrieve metadata about the database. This is explained in the
following sections.
Statement objects allow you to execute
basic SQL queries and retrieve the results through the
ResultSet class which is described later.
To create a Statement instance, you call
the createStatement() method on the
Connection object you have retrieved via one
of the DriverManager.getConnection() or
DataSource.getConnection() methods
described earlier.
Once you have a Statement instance, you
can execute a SELECT query by calling the
executeQuery(String) method with the SQL you
want to use.
To update data in the database, use the
executeUpdate(String SQL) method. This method
returns the number of rows affected by the update statement.
If you don't know ahead of time whether the SQL statement will
be a SELECT or an
UPDATE/INSERT, then you
can use the execute(String SQL) method. This
method will return true if the SQL query was a
SELECT, or false if it was an
UPDATE, INSERT, or
DELETE statement. If the statement was a
SELECT query, you can retrieve the results by
calling the getResultSet() method. If the
statement was an UPDATE,
INSERT, or DELETE
statement, you can retrieve the affected rows count by calling
getUpdateCount() on the
Statement instance.
Example 23.2. Using java.sql.Statement to Execute a SELECT Query
// assume that conn is an already created JDBC connection
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
stmt = conn.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT foo FROM bar");
// or alternatively, if you don't know ahead of time that
// the query will be a SELECT...
if (stmt.execute("SELECT foo FROM bar")) {
rs = stmt.getResultSet();
}
// Now do something with the ResultSet ....
} finally {
// it is a good idea to release
// resources in a finally{} block
// in reverse-order of their creation
// if they are no-longer needed
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) { // ignore }
rs = null;
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) { // ignore }
stmt = null;
}
}
Starting with MySQL server version 5.0 when used with
Connector/J 3.1.1 or newer, the
java.sql.CallableStatement interface is
fully implemented with the exception of the
getParameterMetaData() method.
MySQL's stored procedure syntax is documented in the "Stored Procedures and Functions" section of the MySQL Reference Manual.
Connector/J exposes stored procedure functionality through
JDBC's CallableStatement interface.
The following example shows a stored procedure that returns the
value of inOutParam incremented by 1, and the
string passed in via inputParam as a
ResultSet:
Example 23.3. Stored Procedure Example
CREATE PROCEDURE demoSp(IN inputParam VARCHAR(255), INOUT inOutParam INT)
BEGIN
DECLARE z INT;
SET z = inOutParam + 1;
SET inOutParam = z;
SELECT inputParam;
SELECT CONCAT('zyxw', inputParam);
END
To use the demoSp procedure with
Connector/J, follow these steps:
Prepare the callable statement by using
Connection.prepareCall().Notice that you have to use JDBC escape syntax, and that the parentheses surrounding the parameter placeholders are not optional:
Example 23.4. Using
Connection.prepareCall()import java.sql.CallableStatement; ... // // Prepare a call to the stored procedure 'demoSp' // with two parameters // // Notice the use of JDBC-escape syntax ({call ...}) // CallableStatement cStmt = conn.prepareCall("{call demoSp(?, ?)}"); cStmt.setString(1, "abcdefg");Note
Connection.prepareCall()is an expensive method, due to the metadata retrieval that the driver performs to support output parameters. For performance reasons, you should try to minimize unnecessary calls toConnection.prepareCall()by reusingCallableStatementinstances in your code.Register the output parameters (if any exist)
To retrieve the values of output parameters (parameters specified as
OUTorINOUTwhen you created the stored procedure), JDBC requires that they be specified before statement execution using the variousregisterOutputParameter()methods in theCallableStatementinterface:Example 23.5. Registering Output Parameters
import java.sql.Types; ... // // Connector/J supports both named and indexed // output parameters. You can register output // parameters using either method, as well // as retrieve output parameters using either // method, regardless of what method was // used to register them. // // The following examples show how to use // the various methods of registering // output parameters (you should of course // use only one registration per parameter). // // // Registers the second parameter as output, and // uses the type 'INTEGER' for values returned from // getObject() // cStmt.registerOutParameter(2, Types.INTEGER); // // Registers the named parameter 'inOutParam', and // uses the type 'INTEGER' for values returned from // getObject() // cStmt.registerOutParameter("inOutParam", Types.INTEGER); ...Set the input parameters (if any exist)
Input and in/out parameters are set as for
PreparedStatementobjects. However,CallableStatementalso supports setting parameters by name:Example 23.6. Setting
CallableStatementInput Parameters... // // Set a parameter by index // cStmt.setString(1, "abcdefg"); // // Alternatively, set a parameter using // the parameter name // cStmt.setString("inputParameter", "abcdefg"); // // Set the 'in/out' parameter using an index // cStmt.setInt(2, 1); // // Alternatively, set the 'in/out' parameter // by name // cStmt.setInt("inOutParam", 1); ...Execute the
CallableStatement, and retrieve any result sets or output parameters.Although
CallableStatementsupports calling any of theStatementexecute methods (executeUpdate(),executeQuery()orexecute()), the most flexible method to call isexecute(), as you do not need to know ahead of time if the stored procedure returns result sets:Example 23.7. Retrieving Results and Output Parameter Values
... boolean hadResults = cStmt.execute(); // // Process all returned result sets // while (hadResults) { ResultSet rs = cStmt.getResultSet(); // process result set ... hadResults = cStmt.getMoreResults(); } // // Retrieve output parameters // // Connector/J supports both index-based and // name-based retrieval // int outputValue = cStmt.getInt(2); // index-based outputValue = cStmt.getInt("inOutParam"); // name-based ...
Before version 3.0 of the JDBC API, there was no standard way of
retrieving key values from databases that supported “auto
increment” or identity columns. With older JDBC drivers
for MySQL, you could always use a MySQL-specific method on the
Statement interface, or issue the query
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() after issuing an
INSERT to a table that had an
AUTO_INCREMENT key. Using the MySQL-specific
method call isn't portable, and issuing a
SELECT to get the
AUTO_INCREMENT key's value requires another
round-trip to the database, which isn't as efficient as
possible. The following code snippets demonstrate the three
different ways to retrieve AUTO_INCREMENT
values. First, we demonstrate the use of the new JDBC-3.0 method
getGeneratedKeys() which is now the
preferred method to use if you need to retrieve
AUTO_INCREMENT keys and have access to
JDBC-3.0. The second example shows how you can retrieve the same
value using a standard SELECT
LAST_INSERT_ID() query. The final example shows how
updatable result sets can retrieve the
AUTO_INCREMENT value when using the
insertRow() method.
Example 23.8. Retrieving AUTO_INCREMENT Column Values using
Statement.getGeneratedKeys()
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//
// Create a Statement instance that we can use for
// 'normal' result sets assuming you have a
// Connection 'conn' to a MySQL database already
// available
stmt = conn.createStatement(java.sql.ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY,
java.sql.ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
//
// Issue the DDL queries for the table for this example
//
stmt.executeUpdate("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS autoIncTutorial");
stmt.executeUpdate(
"CREATE TABLE autoIncTutorial ("
+ "priKey INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, "
+ "dataField VARCHAR(64), PRIMARY KEY (priKey))");
//
// Insert one row that will generate an AUTO INCREMENT
// key in the 'priKey' field
//
stmt.executeUpdate(
"INSERT INTO autoIncTutorial (dataField) "
+ "values ('Can I Get the Auto Increment Field?')",
Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
//
// Example of using Statement.getGeneratedKeys()
// to retrieve the value of an auto-increment
// value
//
int autoIncKeyFromApi = -1;
rs = stmt.getGeneratedKeys();
if (rs.next()) {
autoIncKeyFromApi = rs.getInt(1);
} else {
// throw an exception from here
}
rs.close();
rs = null;
System.out.println("Key returned from getGeneratedKeys():"
+ autoIncKeyFromApi);
} finally {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
// ignore
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
// ignore
}
}
}
Example 23.9. Retrieving AUTO_INCREMENT Column Values using
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//
// Create a Statement instance that we can use for
// 'normal' result sets.
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//
// Issue the DDL queries for the table for this example
//
stmt.executeUpdate("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS autoIncTutorial");
stmt.executeUpdate(
"CREATE TABLE autoIncTutorial ("
+ "priKey INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, "
+ "dataField VARCHAR(64), PRIMARY KEY (priKey))");
//
// Insert one row that will generate an AUTO INCREMENT
// key in the 'priKey' field
//
stmt.executeUpdate(
"INSERT INTO autoIncTutorial (dataField) "
+ "values ('Can I Get the Auto Increment Field?')");
//
// Use the MySQL LAST_INSERT_ID()
// function to do the same thing as getGeneratedKeys()
//
int autoIncKeyFromFunc = -1;
rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()");
if (rs.next()) {
autoIncKeyFromFunc = rs.getInt(1);
} else {
// throw an exception from here
}
rs.close();
System.out.println("Key returned from " + "'SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()': "
+ autoIncKeyFromFunc);
} finally {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
// ignore
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
// ignore
}
}
}
Example 23.10. Retrieving AUTO_INCREMENT Column Values in
Updatable ResultSets
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//
// Create a Statement instance that we can use for
// 'normal' result sets as well as an 'updatable'
// one, assuming you have a Connection 'conn' to
// a MySQL database already available
//
stmt = conn.createStatement(java.sql.ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY,
java.sql.ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
//
// Issue the DDL queries for the table for this example
//
stmt.executeUpdate("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS autoIncTutorial");
stmt.executeUpdate(
"CREATE TABLE autoIncTutorial ("
+ "priKey INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, "
+ "dataField VARCHAR(64), PRIMARY KEY (priKey))");
//
// Example of retrieving an AUTO INCREMENT key
// from an updatable result set
//
rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT priKey, dataField "
+ "FROM autoIncTutorial");
rs.moveToInsertRow();
rs.updateString("dataField", "AUTO INCREMENT here?");
rs.insertRow();
//
// the driver adds rows at the end
//
rs.last();
//
// We should now be on the row we just inserted
//
int autoIncKeyFromRS = rs.getInt("priKey");
rs.close();
rs = null;
System.out.println("Key returned for inserted row: "
+ autoIncKeyFromRS);
} finally {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
// ignore
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
// ignore
}
}
}
When you run the preceding example code, you should get the
following output: Key returned from
getGeneratedKeys(): 1 Key returned from
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID(): 1 Key returned for
inserted row: 2 You should be aware, that at times, it can be
tricky to use the SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID()
query, as that function's value is scoped to a connection. So,
if some other query happens on the same connection, the value
will be overwritten. On the other hand, the
getGeneratedKeys() method is scoped by the
Statement instance, so it can be used
even if other queries happen on the same connection, but not on
the same Statement instance.
Use the following instructions to install Connector/J
MySQL Connector/J supports Java-2 JVMs, including JDK-1.2.x, JDK-1.3.x, JDK-1.4.x and JDK-1.5.x, and requires JDK-1.4.x or newer to compile (but not run). MySQL Connector/J does not support JDK-1.1.x or JDK-1.0.x
Because of the implementation of
java.sql.Savepoint, Connector/J 3.1.0
and newer will not run on JDKs older than 1.4 unless the class
verifier is turned off (-Xverify:none), as
the class verifier will try to load the class definition for
java.sql.Savepoint even though it is
not accessed by the driver unless you actually use savepoint
functionality.
Caching functionality provided by Connector/J 3.1.0 or newer
is also not available on JVMs older than 1.4.x, as it relies
on java.util.LinkedHashMap which was
first available in JDK-1.4.0.
MySQL Connector/J supports all known MySQL server versions. Some features (foreign keys, updatable result sets) require more recent versions of MySQL to operate.
When connecting to MySQL server version 4.1 or newer, it is best to use MySQL Connector/J version 3.1, as it has full support for features in the newer versions of the server, including Unicode characters, views, stored procedures and server-side prepared statements.
Although Connector/J version 3.0 will connect to MySQL server, version 4.1 or newer, and implements Unicode characters and the new authorization mechanism, Connector/J 3.0 will not be updated to support new features in current and future server versions.
MySQL Connector/J is distributed as a .zip or .tar.gz archive
containing the sources, the class files a class-file only
“binary” .jar archive named
"mysql-connector-java-[version]-bin.jar",
and starting with Connector/J 3.1.8 a “debug”
build of the driver in a file named
"mysql-connector-java-[version]-bin-g.jar".
Starting with Connector/J 3.1.9, we don't ship the .class files “unbundled,” they are only available in the JAR archives that ship with the driver.
You should not use the “debug” build of the
driver unless instructed to do so when reporting a problem or
bug to MySQL AB, as it is not designed to be run in production
environments, and will have adverse performance impact when
used. The debug binary also depends on the Aspect/J runtime
library, which is located in the
src/lib/aspectjrt.jar file that comes
with the Connector/J distribution.
You will need to use the appropriate graphical or command-line utility to un-archive the distribution (for example, WinZip for the .zip archive, and tar for the .tar.gz archive). Because there are potentially long filenames in the distribution, we use the GNU tar archive format. You will need to use GNU tar (or an application that understands the GNU tar archive format) to unpack the .tar.gz variant of the distribution.
Once you have extracted the distribution archive, you can install the driver by placing mysql-connector-java-[version]-bin.jar in your classpath, either by adding the FULL path to it to your CLASSPATH environment variable, or by directly specifying it with the command line switch -cp when starting your JVM
If you are going to use the driver with the JDBC DriverManager, you would use "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" as the class that implements java.sql.Driver.
Example 23.11. Setting the CLASSPATH Under UNIX
The following command works for 'csh' under UNIX:
$ setenv CLASSPATH /path/to/mysql-connector-java-[version]-bin.jar:$CLASSPATH
The above command can be added to the appropriate startup file for the login shell to make MySQL Connector/J available to all Java applications.
If you want to use MySQL Connector/J with an application server such as Tomcat or JBoss, you will have to read your vendor's documentation for more information on how to configure third-party class libraries, as most application servers ignore the CLASSPATH environment variable. For configuration examples for some J2EE application servers, see Section 23.3.4, “Using Connector/J with J2EE and Other Java Frameworks”. However, the authoritative source for JDBC connection pool configuration information for your particular application server is the documentation for that application server.
If you are developing servlets or JSPs, and your application server is J2EE-compliant, you can put the driver's .jar file in the WEB-INF/lib subdirectory of your webapp, as this is a standard location for third party class libraries in J2EE web applications.
You can also use the MysqlDataSource or MysqlConnectionPoolDataSource classes in the com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional package, if your J2EE application server supports or requires them. Starting with Connector/J 5.0.0, the javax.sql.XADataSource interface is implemented via the com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlXADataSource class, which supports XA distributed transactions when used in combination with MySQL server version 5.0.
The various MysqlDataSource classes support the following parameters (through standard "set" mutators):
user
password
serverName (see the previous section about fail-over hosts)
databaseName
port
MySQL AB tries to keep the upgrade process as easy as possible, however as is the case with any software, sometimes changes need to be made in new versions to support new features, improve existing functionality, or comply with new standards.
This section has information about what users who are upgrading from one version of Connector/J to another (or to a new version of the MySQL server, with respect to JDBC functionality) should be aware of.
Connector/J 3.1 is designed to be backward-compatible with Connector/J 3.0 as much as possible. Major changes are isolated to new functionality exposed in MySQL-4.1 and newer, which includes Unicode character sets, server-side prepared statements, SQLState codes returned in error messages by the server and various performance enhancements that can be enabled or disabled via configuration properties.
Unicode Character Sets — See the next section, as well as Chapter 10, Character Set Support, for information on this new feature of MySQL. If you have something misconfigured, it will usually show up as an error with a message similar to
Illegal mix of collations.Server-side Prepared Statements — Connector/J 3.1 will automatically detect and use server-side prepared statements when they are available (MySQL server version 4.1.0 and newer).
Starting with version 3.1.7, the driver scans SQL you are preparing via all variants of
Connection.prepareStatement()to determine if it is a supported type of statement to prepare on the server side, and if it is not supported by the server, it instead prepares it as a client-side emulated prepared statement. You can disable this feature by passing 'emulateUnsupportedPstmts=false' in your JDBC URL.If your application encounters issues with server-side prepared statements, you can revert to the older client-side emulated prepared statement code that is still presently used for MySQL servers older than 4.1.0 with the following connection property:
useServerPrepStmts=falseDatetimes with all-zero components ('0000-00-00 ...') — These values can not be represented reliably in Java. Connector/J 3.0.x always converted them to NULL when being read from a ResultSet.
Connector/J 3.1 throws an exception by default when these values are encountered as this is the most correct behavior according to the JDBC and SQL standards. This behavior can be modified using the ' zeroDateTimeBehavior ' configuration property. The allowable values are: 'exception' (the default), which throws an SQLException with an SQLState of 'S1009', 'convertToNull', which returns NULL instead of the date, and 'round', which rounds the date to the nearest closest value which is '0001-01-01'.
Starting with Connector/J 3.1.7, ResultSet.getString() can be decoupled from this behavior via ' noDatetimeStringSync=true ' (the default value is 'false') so that you can get retrieve the unaltered all-zero value as a String. It should be noted that this also precludes using any time zone conversions, therefore the driver will not allow you to enable noDatetimeStringSync and useTimezone at the same time.
New SQLState Codes — Connector/J 3.1 uses SQL:1999 SQLState codes returned by the MySQL server (if supported), which are different from the “legacy” X/Open state codes that Connector/J 3.0 uses. If connected to a MySQL server older than MySQL-4.1.0 (the oldest version to return SQLStates as part of the error code), the driver will use a built-in mapping. You can revert to the old mapping by using the following configuration property:
useSqlStateCodes=falseCalling ResultSet.getString() on a BLOB column will now return the address of the byte[] array that represents it, instead of a String representation of the BLOB. BLOBs have no character set, so they can't be converted to java.lang.Strings without data loss or corruption.
To store strings in MySQL with LOB behavior, use one of the TEXT types, which the driver will treat as a java.sql.Clob.
Starting with Connector/J 3.1.8 a “debug” build of the driver in a file named "
mysql-connector-java-[version]-bin-g.jar" is shipped alongside the normal “binary” jar file that is named "mysql-connector-java-[version]-bin.jar".Starting with Connector/J 3.1.9, we don't ship the .class files “unbundled,” they are only available in the JAR archives that ship with the driver.
You should not use the “debug” build of the driver unless instructed to do so when reporting a problem or bug to MySQL AB, as it is not designed to be run in production environments, and will have adverse performance impact when used. The debug binary also depends on the Aspect/J runtime library, which is located in the
src/lib/aspectjrt.jarfile that comes with the Connector/J distribution.
Using the UTF-8 Character Encoding - Prior to MySQL server version 4.1, the UTF-8 character encoding was not supported by the server, however the JDBC driver could use it, allowing storage of multiple character sets in latin1 tables on the server.
Starting with MySQL-4.1, this functionality is deprecated. If you have applications that rely on this functionality, and can not upgrade them to use the official Unicode character support in MySQL server version 4.1 or newer, you should add the following property to your connection URL:
useOldUTF8Behavior=trueServer-side Prepared Statements - Connector/J 3.1 will automatically detect and use server-side prepared statements when they are available (MySQL server version 4.1.0 and newer). If your application encounters issues with server-side prepared statements, you can revert to the older client-side emulated prepared statement code that is still presently used for MySQL servers older than 4.1.0 with the following connection property:
useServerPrepStmts=false
Caution
You should read this section only if you are interested in helping us test our new code. If you just want to get MySQL Connector/J up and running on your system, you should use a standard release distribution.
To install MySQL Connector/J from the development source tree, make sure that you have the following prerequisites:
Subversion, to check out the sources from our repository (available from http://subversion.tigris.org/).
Apache Ant version 1.6 or newer (available from http://ant.apache.org/).
JDK-1.4.2 or later. Although MySQL Connector/J can be installed on older JDKs, to compile it from source you must have at least JDK-1.4.2.
The Subversion source code repository for MySQL Connector/J is located at http://svn.mysql.com/svnpublic/connector-j. In general, you should not check out the entire repository because it contains every branch and tag for MySQL Connector/J and is quite large.
To check out and compile a specific branch of MySQL Connector/J, follow these steps:
At the time of this writing, there are three active branches of Connector/J:
branch_3_0,branch_3_1andbranch_5_0. Check out the latest code from the branch that you want with the following command (replacing[major]and[minor]with appropriate version numbers):shell>
svn co http://svn.mysql.com/svnpublic/connector-j/branches/branch_[major]_[minor]/connector-jThis creates a
connector-jsubdirectory in the current directory that contains the latest sources for the requested branch.Change location to the
connector-jdirectory to make it your current working directory:shell>
cd connector-jIssue the following command to compile the driver and create a
.jarfile suitable for installation:shell>
ant distThis creates a
builddirectory in the current directory, where all build output will go. A directory is created in thebuilddirectory that includes the version number of the sources you are building from. This directory contains the sources, compiled.classfiles, and a.jarfile suitable for deployment. For other possible targets, including ones that will create a fully packaged distribution, issue the following command:shell>
ant --projecthelpA newly created
.jarfile containing the JDBC driver will be placed in the directorybuild/mysql-connector-java-.[version]Install the newly created JDBC driver as you would a binary
.jarfile that you download from MySQL by following the instructions in Section 23.3.2.1.3, “Installing the Driver and Configuring theCLASSPATH”.
- 23.3.3.1. Driver/Datasource Class Names, URL Syntax and Configuration Properties for Connector/J
- 23.3.3.2. JDBC API Implementation Notes
- 23.3.3.3. Java, JDBC and MySQL Types
- 23.3.3.4. Using Character Sets and Unicode
- 23.3.3.5. Connecting Securely Using SSL
- 23.3.3.6. Using Master/Slave Replication with ReplicationConnection
The name of the class that implements java.sql.Driver in MySQL Connector/J is 'com.mysql.jdbc.Driver'. The 'org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver' class name is also usable to remain backward-compatible with MM.MySQL. You should use this class name when registering the driver, or when otherwise configuring software to use MySQL Connector/J.
The JDBC URL format for MySQL Connector/J is as follows, with items in square brackets ([, ]) being optional:
jdbc:mysql://[host][,failoverhost...][:port]/[database][?propertyName1][=propertyValue1][&propertyName2][=propertyValue2]...
If the hostname is not specified, it defaults to '127.0.0.1'. If the port is not specified, it defaults to '3306', the default port number for MySQL servers.
jdbc:mysql://[host:port],[host:port].../[database][?propertyName1][=propertyValue1][&propertyName2][=propertyValue2]...
If the database is not specified, the connection will be made
with no default database. In this case, you will need to either
call the setCatalog() method on the
Connection instance or fully-specify table names using the
database name (i.e. 'SELECT dbname.tablename.colname FROM
dbname.tablename...') in your SQL. Not specifying the database
to use upon connection is generally only useful when building
tools that work with multiple databases, such as GUI database
managers.
MySQL Connector/J has fail-over support. This allows the driver to fail-over to any number of “slave” hosts and still perform read-only queries. Fail-over only happens when the connection is in an autoCommit(true) state, because fail-over can not happen reliably when a transaction is in progress. Most application servers and connection pools set autoCommit to 'true' at the end of every transaction/connection use.
The fail-over functionality has the following behavior:
If the URL property "autoReconnect" is false: Failover only happens at connection initialization, and failback occurs when the driver determines that the first host has become available again.
If the URL property "autoReconnect" is true: Failover happens when the driver determines that the connection has failed (before every query), and falls back to the first host when it determines that the host has become available again (after queriesBeforeRetryMaster queries have been issued).
In either case, whenever you are connected to a "failed-over" server, the connection will be set to read-only state, so queries that would modify data will have exceptions thrown (the query will never be processed by the MySQL server).
Configuration properties define how Connector/J will make a connection to a MySQL server. Unless otherwise noted, properties can be set for a DataSource object or for a Connection object.
Configuration Properties can be set in one of the following ways:
Using the set*() methods on MySQL implementations of java.sql.DataSource (which is the preferred method when using implementations of java.sql.DataSource):
com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource
com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlConnectionPoolDataSource
As a key/value pair in the java.util.Properties instance passed to DriverManager.getConnection() or Driver.connect()
As a JDBC URL parameter in the URL given to java.sql.DriverManager.getConnection(), java.sql.Driver.connect() or the MySQL implementations of javax.sql.DataSource's setURL() method.
Note
If the mechanism you use to configure a JDBC URL is XML-based, you will need to use the XML character literal & to separate configuration parameters, as the ampersand is a reserved character for XML.
The properties are listed in the following table:
Table 23.1. Connection Properties
| Property Name | Definition | Required? | Default Value | Since Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connection/Authentication | ||||
| user | The user to connect as | No | all | |
| password | The password to use when connecting | No | all | |
| socketFactory | The name of the class that the driver should use for creating socket connections to the server. This class must implement the interface 'com.mysql.jdbc.SocketFactory' and have public no-args constructor. | No | com.mysql.jdbc.StandardSocketFactory | 3.0.3 |
| connectTimeout | Timeout for socket connect (in milliseconds), with 0 being no timeout. Only works on JDK-1.4 or newer. Defaults to '0'. | No | 0 | 3.0.1 |
| socketTimeout | Timeout on network socket operations (0, the default means no timeout). | No | 0 | 3.0.1 |
| useConfigs | Load the comma-delimited list of configuration properties before parsing the URL or applying user-specified properties. These configurations are explained in the 'Configurations' of the documentation. | No | 3.1.5 | |
| interactiveClient | Set the CLIENT_INTERACTIVE flag, which tells MySQL to timeout connections based on INTERACTIVE_TIMEOUT instead of WAIT_TIMEOUT | No | false | 3.1.0 |
| propertiesTransform | An implementation of com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionPropertiesTransform that the driver will use to modify URL properties passed to the driver before attempting a connection | No | 3.1.4 | |
| useCompression | Use zlib compression when communicating with the server (true/false)? Defaults to 'false'. | No | false | 3.0.17 |
| High Availability and Clustering | ||||
| autoReconnect | Should the driver try to re-establish stale and/or dead connections? If enabled the driver will throw an exception for a queries issued on a stale or dead connection, which belong to the current transaction, but will attempt reconnect before the next query issued on the connection in a new transaction. The use of this feature is not recommended, because it has side effects related to session state and data consistency when applications don'thandle SQLExceptions properly, and is only designed to be used when you are unable to configure your application to handle SQLExceptions resulting from dead andstale connections properly. Alternatively, investigate setting the MySQL server variable "wait_timeout"to some high value rather than the default of 8 hours. | No | false | 1.1 |
| autoReconnectForPools | Use a reconnection strategy appropriate for connection pools (defaults to 'false') | No | false | 3.1.3 |
| failOverReadOnly | When failing over in autoReconnect mode, should the connection be set to 'read-only'? | No | true | 3.0.12 |
| reconnectAtTxEnd | If autoReconnect is set to true, should the driver attempt reconnectionsat the end of every transaction? | No | false | 3.0.10 |
| roundRobinLoadBalance | When autoReconnect is enabled, and failoverReadonly is false, should we pick hosts to connect to on a round-robin basis? | No | false | 3.1.2 |
| queriesBeforeRetryMaster | Number of queries to issue before falling back to master when failed over (when using multi-host failover). Whichever condition is met first, 'queriesBeforeRetryMaster' or 'secondsBeforeRetryMaster' will cause an attempt to be made to reconnect to the master. Defaults to 50. | No | 50 | 3.0.2 |
| secondsBeforeRetryMaster | How long should the driver wait, when failed over, before attempting to reconnect to the master server? Whichever condition is met first, 'queriesBeforeRetryMaster' or 'secondsBeforeRetryMaster' will cause an attempt to be made to reconnect to the master. Time in seconds, defaults to 30 | No | 30 | 3.0.2 |
| enableDeprecatedAutoreconnect | Auto-reconnect functionality is deprecated starting with version 3.2, and will be removed in version 3.3. Set this property to 'true' to disable the check for the feature being configured. | No | false | 3.2.1 |
| resourceId | A globally unique name that identifies the resource that this datasource or connection is connected to, used for XAResource.isSameRM() when the driver can't determine this value based on hostnames used in the URL | No | 5.0.1 | |
| Security | ||||
| allowMultiQueries | Allow the use of ';' to delimit multiple queries during one statement (true/false, defaults to 'false' | No | false | 3.1.1 |
| useSSL | Use SSL when communicating with the server (true/false), defaults to 'false' | No | false | 3.0.2 |
| requireSSL | Require SSL connection if useSSL=true? (defaults to 'false'). | No | false | 3.1.0 |
| allowUrlInLocalInfile | Should the driver allow URLs in 'LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE' statements? | No | false | 3.1.4 |
| paranoid | Take measures to prevent exposure sensitive information in error messages and clear data structures holding sensitive data when possible? (defaults to 'false') | No | false | 3.0.1 |
| Performance Extensions | ||||
| metadataCacheSize | The number of queries to cacheResultSetMetadata for if cacheResultSetMetaData is set to 'true' (default 50) | No | 50 | 3.1.1 |
| prepStmtCacheSize | If prepared statement caching is enabled, how many prepared statements should be cached? | No | 25 | 3.0.10 |
| prepStmtCacheSqlLimit | If prepared statement caching is enabled, what's the largest SQL the driver will cache the parsing for? | No | 256 | 3.0.10 |
| useCursorFetch | If connected to MySQL > 5.0.2, and setFetchSize() > 0 on a statement, should that statement use cursor-based fetching to retrieve rows? | No | false | 5.0.0 |
| blobSendChunkSize | Chunk to use when sending BLOB/CLOBs via ServerPreparedStatements | No | 1048576 | 3.1.9 |
| cacheCallableStmts | Should the driver cache the parsing stage of CallableStatements | No | false | 3.1.2 |
| cachePrepStmts | Should the driver cache the parsing stage of PreparedStatements of client-side prepared statements, the "check" for suitability of server-side prepared and server-side prepared statements themselves? | No | false | 3.0.10 |
| cacheResultSetMetadata | Should the driver cache ResultSetMetaData for Statements and PreparedStatements? (Req. JDK-1.4+, true/false, default 'false') | No | false | 3.1.1 |
| cacheServerConfiguration | Should the driver cache the results of 'SHOW VARIABLES' and 'SHOW COLLATION' on a per-URL basis? | No | false | 3.1.5 |
| defaultFetchSize | The driver will call setFetchSize(n) with this value on all newly-created Statements | No | 0 | 3.1.9 |
| dontTrackOpenResources | The JDBC specification requires the driver to automatically track and close resources, however if your application doesn't do a good job of explicitly calling close() on statements or result sets, this can cause memory leakage. Setting this property to true relaxes this constraint, and can be more memory efficient for some applications. | No | false | 3.1.7 |
| dynamicCalendars | Should the driver retrieve the default calendar when required, or cache it per connection/session? | No | false | 3.1.5 |
| elideSetAutoCommits | If using MySQL-4.1 or newer, should the driver only issue 'set autocommit=n' queries when the server's state doesn't match the requested state by Connection.setAutoCommit(boolean)? | No | false | 3.1.3 |
| holdResultsOpenOverStatementClose | Should the driver close result sets on Statement.close() as required by the JDBC specification? | No | false | 3.1.7 |
| locatorFetchBufferSize | If 'emulateLocators' is configured to 'true', what size buffer should be used when fetching BLOB data for getBinaryInputStream? | No | 1048576 | 3.2.1 |
| rewriteBatchedStatements | Should the driver use multiqueries (irregardless of the setting of "allowMultiQueries") as well as rewriting of prepared statements for INSERT into multi-value inserts when executeBatch() is called? Notice that this has the potential for SQL injection if using plain java.sql.Statements and your code doesn't sanitize input correctly. Notice that for prepared statements, server-side prepared statements can not currently take advantage of this rewrite option, and that if you don't specify stream lengths when using PreparedStatement.set*Stream(),the driver won't be able to determine the optimium number of parameters per batch and you might receive anan error from the driver that the resultant packet is too large. Statement.getGeneratedKeys() for these rewritten statements only works when the entire batch includes INSERT statements. | No | false | 3.1.13 |
| useFastIntParsing | Use internal String->Integer conversion routines to avoid excessive object creation? | No | true | 3.1.4 |
| useLocalSessionState | Should the driver refer to the internal values of autocommit and transaction isolation that are set by Connection.setAutoCommit() and Connection.setTransactionIsolation(), rather than querying the database? | No | false | 3.1.7 |
| useReadAheadInput | Use newer, optimized non-blocking, buffered input stream when reading from the server? | No | true | 3.1.5 |
| Debuging/Profiling | ||||
| logger | The name of a class that implements 'com.mysql.jdbc.log.Log' that will be used to log messages to.(default is 'com.mysql.jdbc.log.StandardLogger', which logs to STDERR) | No | com.mysql.jdbc.log.StandardLogger | 3.1.1 |
| profileSQL | Trace queries and their execution/fetch times to the configured logger (true/false) defaults to 'false' | No | false | 3.1.0 |
| reportMetricsIntervalMillis | If 'gatherPerfMetrics' is enabled, how often should they be logged (in ms)? | No | 30000 | 3.1.2 |
| maxQuerySizeToLog | Controls the maximum length/size of a query that will get logged when profiling or tracing | No | 2048 | 3.1.3 |
| packetDebugBufferSize | The maximum number of packets to retain when 'enablePacketDebug' is true | No | 20 | 3.1.3 |
| slowQueryThresholdMillis | If 'logSlowQueries' is enabled, how long should a query (in ms) before it is logged as 'slow'? | No | 2000 | 3.1.2 |
| useUsageAdvisor | Should the driver issue 'usage' warnings advising proper and efficient usage of JDBC and MySQL Connector/J to the log (true/false, defaults to 'false')? | No | false | 3.1.1 |
| autoGenerateTestcaseScript | Should the driver dump the SQL it is executing, including server-side prepared statements to STDERR? | No | false | 3.1.9 |
| dumpMetadataOnColumnNotFound | Should the driver dump the field-level metadata of a result set into the exception message when ResultSet.findColumn() fails? | No | false | 3.1.13 |
| dumpQueriesOnException | Should the driver dump the contents of the query sent to the server in the message for SQLExceptions? | No | false | 3.1.3 |
| enablePacketDebug | When enabled, a ring-buffer of 'packetDebugBufferSize' packets will be kept, and dumped when exceptions are thrown in key areas in the driver's code | No | false | 3.1.3 |
| explainSlowQueries | If 'logSlowQueries' is enabled, should the driver automatically issue an 'EXPLAIN' on the server and send the results to the configured log at a WARN level? | No | false | 3.1.2 |
| logSlowQueries | Should queries that take longer than 'slowQueryThresholdMillis' be logged? | No | false | 3.1.2 |
| traceProtocol | Should trace-level network protocol be logged? | No | false | 3.1.2 |
| Miscellaneous | ||||
| useUnicode | Should the driver use Unicode character encodings when handling strings? Should only be used when the driver can't determine the character set mapping, or you are trying to 'force' the driver to use a character set that MySQL either doesn't natively support (such as UTF-8), true/false, defaults to 'true' | No | true | 1.1g |
| characterEncoding | If 'useUnicode' is set to true, what character encoding should the driver use when dealing with strings? (defaults is to 'autodetect') | No | 1.1g | |
| characterSetResults | Character set to tell the server to return results as. | No | 3.0.13 | |
| connectionCollation | If set, tells the server to use this collation via 'set collation_connection' | No | 3.0.13 | |
| sessionVariables | A comma-separated list of name/value pairs to be sent as SET SESSION ... to the server when the driver connects. | No | 3.1.8 | |
| allowNanAndInf | Should the driver allow NaN or +/- INF values in PreparedStatement.setDouble()? | No | false | 3.1.5 |
| autoClosePStmtStreams | Should the driver automatically call .close() on streams/readers passed as arguments via set*() methods? | No | false | 3.1.12 |
| autoDeserialize | Should the driver automatically detect and de-serialize objects stored in BLOB fields? | No | false | 3.1.5 |
| capitalizeTypeNames | Capitalize type names in DatabaseMetaData? (usually only useful when using WebObjects, true/false, defaults to 'false') | No | false | 2.0.7 |
| clobCharacterEncoding | The character encoding to use for sending and retrieving TEXT, MEDIUMTEXT and LONGTEXT values instead of the configured connection characterEncoding | No | 5.0.0 | |
| clobberStreamingResults | This will cause a 'streaming' ResultSet to be automatically closed, and any outstanding data still streaming from the server to be discarded if another query is executed before all the data has been read from the server. | No | false | 3.0.9 |
| continueBatchOnError | Should the driver continue processing batch commands if one statement fails. The JDBC spec allows either way (defaults to 'true'). | No | true | 3.0.3 |
| createDatabaseIfNotExist | Creates the database given in the URL if it doesn't yet exist. Assumes the configured user has permissions to create databases. | No | false | 3.1.9 |
| emptyStringsConvertToZero | Should the driver allow conversions from empty string fields to numeric values of '0'? | No | true | 3.1.8 |
| emulateLocators | N/A | No | false | 3.1.0 |
| emulateUnsupportedPstmts | Should the driver detect prepared statements that are not supported by the server, and replace them with client-side emulated versions? | No | true | 3.1.7 |
| ignoreNonTxTables | Ignore non-transactional table warning for rollback? (defaults to 'false'). | No | false | 3.0.9 |
| jdbcCompliantTruncation | Should the driver throw java.sql.DataTruncation exceptions when data is truncated as is required by the JDBC specification when connected to a server that supports warnings(MySQL 4.1.0 and newer)? | No | true | 3.1.2 |
| maxRows | The maximum number of rows to return (0, the default means return all rows). | No | -1 | all versions |
| noDatetimeStringSync | Don't ensure that ResultSet.getDatetimeType().toString().equals(ResultSet.getString()) | No | false | 3.1.7 |
| noTimezoneConversionForTimeType | Don't convert TIME values using the server timezone if 'useTimezone'='true' | No | false | 5.0.0 |
| nullCatalogMeansCurrent | When DatabaseMetadataMethods ask for a 'catalog' parameter, does the value null mean use the current catalog? (this is not JDBC-compliant, but follows legacy behavior from earlier versions of the driver) | No | true | 3.1.8 |
| nullNamePatternMatchesAll | Should DatabaseMetaData methods that accept *pattern parameters treat null the same as '%' (this is not JDBC-compliant, however older versions of the driver accepted this departure from the specification) | No | true | 3.1.8 |
| overrideSupportsIntegrityEnhancementFacility | Should the driver return "true" for DatabaseMetaData.supportsIntegrityEnhancementFacility() even if the database doesn't support it to workaround applications that require this method to return "true" to signal support of foreign keys, even though the SQL specification states that this facility contains much more than just foreign key support (one such application being OpenOffice)? | No | false | 3.1.12 |
| pedantic | Follow the JDBC spec to the letter. | No | false | 3.0.0 |
| processEscapeCodesForPrepStmts | Should the driver process escape codes in queries that are prepared? | No | true | 3.1.12 |
| relaxAutoCommit | If the version of MySQL the driver connects to does not support transactions, still allow calls to commit(), rollback() and setAutoCommit() (true/false, defaults to 'false')? | No | false | 2.0.13 |
| retainStatementAfterResultSetClose | Should the driver retain the Statement reference in a ResultSet after ResultSet.close() has been called. This is not JDBC-compliant after JDBC-4.0. | No | false | 3.1.11 |
| rollbackOnPooledClose | Should the driver issue a rollback() when the logical connection in a pool is closed? | No | true | 3.0.15 |
| runningCTS13 | Enables workarounds for bugs in Sun's JDBC compliance testsuite version 1.3 | No | false | 3.1.7 |
| serverTimezone | Override detection/mapping of timezone. Used when timezone from server doesn't map to Java timezone | No | 3.0.2 | |
| strictFloatingPoint | Used only in older versions of compliance test | No | false | 3.0.0 |
| strictUpdates | Should the driver do strict checking (all primary keys selected) of updatable result sets (true, false, defaults to 'true')? | No | true | 3.0.4 |
| tinyInt1isBit | Should the driver treat the datatype TINYINT(1) as the BIT type (because the server silently converts BIT -> TINYINT(1) when creating tables)? | No | true | 3.0.16 |
| transformedBitIsBoolean | If the driver converts TINYINT(1) to a different type, should it use BOOLEAN instead of BIT for future compatibility with MySQL-5.0, as MySQL-5.0 has a BIT type? | No | false | 3.1.9 |
| ultraDevHack | Create PreparedStatements for prepareCall() when required, because UltraDev is broken and issues a prepareCall() for _all_ statements? (true/false, defaults to 'false') | No | false | 2.0.3 |
| useGmtMillisForDatetimes | Convert between session timezone and GMT before creating Date and Timestamp instances (value of "false" is legacy behavior, "true" leads to more JDBC-compliant behavior. | No | false | 3.1.12 |
| useHostsInPrivileges | Add '@hostname' to users in DatabaseMetaData.getColumn/TablePrivileges() (true/false), defaults to 'true'. | No | true | 3.0.2 |
| useInformationSchema | When connected to MySQL-5.0.7 or newer, should the driver use the INFORMATION_SCHEMA to derive information used by DatabaseMetaData? | No | false | 5.0.0 |
| useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift | Should the driver use JDBC-compliant rules when converting TIME/TIMESTAMP/DATETIME values' timezone information for those JDBC arguments which take a java.util.Calendar argument? (Notice that this option is exclusive of the "useTimezone=true" configuration option.) | No | false | 5.0.0 |
| useOldUTF8Behavior | Use the UTF-8 behavior the driver did when communicating with 4.0 and older servers | No | false | 3.1.6 |
| useOnlyServerErrorMessages | Don't prepend 'standard' SQLState error messages to error messages returned by the server. | No | true | 3.0.15 |
| useServerPrepStmts | Use server-side prepared statements if the server supports them? (defaults to 'true'). | No | true | 3.1.0 |
| useSqlStateCodes | Use SQL Standard state codes instead of 'legacy' X/Open/SQL state codes (true/false), default is 'true' | No | true | 3.1.3 |
| useStreamLengthsInPrepStmts | Honor stream length parameter in PreparedStatement/ResultSet.setXXXStream() method calls (true/false, defaults to 'true')? | No | true | 3.0.2 |
| useTimezone | Convert time/date types between client and server timezones (true/false, defaults to 'false')? | No | false | 3.0.2 |
| useUnbufferedInput | Don't use BufferedInputStream for reading data from the server | No | true | 3.0.11 |
| yearIsDateType | Should the JDBC driver treat the MySQL type "YEAR" as a java.sql.Date, or as a SHORT? | No | true | 3.1.9 |
| zeroDateTimeBehavior | What should happen when the driver encounters DATETIME values that are composed entirely of zeroes (used by MySQL to represent invalid dates)? Valid values are 'exception', 'round' and 'convertToNull'. | No | exception | 3.1.4 |
Connector/J also supports access to MySQL via named pipes on Windows NT/2000/XP using the 'NamedPipeSocketFactory' as a plugin-socket factory via the 'socketFactory' property. If you don't use a 'namedPipePath' property, the default of '\\.\pipe\MySQL' will be used. If you use the NamedPipeSocketFactory, the hostname and port number values in the JDBC url will be ignored.
Adding the following property to your URL will enable the NamedPipeSocketFactory:
socketFactory=com.mysql.jdbc.NamedPipeSocketFactory
Named pipes only work when connecting to a MySQL server on the same physical machine as the one the JDBC driver is being used on. In simple performance tests, it appears that named pipe access is between 30%-50% faster than the standard TCP/IP access.
You can create your own socket factories by following the
example code in
com.mysql.jdbc.NamedPipeSocketFactory, or
com.mysql.jdbc.StandardSocketFactory.
MySQL Connector/J passes all of the tests in the publicly-available version of Sun's JDBC compliance test suite. However, in many places the JDBC specification is vague about how certain functionality should be implemented, or the specification allows leeway in implementation.
This section gives details on a interface-by-interface level about how certain implementation decisions may affect how you use MySQL Connector/J.
Blob
The Blob implementation does not allow in-place modification (they are 'copies', as reported by the DatabaseMetaData.locatorsUpdateCopies() method). Because of this, you should use the corresponding PreparedStatement.setBlob() or ResultSet.updateBlob() (in the case of updatable result sets) methods to save changes back to the database.
Starting with Connector/J version 3.1.0, you can emulate Blobs with locators by adding the property 'emulateLocators=true' to your JDBC URL. You must then use a column alias with the value of the column set to the actual name of the Blob column in the SELECT that you write to retrieve the Blob. The SELECT must also reference only one table, the table must have a primary key, and the SELECT must cover all columns that make up the primary key. The driver will then delay loading the actual Blob data until you retrieve the Blob and call retrieval methods (getInputStream(), getBytes(), and so forth) on it.
CallableStatement
Starting with Connector/J 3.1.1, stored procedures are supported when connecting to MySQL version 5.0 or newer via the
CallableStatementinterface. Currently, thegetParameterMetaData()method ofCallableStatementis not supported.Clob
The Clob implementation does not allow in-place modification (they are 'copies', as reported by the DatabaseMetaData.locatorsUpdateCopies() method). Because of this, you should use the PreparedStatement.setClob() method to save changes back to the database. The JDBC API does not have a ResultSet.updateClob() method.
Connection
Unlike older versions of MM.MySQL the
isClosed()method does not “ping” the server to determine if it is alive. In accordance with the JDBC specification, it only returns true if 'closed()' has been called on the connection. If you need to determine if the connection is still valid, you should issue a simple query, such as "SELECT 1". The driver will throw an exception if the connection is no longer valid.DatabaseMetaData
Foreign Key information (getImported/ExportedKeys() and getCrossReference()) is only available from 'InnoDB'-type tables. However, the driver uses 'SHOW CREATE TABLE' to retrieve this information, so when other storage engines support foreign keys, the driver will transparently support them as well.
Driver
PreparedStatement
PreparedStatements are implemented by the driver, as MySQL does not have a prepared statement feature. Because of this, the driver does not implement getParameterMetaData() or getMetaData() as it would require the driver to have a complete SQL parser in the client.
Starting with version 3.1.0 MySQL Connector/J, server-side prepared statements and 'binary-encoded' result sets are used when the server supports them.
Take care when using a server-side prepared statement with “large” parameters that are set via setBinaryStream(), setAsciiStream(), setUnicodeStream(), setBlob(), or setClob(). If you want to re-execute the statement with any “large” parameter changed to a non-“large” parameter, it is necessary to call clearParameters() and set all parameters again. The reason for this is as follows:
The driver streams the 'large' data 'out-of-band' to the prepared statement on the server side when the parameter is set (before execution of the prepared statement).
Once that has been done, the stream used to read the data on the client side is closed (as per the JDBC spec), and can't be read from again.
If a parameter changes from “large” to non-“large,” the driver must reset the server-side state of the prepared statement to allow the parameter that is being changed to take the place of the prior “large” value. This removes all of the 'large' data that has already been sent to the server, thus requiring the data to be re-sent, via the setBinaryStream(), setAsciiStream(), setUnicodeStream(), setBlob() or setClob() methods.
Consequently, if you want to change the “type” of a parameter to a non-“large” one, you must call clearParameters() and set all parameters of the prepared statement again before it can be re-executed.
ResultSet
By default, ResultSets are completely retrieved and stored in memory. In most cases this is the most efficient way to operate, and due to the design of the MySQL network protocol is easier to implement. If you are working with ResultSets that have a large number of rows or large values, and can not allocate heap space in your JVM for the memory required, you can tell the driver to 'stream' the results back one row at a time.
To enable this functionality, you need to create a Statement instance in the following manner:
stmt = conn.createStatement(java.sql.ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY, java.sql.ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY); stmt.setFetchSize(Integer.MIN_VALUE);The combination of a forward-only, read-only result set, with a fetch size of Integer.MIN_VALUE serves as a signal to the driver to “stream” result sets row-by-row. After this any result sets created with the statement will be retrieved row-by-row.
There are some caveats with this approach. You will have to read all of the rows in the result set (or close it) before you can issue any other queries on the connection, or an exception will be thrown.
The earliest the locks these statements hold can be released (whether they be
MyISAMtable-level locks or row-level locks in some other storage engine such asInnoDB) is when the statement completes.If the statement is within scope of a transaction, then locks are released when the transaction completes (which implies that the statement needs to complete first). As with most other databases, statements are not complete until all the results pending on the statement are read or the active result set for the statement is closed.
Therefore, if using “streaming” results, you should process them as quickly as possible if you want to maintain concurrent access to the tables referenced by the statement producing the result set.
ResultSetMetaData
The "isAutoIncrement()" method only works when using MySQL servers 4.0 and newer.
Statement
When using versions of the JDBC driver earlier than 3.2.1, and connected to server versions earlier than 5.0.3, the "setFetchSize()" method has no effect, other than to toggle result set streaming as described above.
MySQL does not support SQL cursors, and the JDBC driver doesn't emulate them, so "setCursorName()" has no effect.
MySQL Connector/J is flexible in the way it handles conversions between MySQL data types and Java data types.
In general, any MySQL data type can be converted to a java.lang.String, and any numerical type can be converted to any of the Java numerical types, although round-off, overflow, or loss of precision may occur.
Starting with Connector/J 3.1.0, the JDBC driver will issue warnings or throw DataTruncation exceptions as is required by the JDBC specification unless the connection was configured not to do so by using the property "jdbcCompliantTruncation" and setting it to "false".
The conversions that are always guaranteed to work are listed in the following table:
Table 23.2. Conversion Table
| These MySQL Data Types | Can always be converted to these Java types |
|---|---|
| CHAR, VARCHAR, BLOB, TEXT, ENUM, and SET | java.lang.String, java.io.InputStream, java.io.Reader,
java.sql.Blob, java.sql.Clob |
| FLOAT, REAL, DOUBLE PRECISION, NUMERIC, DECIMAL, TINYINT, SMALLINT, MEDIUMINT, INTEGER, BIGINT | java.lang.String, java.lang.Short, java.lang.Integer,
java.lang.Long, java.lang.Double,
java.math.BigDecimal
Noteround-off, overflow or loss of precision may occur if you choose a Java numeric data type that has less precision or capacity than the MySQL data type you are converting to/from. |
| DATE, TIME, DATETIME, TIMESTAMP | java.lang.String, java.sql.Date,
java.sql.Timestamp |
The ResultSet.getObject() method uses the
following type conversions between MySQL and Java types,
following the JDBC specification where appropriate:
Table 23.3. MySQL Types to Java Types for ResultSet.getObject()
| MySQL Type Name | Returned as Java Class |
|---|---|
| BIT(1) (new in MySQL-5.0) | java.lang.Boolean |
| BIT( > 1) (new in MySQL-5.0) | byte[] |
| TINYINT | java.lang.Boolean if the configuration property
"tinyInt1isBit" is set to "true" (the default) and the
storage size is "1", or
java.lang.Integer if not. |
| BOOL , BOOLEAN | See TINYINT, above as these are aliases for TINYINT(1), currently. |
| SMALLINT[(M)] [UNSIGNED] | java.lang.Integer (regardless if UNSIGNED or not) |
| MEDIUMINT[(M)] [UNSIGNED] | java.lang.Integer, if UNSIGNED
java.lang.Long |
| INT,INTEGER[(M)] [UNSIGNED] | java.lang.Integer, if UNSIGNED
java.lang.Long |
| BIGINT[(M)] [UNSIGNED] | java.lang.Long, if UNSIGNED
java.math.BigInteger |
| FLOAT[(M,D)] | java.lang.Float |
| DOUBLE[(M,B)] | java.lang.Double |
| DECIMAL[(M[,D])] | java.math.BigDecimal |
| DATE | java.sql.Date |
| DATETIME | java.sql.Timestamp |
| TIMESTAMP[(M)] | java.sql.Timestamp |
| TIME | java.sql.Time |
| YEAR[(2|4)] | java.sql.Date (with the date set two January 1st,
at midnight) |
| CHAR(M) | java.lang.String (unless the character set for
the column is BINARY, then
byte[] is returned. |
| VARCHAR(M) [BINARY] | java.lang.String (unless the character set for
the column is BINARY, then
byte[] is returned. |
| BINARY(M) | byte[] |
| VARBINARY(M) | byte[] |
| TINYBLOB | byte[] |
| TINYTEXT | java.lang.String |
| BLOB | byte[] |
| TEXT | java.lang.String |
| MEDIUMBLOB | byte[] |
| MEDIUMTEXT | java.lang.String |
| LONGBLOB | byte[] |
| LONGTEXT | java.lang.String |
| ENUM('value1','value2',...) | java.lang.String |
| SET('value1','value2',...) | java.lang.String |
All strings sent from the JDBC driver to the server are
converted automatically from native Java Unicode form to the
client character encoding, including all queries sent via
Statement.execute(),
Statement.executeUpdate(),
Statement.executeQuery() as well as all
PreparedStatement
and
CallableStatement
parameters with the exclusion of parameters set using
setBytes(),
setBinaryStream(),
setAsciiStream(),
setUnicodeStream() and
setBlob() .
Prior to MySQL Server 4.1, Connector/J supported a single
character encoding per connection, which could either be
automatically detected from the server configuration, or could
be configured by the user through the
"useUnicode" and
"characterEncoding" properties.
Starting with MySQL Server 4.1, Connector/J supports a single
character encoding between client and server, and any number of
character encodings for data returned by the server to the
client in ResultSets.
The character encoding between client and server is
automatically detected upon connection. The encoding used by the
driver is specified on the server via the
character_set system variable for server
versions older than 4.1.0 and
character_set_server for server versions
4.1.0 and newer. For more information, see
Section 10.3.1, “Server Character Set and Collation”.
To override the automatically-detected encoding on the client
side, use the characterEncoding property
in the URL used to connect to the server.
When specifying character encodings on the client side, Java-style names should be used. The following table lists Java-style names for MySQL character sets:
Table 23.4. MySQL to Java Encoding Name Translations
| MySQL Character Set Name | Java-Style Character Encoding Name |
|---|---|
| usa7 | US-ASCII |
| big5 | Big5 |
| gbk | GBK |
| sjis | SJIS (or Cp932 or MS932 for MySQL Server < 4.1.11) |
| cp932 | Cp932 or MS932 (MySQL Server > 4.1.11) |
| gb2312 | EUC_CN |
| ujis | EUC_JP |
| euc_kr | EUC_KR |
| latin1 | ISO8859_1 |
| latin1_de | ISO8859_1 |
| german1 | ISO8859_1 |
| danish | ISO8859_1 |
| latin2 | ISO8859_2 |
| czech | ISO8859_2 |
| hungarian | ISO8859_2 |
| croat | ISO8859_2 |
| greek | ISO8859_7 |
| hebrew | ISO8859_8 |
| latin5 | ISO8859_9 |
| latvian | ISO8859_13 |
| latvian1 | ISO8859_13 |
| estonia | ISO8859_13 |
| dos | Cp437 |
| pclatin2 | Cp852 |
| cp866 | Cp866 |
| koi8_ru | KOI8_R |
| tis620 | TIS620 |
| win1250 | Cp1250 |
| win1250ch | Cp1250 |
| win1251 | Cp1251 |
| cp1251 | Cp1251 |
| win1251ukr | Cp1251 |
| cp1257 | Cp1257 |
| macroman | MacRoman |
| macce | MacCentralEurope |
| utf8 | UTF-8 |
| ucs2 | UnicodeBig |
Warning
Do not issue the query 'set names' with Connector/J, as the driver will not detect that the character set has changed, and will continue to use the character set detected during the initial connection setup.
To allow multiple character sets to be sent from the client, the
"UTF-8" encoding should be used, either by configuring "utf8" as
the default server character set, or by configuring the JDBC
driver to use "UTF-8" through the
characterEncoding property.
SSL in MySQL Connector/J encrypts all data (other than the initial handshake) between the JDBC driver and the server. The performance penalty for enabling SSL is an increase in query processing time between 35% and 50%, depending on the size of the query, and the amount of data it returns.
For SSL Support to work, you must have the following:
A JDK that includes JSSE (Java Secure Sockets Extension), like JDK-1.4.1 or newer. SSL does not currently work with a JDK that you can add JSSE to, like JDK-1.2.x or JDK-1.3.x due to the following JSSE bug: http://developer.java.sun.com/developer/bugParade/bugs/4273544.html
A MySQL server that supports SSL and has been compiled and configured to do so, which is MySQL-4.0.4 or later, see: http://www.mysql.com/doc/en/secure-connections.html
A client certificate (covered later in this section)
You will first need to import the MySQL server CA Certificate into a Java truststore. A sample MySQL server CA Certificate is located in the 'SSL' subdirectory of the MySQL source distribution. This is what SSL will use to determine if you are communicating with a secure MySQL server.
To use Java's 'keytool' to create a truststore in the current directory , and import the server's CA certificate ('cacert.pem'), you can do the following (assuming that'keytool' is in your path. It's located in the 'bin' subdirectory of your JDK or JRE):
shell> keytool -import -alias mysqlServerCACert -file cacert.pem -keystore truststore
Keytool will respond with the following information:
Enter keystore password: *********
Owner: EMAILADDRESS=walrus@example.com, CN=Walrus, O=MySQL AB, L=Orenburg, ST=Some
-State, C=RU
Issuer: EMAILADDRESS=walrus@example.com, CN=Walrus, O=MySQL AB, L=Orenburg, ST=Som
e-State, C=RU
Serial number: 0
Valid from: Fri Aug 02 16:55:53 CDT 2002 until: Sat Aug 02 16:55:53 CDT 2003
Certificate fingerprints:
MD5: 61:91:A0:F2:03:07:61:7A:81:38:66:DA:19:C4:8D:AB
SHA1: 25:77:41:05:D5:AD:99:8C:14:8C:CA:68:9C:2F:B8:89:C3:34:4D:6C
Trust this certificate? [no]: yes
Certificate was added to keystoreYou will then need to generate a client certificate, so that the MySQL server knows that it is talking to a secure client:
shell> keytool -genkey -keyalg rsa -alias mysqlClientCertificate -keystore keystore
Keytool will prompt you for the following information, and create a keystore named 'keystore' in the current directory.
You should respond with information that is appropriate for your situation:
Enter keystore password: *********
What is your first and last name?
[Unknown]: Matthews
What is the name of your organizational unit?
[Unknown]: Software Development
What is the name of your organization?
[Unknown]: MySQL AB
What is the name of your City or Locality?
[Unknown]: Flossmoor
What is the name of your State or Province?
[Unknown]: IL
What is the two-letter country code for this unit?
[Unknown]: US
Is <CN=Matthews, OU=Software Development, O=MySQL AB,
L=Flossmoor, ST=IL, C=US> correct?
[no]: y
Enter key password for <mysqlClientCertificate>
(RETURN if same as keystore password):Finally, to get JSSE to use the keystore and truststore that you have generated, you need to set the following system properties when you start your JVM, replacing 'path_to_keystore_file' with the full path to the keystore file you created, 'path_to_truststore_file' with the path to the truststore file you created, and using the appropriate password values for each property.
-Djavax.net.ssl.keyStore=path_to_keystore_file -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword=********* -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=path_to_truststore_file -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=*********
You will also need to set 'useSSL' to 'true' in your connection parameters for MySQL Connector/J, either by adding 'useSSL=true' to your URL, or by setting the property 'useSSL' to 'true' in the java.util.Properties instance you pass to DriverManager.getConnection().
You can test that SSL is working by turning on JSSE debugging (as detailed below), and look for the following key events:
...
*** ClientHello, v3.1
RandomCookie: GMT: 1018531834 bytes = { 199, 148, 180, 215, 74, 12, 54, 244, 0, 168, 55, 103, 215, 64, 16, 138, 225, 190, 132, 153, 2, 217, 219, 239, 202, 19, 121, 78 }
Session ID: {}
Cipher Suites: { 0, 5, 0, 4, 0, 9, 0, 10, 0, 18, 0, 19, 0, 3, 0, 17 }
Compression Methods: { 0 }
***
[write] MD5 and SHA1 hashes: len = 59
0000: 01 00 00 37 03 01 3D B6 90 FA C7 94 B4 D7 4A 0C ...7..=.......J.
0010: 36 F4 00 A8 37 67 D7 40 10 8A E1 BE 84 99 02 D9 6...7g.@........
0020: DB EF CA 13 79 4E 00 00 10 00 05 00 04 00 09 00 ....yN..........
0030: 0A 00 12 00 13 00 03 00 11 01 00 ...........
main, WRITE: SSL v3.1 Handshake, length = 59
main, READ: SSL v3.1 Handshake, length = 74
*** ServerHello, v3.1
RandomCookie: GMT: 1018577560 bytes = { 116, 50, 4, 103, 25, 100, 58, 202, 79, 185, 178, 100, 215, 66, 254, 21, 83, 187, 190, 42, 170, 3, 132, 110, 82, 148, 160, 92 }
Session ID: {163, 227, 84, 53, 81, 127, 252, 254, 178, 179, 68, 63, 182, 158, 30, 11, 150, 79, 170, 76, 255, 92, 15, 226, 24, 17, 177, 219, 158, 177, 187, 143}
Cipher Suite: { 0, 5 }
Compression Method: 0
***
%% Created: [Session-1, SSL_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA]
** SSL_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA
[read] MD5 and SHA1 hashes: len = 74
0000: 02 00 00 46 03 01 3D B6 43 98 74 32 04 67 19 64 ...F..=.C.t2.g.d
0010: 3A CA 4F B9 B2 64 D7 42 FE 15 53 BB BE 2A AA 03 :.O..d.B..S..*..
0020: 84 6E 52 94 A0 5C 20 A3 E3 54 35 51 7F FC FE B2 .nR..\ ..T5Q....
0030: B3 44 3F B6 9E 1E 0B 96 4F AA 4C FF 5C 0F E2 18 .D?.....O.L.\...
0040: 11 B1 DB 9E B1 BB 8F 00 05 00 ..........
main, READ: SSL v3.1 Handshake, length = 1712
...JSSE provides debugging (to STDOUT) when you set the following system property: -Djavax.net.debug=all This will tell you what keystores and truststores are being used, as well as what is going on during the SSL handshake and certificate exchange. It will be helpful when trying to determine what is not working when trying to get an SSL connection to happen.
Starting with Connector/J 3.1.7, we've made available a variant
of the driver that will automatically send queries to a
read/write master, or a failover or round-robin loadbalanced set
of slaves based on the state of
Connection.getReadOnly() .
An application signals that it wants a transaction to be
read-only by calling
Connection.setReadOnly(true), this
“replication-aware” connection will use one of the
slave connections, which are load-balanced per-vm using a
round-robin scheme (a given connection is “sticky”
to a slave unless that slave is removed from service). If you
have a write transaction, or if you have a read that is
“time-sensitive” (remember, replication in MySQL is
asynchronous), set the connection to be not read-only, by
calling Connection.setReadOnly(false) and
the driver will ensure that further calls are sent to the
“master” MySQL server. The driver takes care of
propagating the current state of autocommit, isolation level,
and catalog between all of the connections that it uses to
accomplish this load balancing functionality.
To enable this functionality, use the "
com.mysql.jdbc.ReplicationDriver " class
when configuring your application server's connection pool or
when creating an instance of a JDBC driver for your standalone
application. Because it accepts the same URL format as the
standard MySQL JDBC driver,
ReplicationDriver does not currently work
with java.sql.DriverManager -based
connection creation unless it is the only MySQL JDBC driver
registered with the DriverManager .
Here is a short, simple example of how ReplicationDriver might be used in a standalone application.
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.util.Properties;
import com.mysql.jdbc.ReplicationDriver;
public class ReplicationDriverDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ReplicationDriver driver = new ReplicationDriver();
Properties props = new Properties();
// We want this for failover on the slaves
props.put("autoReconnect", "true");
// We want to load balance between the slaves
props.put("roundRobinLoadBalance", "true");
props.put("user", "foo");
props.put("password", "bar");
//
// Looks like a normal MySQL JDBC url, with a comma-separated list
// of hosts, the first being the 'master', the rest being any number
// of slaves that the driver will load balance against
//
Connection conn =
driver.connect("jdbc:mysql://master,slave1,slave2,slave3/test",
props);
//
// Perform read/write work on the master
// by setting the read-only flag to "false"
//
conn.setReadOnly(false);
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
conn.createStatement().executeUpdate("UPDATE some_table ....");
conn.commit();
//
// Now, do a query from a slave, the driver automatically picks one
// from the list
//
conn.setReadOnly(true);
ResultSet rs = conn.createStatement().executeQuery("SELECT a,b,c FROM some_other_table");
.......
}
}
This section describes how to use Connector/J in several contexts.
This section provides general background on J2EE concepts that pertain to use of Connector/J.
Connection pooling is a technique of creating and managing a pool of connections that are ready for use by any thread that needs them.
This technique of “pooling” connections is based on the fact that most applications only need a thread to have access to a JDBC connection when they are actively processing a transaction, which usually take only milliseconds to complete. When not processing a transaction, the connection would otherwise sit idle. Instead, connection pooling allows the idle connection to be used by some other thread to do useful work.
In practice, when a thread needs to do work against a MySQL or other database with JDBC, it requests a connection from the pool. When the thread is finished using the connection, it returns it to the pool, so that it may be used by any other threads that want to use it.
When the connection is “loaned out” from the pool, it is used exclusively by the thread that requested it. From a programming point of view, it is the same as if your thread called DriverManager.getConnection() every time it needed a JDBC connection, however with connection pooling, your thread may end up using either a new, or already-existing connection.
Connection pooling can greatly increase the performance of your Java application, while reducing overall resource usage. The main benefits to connection pooling are:
Reduced connection creation time
Although this is not usually an issue with the quick connection setup that MySQL offers compared to other databases, creating new JDBC connections still incurs networking and JDBC driver overhead that will be avoided if connections are “recycled.”
Simplified programming model
When using connection pooling, each individual thread can act as though it has created its own JDBC connection, allowing you to use straight-forward JDBC programming techniques.
Controlled resource usage
If you don't use connection pooling, and instead create a new connection every time a thread needs one, your application's resource usage can be quite wasteful and lead to unpredictable behavior under load.
Remember that each connection to MySQL has overhead (memory, CPU, context switches, and so forth) on both the client and server side. Every connection limits how many resources there are available to your application as well as the MySQL server. Many of these resources will be used whether or not the connection is actually doing any useful work!
Connection pools can be tuned to maximize performance, while keeping resource utilization below the point where your application will start to fail rather than just run slower.
Luckily, Sun has standardized the concept of connection pooling in JDBC through the JDBC-2.0 "Optional" interfaces, and all major application servers have implementations of these APIs that work fine with MySQL Connector/J.
Generally, you configure a connection pool in your application server configuration files, and access it via the Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI). The following code shows how you might use a connection pool from an application deployed in a J2EE application server:
Example 23.12. Using a Connection Pool with a J2EE Application Server
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class MyServletJspOrEjb {
public void doSomething() throws Exception {
/*
* Create a JNDI Initial context to be able to
* lookup the DataSource
*
* In production-level code, this should be cached as
* an instance or static variable, as it can
* be quite expensive to create a JNDI context.
*
* Note: This code only works when you are using servlets
* or EJBs in a J2EE application server. If you are
* using connection pooling in standalone Java code, you
* will have to create/configure datasources using whatever
* mechanisms your particular connection pooling library
* provides.
*/
InitialContext ctx = new InitialContext();
/*
* Lookup the DataSource, which will be backed by a pool
* that the application server provides. DataSource instances
* are also a good candidate for caching as an instance
* variable, as JNDI lookups can be expensive as well.
*/
DataSource ds = (DataSource)ctx.lookup("java:comp/env/jdbc/MySQLDB");
/*
* The following code is what would actually be in your
* Servlet, JSP or EJB 'service' method...where you need
* to work with a JDBC connection.
*/
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
conn = ds.getConnection();
/*
* Now, use normal JDBC programming to work with
* MySQL, making sure to close each resource when you're
* finished with it, which allows the connection pool
* resources to be recovered as quickly as possible
*/
stmt = conn.createStatement();
stmt.execute("SOME SQL QUERY");
stmt.close();
stmt = null;
conn.close();
conn = null;
} finally {
/*
* close any jdbc instances here that weren't
* explicitly closed during normal code path, so
* that we don't 'leak' resources...
*/
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (sqlexception sqlex) {
// ignore -- as we can't do anything about it here
}
stmt = null;
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (sqlexception sqlex) {
// ignore -- as we can't do anything about it here
}
conn = null;
}
}
}
}As shown in the example above, after obtaining the JNDI InitialContext, and looking up the DataSource, the rest of the code should look familiar to anyone who has done JDBC programming in the past.
The most important thing to remember when using connection pooling is to make sure that no matter what happens in your code (exceptions, flow-of-control, and so forth), connections, and anything created by them (such as statements or result sets) are closed, so that they may be re-used, otherwise they will be “stranded,” which in the best case means that the MySQL server resources they represent (such as buffers, locks, or sockets) may be tied up for some time, or worst case, may be tied up forever.
What's the Best Size for my Connection Pool?
As with all other configuration rules-of-thumb, the answer is “It depends.” Although the optimal size depends on anticipated load and average database transaction time, the optimum connection pool size is smaller than you might expect. If you take Sun's Java Petstore blueprint application for example, a connection pool of 15-20 connections can serve a relatively moderate load (600 concurrent users) using MySQL and Tomcat with response times that are acceptable.
To correctly size a connection pool for your application, you should create load test scripts with tools such as Apache JMeter or The Grinder, and load test your application.
An easy way to determine a starting point is to configure your connection pool's maximum number of connections to be “unbounded,” run a load test, and measure the largest amount of concurrently used connections. You can then work backward from there to determine what values of minimum and maximum pooled connections give the best performance for your particular application.
The following instructions are based on the instructions for Tomcat-5.x, available at http://jakarta.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-5.0-doc/jndi-datasource-examples-howto.html which is current at the time this document was written.
First, install the .jar file that comes with Connector/J in
$CATALINA_HOME/common/lib so that it is
available to all applications installed in the container.
Next, Configure the JNDI DataSource by adding a declaration
resource to $CATALINA_HOME/conf/server.xml
in the context that defines your web application:
<Context ....>
...
<Resource name="jdbc/MySQLDB"
auth="Container"
type="javax.sql.DataSource"/>
<!-- The name you used above, must match _exactly_ here!
The connection pool will be bound into JNDI with the name
"java:/comp/env/jdbc/MySQLDB"
-->
<ResourceParams name="jdbc/MySQLDB">
<parameter>
<name>factory</name>
<value>org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSourceFactory</value>
</parameter>
<!-- Don't set this any higher than max_connections on your
MySQL server, usually this should be a 10 or a few 10's
of connections, not hundreds or thousands -->
<parameter>
<name>maxActive</name>
<value>10</value>
</parameter>
<!-- You don't want to many idle connections hanging around
if you can avoid it, only enough to soak up a spike in
the load -->
<parameter>
<name>maxIdle</name>
<value>5</value>
</parameter>
<!-- Don't use autoReconnect=true, it's going away eventually
and it's a crutch for older connection pools that couldn't
test connections. You need to decide whether your application is
supposed to deal with SQLExceptions (hint, it should), and
how much of a performance penalty you're willing to pay
to ensure 'freshness' of the connection -->
<parameter>
<name>validationQuery</name>
<value>SELECT 1</value>
</parameter>
<!-- The most conservative approach is to test connections
before they're given to your application. For most applications
this is okay, the query used above is very small and takes
no real server resources to process, other than the time used
to traverse the network.
If you have a high-load application you'll need to rely on
something else. -->
<parameter>
<name>testOnBorrow</name>
<value>true</value>
</parameter>
<!-- Otherwise, or in addition to testOnBorrow, you can test
while connections are sitting idle -->
<parameter>
<name>testWhileIdle</name>
<value>true</value>
</parameter>
<!-- You have to set this value, otherwise even though
you've asked connections to be tested while idle,
the idle evicter thread will never run -->
<parameter>
<name>timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis</name>
<value>10000</value>
</parameter>
<!-- Don't allow connections to hang out idle too long,
never longer than what wait_timeout is set to on the
server...A few minutes or even fraction of a minute
is sometimes okay here, it depends on your application
and how much spikey load it will see -->
<parameter>
<name>minEvictableIdleTimeMillis</name>
<value>60000</value>
</parameter>
<!-- Username and password used when connecting to MySQL -->
<parameter>
<name>username</name>
<value>someuser</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<name>password</name>
<value>somepass</value>
</parameter>
<!-- Class name for the Connector/J driver -->
<parameter>
<name>driverClassName</name>
<value>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</value>
</parameter>
<!-- The JDBC connection url for connecting to MySQL, notice
that if you want to pass any other MySQL-specific parameters
you should pass them here in the URL, setting them using the
parameter tags above will have no effect, you will also
need to use & to separate parameter values as the
ampersand is a reserved character in XML -->
<parameter>
<name>url</name>
<value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test</value>
</parameter>
</ResourceParams>
</Context>In general, you should follow the installation instructions that come with your version of Tomcat, as the way you configure datasources in Tomcat changes from time-to-time, and unfortunately if you use the wrong syntax in your XML file, you will most likely end up with an exception similar to the following:
Error: java.sql.SQLException: Cannot load JDBC driver class 'null ' SQL state: null
These instructions cover JBoss-4.x. To make the JDBC driver
classes available to the application server, copy the .jar file
that comes with Connector/J to the lib
directory for your server configuration (which is usually called
"default"). Then, in the same configuration
directory, in the subdirectory named “deploy,”
create a datasource configuration file that ends with "-ds.xml",
which tells JBoss to deploy this file as a JDBC Datasource. The
file should have the following contents:
<datasources>
<local-tx-datasource>
<!-- This connection pool will be bound into JNDI with the name
"java:/MySQLDB" -->
<jndi-name>MySQLDB</jndi-name>
<connection-url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbname</connection-url>
<driver-class>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driver-class>
<user-name>user</user-name>
<password>pass</password>
<min-pool-size>5</min-pool-size>
<!-- Don't set this any higher than max_connections on your
MySQL server, usually this should be a 10 or a few 10's
of connections, not hundreds or thousands -->
<max-pool-size>20</max-pool-size>
<!-- Don't allow connections to hang out idle too long,
never longer than what wait_timeout is set to on the
server...A few minutes is usually okay here,
it depends on your application
and how much spikey load it will see -->
<idle-timeout-minutes>5</idle-timeout-minutes>
<!-- If you're using Connector/J 3.1.8 or newer, you can use
our implementation of these to increase the robustness
of the connection pool. -->
<exception-sorter-class-name>com.mysql.jdbc.integration.jboss.ExtendedMysqlExceptionSorter</exception-sorter-class-name>
<valid-connection-checker-class-name>com.mysql.jdbc.integration.jboss.MysqlValidConnectionChecker</valid-connection-checker-class-name>
</local-tx-datasource>
</datasources> This section describes how to solve problems that you may encounter when using Connector/J.
There are a few issues that seem to be commonly encountered often by users of MySQL Connector/J. This section deals with their symptoms, and their resolutions.
24.3.5.1.1:
Question:
When I try to connect to the database with MySQL Connector/J, I get the following exception:
SQLException: Server configuration denies access to data source SQLState: 08001 VendorError: 0
What's going on? I can connect just fine with the MySQL command-line client.
Answer:
MySQL Connector/J must use TCP/IP sockets to connect to MySQL, as Java does not support Unix Domain Sockets. Therefore, when MySQL Connector/J connects to MySQL, the security manager in MySQL server will use its grant tables to determine whether the connection should be allowed.
You must add grants to allow this to happen. The following is an example of how to do this (but not the most secure).
From the mysql command-line client, logged in as a user that can grant privileges, issue the following command:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON [dbname].* to
'[user]'@'[hostname]' identified by
'[password]'replacing [dbname] with the name of your database, [user] with the user name, [hostname] with the host that MySQL Connector/J will be connecting from, and [password] with the password you want to use. Be aware that RedHat Linux is broken with respect to the hostname portion for the case when you are connecting from localhost. You need to use "localhost.localdomain" for the [hostname] value in this case. Follow this by issuing the "FLUSH PRIVILEGES" command.
Note
Testing your connectivity with the
mysql command-line client will not
work unless you add the --host flag,
and use something other than
localhost for the host. The
mysql command-line client will use
Unix domain sockets if you use the special hostname
localhost. If you are testing
connectivity to localhost, use
127.0.0.1 as the hostname instead.
Warning
If you don't understand what the 'GRANT' command does, or how it works, you should read and understand the 'General Security Issues and the MySQL Access Privilege System' section of the MySQL manual before attempting to change privileges.
Changing privileges and permissions improperly in MySQL can potentially cause your server installation to not have optimal security properties.
24.3.5.1.2:
Question:
My application throws an SQLException 'No Suitable Driver'. Why is this happening?
Answer:
One of two things are happening. Either the driver is not in your CLASSPATH or your URL format is incorrect (see the Section 23.3.2, “Installing Connector/J” section.).
24.3.5.1.3:
Question:
I'm trying to use MySQL Connector/J in an applet or application and I get an exception similar to:
SQLException: Cannot connect to MySQL server on host:3306. Is there a MySQL server running on the machine/port you are trying to connect to? (java.security.AccessControlException) SQLState: 08S01 VendorError: 0
Answer:
Either you're running an Applet, your MySQL server has been installed with the "--skip-networking" option set, or your MySQL server has a firewall sitting in front of it.
Applets can only make network connections back to the machine that runs the web server that served the .class files for the applet. This means that MySQL must run on the same machine (or you must have some sort of port re-direction) for this to work. This also means that you will not be able to test applets from your local file system, you must always deploy them to a web server.
MySQL Connector/J can only communicate with MySQL using TCP/IP, as Java does not support Unix domain sockets. TCP/IP communication with MySQL might be affected if MySQL was started with the "--skip-networking" flag, or if it is firewalled.
If MySQL has been started with the "--skip-networking"
option set (the Debian Linux package of MySQL server does
this for example), you need to comment it out in the file
/etc/mysql/my.cnf or /etc/my.cnf. Of course your my.cnf
file might also exist in the data
directory of your MySQL server, or anywhere else
(depending on how MySQL was compiled for your system).
Binaries created by MySQL AB always look in /etc/my.cnf
and [datadir]/my.cnf. If your MySQL server has been
firewalled, you will need to have the firewall configured
to allow TCP/IP connections from the host where your Java
code is running to the MySQL server on the port that MySQL
is listening to (by default, 3306).
24.3.5.1.4:
Question:
I have a servlet/application that works fine for a day, and then stops working overnight
Answer:
MySQL closes connections after 8 hours of inactivity. You either need to use a connection pool that handles stale connections or use the "autoReconnect" parameter (see Section 23.3.3.1, “Driver/Datasource Class Names, URL Syntax and Configuration Properties for Connector/J”).
Also, you should be catching SQLExceptions in your application and dealing with them, rather than propagating them all the way until your application exits, this is just good programming practice. MySQL Connector/J will set the SQLState (see java.sql.SQLException.getSQLState() in your APIDOCS) to "08S01" when it encounters network-connectivity issues during the processing of a query. Your application code should then attempt to re-connect to MySQL at this point.
The following (simplistic) example shows what code that can handle these exceptions might look like:
Example 23.13. Example of transaction with retry logic
public void doBusinessOp() throws SQLException {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
//
// How many times do you want to retry the transaction
// (or at least _getting_ a connection)?
//
int retryCount = 5;
boolean transactionCompleted = false;
do {
try {
conn = getConnection(); // assume getting this from a
// javax.sql.DataSource, or the
// java.sql.DriverManager
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
//
// Okay, at this point, the 'retry-ability' of the
// transaction really depends on your application logic,
// whether or not you're using autocommit (in this case
// not), and whether you're using transacational storage
// engines
//
// For this example, we'll assume that it's _not_ safe
// to retry the entire transaction, so we set retry count
// to 0 at this point
//
// If you were using exclusively transaction-safe tables,
// or your application could recover from a connection going
// bad in the middle of an operation, then you would not
// touch 'retryCount' here, and just let the loop repeat
// until retryCount == 0.
//
retryCount = 0;
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String query = "SELECT foo FROM bar ORDER BY baz";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(query);
while (rs.next()) {
}
rs.close();
rs = null;
stmt.close();
stmt = null;
conn.commit();
conn.close();
conn = null;
transactionCompleted = true;
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
//
// The two SQL states that are 'retry-able' are 08S01
// for a communications error, and 40001 for deadlock.
//
// Only retry if the error was due to a stale connection,
// communications problem or deadlock
//
String sqlState = sqlEx.getSQLState();
if ("08S01".equals(sqlState) || "40001".equals(sqlState)) {
retryCount--;
} else {
retryCount = 0;
}
} finally {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
// You'd probably want to log this . . .
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
// You'd probably want to log this as well . . .
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
//
// If we got here, and conn is not null, the
// transaction should be rolled back, as not
// all work has been done
try {
conn.rollback();
} finally {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
//
// If we got an exception here, something
// pretty serious is going on, so we better
// pass it up the stack, rather than just
// logging it. . .
throw sqlEx;
}
}
}
} while (!transactionCompleted && (retryCount > 0));
}
24.3.5.1.5:
Question:
I'm trying to use JDBC-2.0 updatable result sets, and I get an exception saying my result set is not updatable.
Answer:
Because MySQL does not have row identifiers, MySQL Connector/J can only update result sets that have come from queries on tables that have at least one primary key, the query must select every primary key and the query can only span one table (that is, no joins). This is outlined in the JDBC specification.
The normal place to report bugs is http://bugs.mysql.com/, which is the address for our bugs database. This database is public, and can be browsed and searched by anyone. If you log in to the system, you will also be able to enter new reports.
If you have found a sensitive security bug in MySQL, you can send email to security@mysql.com.
Writing a good bug report takes patience, but doing it right the first time saves time both for us and for yourself. A good bug report, containing a full test case for the bug, makes it very likely that we will fix the bug in the next release.
This section will help you write your report correctly so that you don't waste your time doing things that may not help us much or at all.
If you have a repeatable bug report, please report it to the bugs database at http://bugs.mysql.com/.
Any bug that we are able to repeat has a high chance of being fixed in the next MySQL release.
To report other problems, you can use one of the MySQL mailing lists.
Remember that it is possible for us to respond to a message containing too much information, but not to one containing too little. People often omit facts because they think they know the cause of a problem and assume that some details don't matter.
A good principle is this: If you are in doubt about stating something, state it. It is faster and less troublesome to write a couple more lines in your report than to wait longer for the answer if we must ask you to provide information that was missing from the initial report.
The most common errors made in bug reports are (a) not including the version number of Connector/J or MySQL used, and (b) not fully describing the platform on which Connector/J is installed (including the JVM version, and the platform type and version number that MySQL itself is installed on).
This is highly relevant information, and in 99 cases out of 100, the bug report is useless without it. Very often we get questions like, ``Why doesn't this work for me?'' Then we find that the feature requested wasn't implemented in that MySQL version, or that a bug described in a report has already been fixed in newer MySQL versions.
Sometimes the error is platform-dependent; in such cases, it is next to impossible for us to fix anything without knowing the operating system and the version number of the platform.
If at all possible, you should create a repeatable, stanalone testcase that doesn't involve any third-party classes.
To streamline this process, we ship a base class for testcases
with Connector/J, named
'com.mysql.jdbc.util.BaseBugReport'. To
create a testcase for Connector/J using this class, create your
own class that inherits from
com.mysql.jdbc.util.BaseBugReport and
override the methods setUp(),
tearDown() and
runTest ().
In the setUp() method, create code that
creates your tables, and populates them with any data needed to
demonstrate the bug.
In the runTest () method, create code
that demonstrates the bug using the tables and data you created
in the setUp method.
In the tearDown() method, drop any
tables you created in the setUp()
method.
In any of the above three methods, you should use one of the
variants of the getConnection () method
to create a JDBC connection to MySQL:
getConnection() - Provides a connection to the JDBC URL specified in getUrl(). If a connection already exists, that connection is returned, otherwise a new connection is created.
getNewConnection() - Use this if you need to get a new connection for your bug report (i.e. there's more than one connection involved).
getConnection(String url) - Returns a connection using the given URL.
getConnection(String url, Properties props) - Returns a connection using the given URL and properties.
If you need to use a JDBC URL that is different from
'jdbc:mysql:///test', override the method
getUrl() as well.
Use the assertTrue(boolean expression)
and assertTrue(String failureMessage, boolean
expression) methods to create conditions that must
be met in your testcase demonstrating the behavior you are
expecting (vs. the behavior you are observing, which is why you
are most likely filing a bug report).
Finally, create a main () method that
creates a new instance of your testcase, and calls the
run method:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new MyBugReport().run();
}Once you have finished your testcase, and have verified that it demonstrates the bug you are reporting, upload it with your bug report to http://bugs.mysql.com/.
- 23.3.6.1. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 5.0.0-beta (22 December 2005)
- 23.3.6.2. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.13 (26 May 2006)
- 23.3.6.3. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.12 (30 November 2005)
- 23.3.6.4. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.11-stable (07 October 2005)
- 23.3.6.5. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.10-stable (23 June 2005)
- 23.3.6.6. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.9-stable (22 June 2005)
- 23.3.6.7. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.8-stable (14 April 2005)
- 23.3.6.8. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.7-stable (18 February 2005)
- 23.3.6.9. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.6-stable (23 December 2004)
- 23.3.6.10. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.5-gamma (02 December 2004)
- 23.3.6.11. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.4-beta (04 September 2004)
- 23.3.6.12. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.3-beta (07 July 2004)
- 23.3.6.13. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.2-alpha (09 June 2004)
- 23.3.6.14. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.1-alpha (14 February 2004)
- 23.3.6.15. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.1.0-alpha (18 February 2003)
- 23.3.6.16. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.17-ga (23 June 2005)
- 23.3.6.17. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.16-ga (15 November 2004)
- 23.3.6.18. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.15-production (04 September 2004)
- 23.3.6.19. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.14-production (28 May 2004)
- 23.3.6.20. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.13-production (27 May 2004)
- 23.3.6.21. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.12-production (18 May 2004)
- 23.3.6.22. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.11-stable (19 February 2004)
- 23.3.6.23. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.10-stable (13 January 2004)
- 23.3.6.24. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.9-stable (07 October 2003)
- 23.3.6.25. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.8-stable (23 May 2003)
- 23.3.6.26. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.7-stable (08 April 2003)
- 23.3.6.27. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.6-stable (18 February 2003)
- 23.3.6.28. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.5-gamma (22 January 2003)
- 23.3.6.29. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.4-gamma (06 January 2003)
- 23.3.6.30. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.3-dev (17 December 2002)
- 23.3.6.31. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.2-dev (08 November 2002)
- 23.3.6.32. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.1-dev (21 September 2002)
- 23.3.6.33. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 3.0.0-dev (31 July 2002)
- 23.3.6.34. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.14 (16 May 2002)
- 23.3.6.35. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.13 (24 April 2002)
- 23.3.6.36. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.12 (07 April 2002)
- 23.3.6.37. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.11 (27 January 2002)
- 23.3.6.38. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.10 (24 January 2002)
- 23.3.6.39. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.9 (13 January 2002)
- 23.3.6.40. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.8 (25 November 2001)
- 23.3.6.41. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.7 (24 October 2001)
- 23.3.6.42. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.6 (16 June 2001)
- 23.3.6.43. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.5 (13 June 2001)
- 23.3.6.44. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.3 (03 December 2000)
- 23.3.6.45. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.1 (06 April 2000)
- 23.3.6.46. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.0pre5 (21 February 2000)
- 23.3.6.47. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.0pre4 (10 January 2000)
- 23.3.6.48. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 2.0.0pre (17 August 1999)
- 23.3.6.49. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 1.2b (04 July 1999)
- 23.3.6.50. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 1.2a (14 April 1999)
- 23.3.6.51. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 1.1i (24 March 1999)
- 23.3.6.52. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 1.1h (08 March 1999)
- 23.3.6.53. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 1.1g (19 February 1999)
- 23.3.6.54. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 1.1f (31 December 1998)
- 23.3.6.55. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 1.1b (03 November 1998)
- 23.3.6.56. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 1.1 (02 September 1998)
- 23.3.6.57. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 1.0 (24 August 1998)
- 23.3.6.58. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 0.9d (04 August 1998)
- 23.3.6.59. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 0.9 (28 July 1998)
- 23.3.6.60. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 0.8 (06 July 1998)
- 23.3.6.61. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 0.7 (01 July 1998)
- 23.3.6.62. Changes in MySQL Connector/J 0.6 (21 May 1998)
XADataSourceimplemented (ported from 3.2 branch which won't be released as a product). Usecom.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlXADataSourceas your datasource class name in your application server to utilize XA transactions in MySQL-5.0.10 and newer.PreparedStatement.setString()didn't work correctly whensql_modeon server containedNO_BACKSLASH_ESCAPESand no characters that needed escaping were present in the string.Attempt detection of the MySQL type
BINARY(it's an alias, so this isn't always reliable), and use thejava.sql.Types.BINARYtype mapping for it.Moved
-bin-g.jarfile into separatedebugsubdirectory to avoid confusion.Don't allow
.setAutoCommit(true), or.commit()or.rollback()on an XA-managed connection as per the JDBC specification.If the connection
useTimezoneis set totrue, then also respect time zone conversions in escape-processed string literals (for example,"{ts ...}"and"{t ...}").Return original column name for
RSMD.getColumnName()if the column was aliased, alias name for.getColumnLabel()(if aliased), and original table name for.getTableName(). Note this only works for MySQL-4.1 and newer, as older servers don't make this information available to clients.Setting
useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true(it's not the default) causes the driver to use GMT for allTIMESTAMP/DATETIMEtime zones, and the current VM time zone for any other type that refers to time zones. This feature can not be used whenuseTimezone=trueto convert between server and client time zones.Add one level of indirection of internal representation of
CallableStatementparameter metadata to avoid class not found issues on JDK-1.3 forParameterMetadatainterface (which doesn't exist prior to JDBC-3.0).Added unit tests for
XADatasource, as well as friendlier exceptions for XA failures compared to the "stock"XAException(which has no messages).Idle timeouts cause
XAConnectionsto whine about rolling themselves back. (Bug#14729)Added support for Connector/MXJ integration via url subprotocol
jdbc:mysql:mxj://....Moved all
SQLExceptionconstructor usage to a factory inSQLError(ground-work for JDBC-4.0SQLState-based exception classes).Removed Java5-specific calls to
BigDecimalconstructor (when result set value is'',(int)0was being used as an argument indirectly via method return value. This signature doesn't exist prior to Java5.)Added service-provider entry to
META-INF/services/java.sql.Driverfor JDBC-4.0 support.Return "[VAR]BINARY" for
RSMD.getColumnTypeName()when that is actually the type, and it can be distinguished (MySQL-4.1 and newer).When fix for Bug#14562 was merged from 3.1.12, added functionality for
CallableStatement's parameter metadata to return correct information for.getParameterClassName().Fuller synchronization of
Connectionto avoid deadlocks when using multithreaded frameworks that multithread a single connection (usually not recommended, but the JDBC spec allows it anyways), part of fix to Bug#14972).Implementation of
Statement.cancel()andStatement.setQueryTimeout(). Both require MySQL-5.0.0 or newer server, require a separate connection to issue theKILL QUERYstatement, and in the case ofsetQueryTimeout()creates an additional thread to handle the timeout functionality.Note: Failures to cancel the statement for
setQueryTimeout()may manifest themselves asRuntimeExceptionsrather than failing silently, as there is currently no way to unblock the thread that is executing the query being cancelled due to timeout expiration and have it throw the exception instead.
INOUTparameter does not storeINvalue. (Bug#15464)Exception thrown for new decimal type when using updatable result sets. (Bug#14609)
No "dos" character set in MySQL > 4.1.0. (Bug#15544)
PreparedStatement.setObject()serializesBigIntegeras object, rather than sending as numeric value (and is thus not complementary to.getObject()on anUNSIGNED LONGtype). (Bug#15383)ResultSet.getShort()forUNSIGNED TINYINTreturned wrong values. (Bug#11874)lib-nodistdirectory missing from package breaks out-of-box build. (Bug#15676)DBMD.getColumns()returns wrong type forBIT. (Bug#15854)Fixed issue where driver was unable to initialize character set mapping tables. Removed reliance on
.propertiesfiles to hold this information, as it turns out to be too problematic to code around class loader hierarchies that change depending on how an application is deployed. Moved information back into theCharsetMappingclass. (Bug#14938)Fixed updatable result set doesn't return
AUTO_INCREMENTvalues forinsertRow()when multiple column primary keys are used. (the driver was checking for the existence of single-column primary keys and an autoincrement value > 0 instead of a straightforwardisAutoIncrement()check). (Bug#16841)Fixed
Statement.getGeneratedKeys()throwsNullPointerExceptionwhen no query has been processed. (Bug#17099)Fixed driver trying to call methods that don't exist on older and newer versions of Log4j. The fix is not trying to auto-detect presense of log4j, too many different incompatible versions out there in the wild to do this reliably. (Bug#13469)
If you relied on autodetection before, you will need to add "logger=com.mysql.jdbc.log.Log4JLogger" to your JDBC URL to enable Log4J usage, or alternatively use the new "CommonsLogger" class to take care of this.
Added support for Apache Commons logging, use "com.mysql.jdbc.log.CommonsLogger" as the value for the "logger" configuration property.
LogFactory now prepends "com.mysql.jdbc.log" to log class name if it can't be found as-specified. This allows you to use "short names" for the built-in log factories, for example "logger=CommonsLogger" instead of "logger=com.mysql.jdbc.log.CommonsLogger".
Fixed issue with
ReplicationConnectionincorrectly copying state, doesn't transfer connection context correctly when transitioning between the same read-only states. (Bug#15570)Fixed issue where server-side prepared statements don't cause truncation exceptions to be thrown when truncation happens. (Bug#18041)
Added performance feature, re-writing of batched executes for
Statement.executeBatch()(for all DML statements) andPreparedStatement.executeBatch()(for INSERTs with VALUE clauses only). Enable by using "rewriteBatchedStatements=true" in your JDBC URL.Fixed
CallableStatement.registerOutParameter()not working when some parameters pre-populated. Still waiting for feedback from JDBC experts group to determine what correct parameter count fromgetMetaData()should be, however. (Bug#17898)Fixed calling
clearParameters()on a closed prepared statement causes NPE. (Bug#17587)Map "latin1" on MySQL server to CP1252 for MySQL > 4.1.0.
Added additional accessor and mutator methods on ConnectionProperties so that DataSource users can use same naming as regular URL properties.
Fixed data truncation and
getWarnings()only returns last warning in set. (Bug#18740)Improved performance of retrieving
BigDecimal,Time,TimestampandDatevalues from server-side prepared statements by creating fewer short-lived instances ofStringswhen the native type is not an exact match for the requested type. Fixes Bug#18496 forBigDecimals.Fixed aliased column names where length of name > 251 are corrupted. (Bug#18554)
Fixed
ResultSet.wasNull()not always reset correctly for booleans when done via conversion for server-side prepared statements. (Bug#17450)Fixed invalid classname returned for
ResultSetMetaData.getColumnClassName()forBIGINT type. (Bug#19282)Fixed case where driver wasn't reading server status correctly when fetching server-side prepared statement rows, which in some cases could cause warning counts to be off, or multiple result sets to not be read off the wire.
Driver now aware of fix for
BITtype metadata that went into MySQL-5.0.21 for server not reporting length consistently (Bug#13601).Fixed PreparedStatement.setObject(int, Object, int)doesn't respect scale of BigDecimals. (Bug#19615)Fixed
ResultSet.wasNull()returns incorrect value when extracting native string from server-side prepared statement generated result set. (Bug#19282)
Fixed client-side prepared statement bug with embedded
?characters inside quoted identifiers (it was recognized as a placeholder, when it was not).Don't allow
executeBatch()forCallableStatementswith registeredOUT/INOUTparameters (JDBC compliance).Fall back to platform-encoding for
URLDecoder.decode()when parsing driver URL properties if the platform doesn't have a two-argument version of this method.Java type conversion may be incorrect for
MEDIUMINT. (Bug#14562)Added configuration property
useGmtMillisForDatetimeswhich when set totruecausesResultSet.getDate(),.getTimestamp()to return correct millis-since GMT when.getTime()is called on the return value (currently default isfalsefor legacy behavior).Fixed
DatabaseMetaData.stores*Identifiers():If
lower_case_table_names=0(on server):storesLowerCaseIdentifiers()returnsfalsestoresLowerCaseQuotedIdentifiers()returnsfalsestoresMixedCaseIdentifiers()returnstruestoresMixedCaseQuotedIdentifiers()returnstruestoresUpperCaseIdentifiers()returnsfalsestoresUpperCaseQuotedIdentifiers()returnstrue
If
lower_case_table_names=1(on server):storesLowerCaseIdentifiers()returnstruestoresLowerCaseQuotedIdentifiers()returnstruestoresMixedCaseIdentifiers()returnsfalsestoresMixedCaseQuotedIdentifiers()returns falsestoresUpperCaseIdentifiers()returnsfalsestoresUpperCaseQuotedIdentifiers()returnstrue
DatabaseMetaData.getColumns()doesn't returnTABLE_NAMEcorrectly. (Bug#14815)Escape processor replaces quote character in quoted string with string delimiter. (Bug#14909)
OpenOffice expects
DBMD.supportsIntegrityEnhancementFacility()to returntrueif foreign keys are supported by the datasource, even though this method also covers support for check constraints, which MySQL doesn't have. Setting the configuration propertyoverrideSupportsIntegrityEnhancementFacilitytotruecauses the driver to returntruefor this method. (Bug#12975)Added
com.mysql.jdbc.testsuite.url.defaultsystem property to set default JDBC url for testsuite (to speed up bug resolution when I'm working in Eclipse).Unable to initialize character set mapping tables (due to J2EE classloader differences). (Bug#14938)
Deadlock while closing server-side prepared statements from multiple threads sharing one connection. (Bug#14972)
logSlowQueriesshould give better info. (Bug#12230)Extraneous sleep on
autoReconnect. (Bug#13775)Driver incorrectly closes streams passed as arguments to
PreparedStatements. Reverts to legacy behavior by setting the JDBC configuration propertyautoClosePStmtStreamstotrue(also included in the 3-0-Compat configuration “bundle”). (Bug#15024)maxQuerySizeToLogis not respected. Added logging of bound values forexecute()phase of server-side prepared statements whenprofileSQL=trueas well. (Bug#13048)Usage advisor complains about unreferenced columns, even though they've been referenced. (Bug#15065)
Don't increase timeout for failover/reconnect. (Bug#6577)
Process escape tokens in
Connection.prepareStatement(...). (Bug#15141) You can disable this behavior by setting the JDBC URL configuration propertyprocessEscapeCodesForPrepStmtstofalse.Reconnect during middle of
executeBatch()should not occur ifautoReconnectis enabled. (Bug#13255)
Spurious
!on console when character encoding isutf8. (Bug#11629)Fixed statements generated for testcases missing
;for “plain” statements.Incorrect generation of testcase scripts for server-side prepared statements. (Bug#11663)
Fixed regression caused by fix for Bug#11552 that caused driver to return incorrect values for unsigned integers when those integers where within the range of the positive signed type.
Moved source code to Subversion repository.
Escape tokenizer doesn't respect stacked single quotes for escapes. (Bug#11797)
GEOMETRYtype not recognized when using server-side prepared statements.ReplicationConnectionwon't switch to slave, throws “Catalog can't be null” exception. (Bug#11879)Properties shared between master and slave with replication connection. (Bug#12218)
Statement.getWarnings()fails with NPE if statement has been closed. (Bug#10630)Only get
char[]from SQL inPreparedStatement.ParseInfo()when needed.Geometry types not handled with server-side prepared statements. (Bug#12104)
StringUtils.getBytes()doesn't work when using multi-byte character encodings and a length in characters is specified. (Bug#11614)Pstmt.setObject(...., Types.BOOLEAN)throws exception. (Bug#11798)maxPerformance.propertiesmis-spells “elideSetAutoCommits”. (Bug#11976)DBMD.storesLower/Mixed/UpperIdentifiers()reports incorrect values for servers deployed on Windows. (Bug#11575)ResultSet.moveToCurrentRow()fails to work when preceded by a call toResultSet.moveToInsertRow(). (Bug#11190)VARBINARYdata corrupted when using server-side prepared statements and.setBytes(). (Bug#11115)explainSlowQuerieshangs with server-side prepared statements. (Bug#12229)Escape processor didn't honor strings demarcated with double quotes. (Bug#11498)
Lifted restriction of changing streaming parameters with server-side prepared statements. As long as
allstreaming parameters were set before execution,.clearParameters()does not have to be called. (due to limitation of client/server protocol, prepared statements can not reset individual stream data on the server side).Reworked
Fieldclass,*Buffer, andMysqlIOto be aware of field lengths >Integer.MAX_VALUE.Updated
DBMD.supportsCorrelatedQueries()to returntruefor versions > 4.1,supportsGroupByUnrelated()to returntrueandgetResultSetHoldability()to returnHOLD_CURSORS_OVER_COMMIT.Handling of catalog argument in
DatabaseMetaData.getIndexInfo(), which also means changes to the following methods inDatabaseMetaData: (Bug#12541)getBestRowIdentifier()getColumns()getCrossReference()getExportedKeys()getImportedKeys()getIndexInfo()getPrimaryKeys()getProcedures()(and thus indirectlygetProcedureColumns())getTables()
The
catalogargument in all of these methods now behaves in the following way:Specifying
NULLmeans that catalog will not be used to filter the results (thus all databases will be searched), unless you've setnullCatalogMeansCurrent=truein your JDBC URL properties.Specifying
""means “current” catalog, even though this isn't quite JDBC spec compliant, it's there for legacy users.Specifying a catalog works as stated in the API docs.
Made
Connection.clientPrepare()available from “wrapped” connections in thejdbc2.optionalpackage (connections built byConnectionPoolDataSourceinstances).
Added
Connection.isMasterConnection()for clients to be able to determine if a multi-host master/slave connection is connected to the first host in the list.Tokenizer for
=in URL properties was causingsessionVariables=....to be parameterized incorrectly. (Bug#12753)Foreign key information that is quoted is parsed incorrectly when
DatabaseMetaDatamethods use that information. (Bug#11781)The
sendBlobChunkSizeproperty is now clamped tomax_allowed_packetwith consideration of stream buffer size and packet headers to avoidPacketTooBigExceptionswhenmax_allowed_packetis similar in size to the defaultsendBlobChunkSizewhich is 1M.CallableStatement.clearParameters()now clears resources associated withINOUT/OUTPUTparameters as well asINPUTparameters.Connection.prepareCall()is database name case-sensitive (on Windows systems). (Bug#12417)cp1251incorrectly mapped towin1251for servers newer than 4.0.x. (Bug#12752)java.sql.Types.OTHERreturned forBINARYandVARBINARYcolumns when usingDatabaseMetaData.getColumns(). (Bug#12970)ServerPreparedStatement.getBinding()now checks if the statement is closed before attempting to reference the list of parameter bindings, to avoid throwing aNullPointerException.ResultSetMetaDatafromStatement.getGeneratedKeys()caused aNullPointerExceptionto be thrown whenever a method that required a connection reference was called. (Bug#13277)Backport of
Fieldclass,ResultSetMetaData.getColumnClassName(), andResultSet.getObject(int)changes from 5.0 branch to fix behavior surroundingVARCHAR BINARY/VARBINARYand related types.Fixed
NullPointerExceptionwhen convertingcatalogparameter in manyDatabaseMetaDataMethodstobyte[]s (for the result set) when the parameter isnull. (nullisn't technically allowed by the JDBC specification, but we've historically allowed it).Backport of
VAR[BINARY|CHAR] [BINARY]types detection from 5.0 branch.Read response in
MysqlIO.sendFileToServer(), even if the local file can't be opened, otherwise next query issued will fail, because it's reading the response to the emptyLOAD DATA INFILEpacket sent to the server.Workaround for Bug#13374:
ResultSet.getStatement()on closed result set returnsNULL(as per JDBC 4.0 spec, but not backward-compatible). Set the connection propertyretainStatementAfterResultSetClosetotrueto be able to retrieve aResultSet's statement after theResultSethas been closed via.getStatement()(the default isfalse, to be JDBC-compliant and to reduce the chance that code using JDBC leaksStatementinstances).URL configuration parameters don't allow ‘
&’ or ‘=’ in their values. The JDBC driver now parses configuration parameters as if they are encoded using the application/x-www-form-urlencoded format as specified byjava.net.URLDecoder(http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/docs/api/java/net/URLDecoder.html). (Bug#13453)If the ‘
%’ character is present in a configuration property, it must now be represented as%25, which is the encoded form of ‘%’ when using application/x-www-form-urlencoded encoding.The configuration property
sessionVariablesnow allows you to specify variables that start with the ‘@’ sign.When
gatherPerfMetricsis enabled for servers older than 4.1.0, aNullPointerExceptionis thrown from the constructor ofResultSetif the query doesn't use any tables. (Bug#13043)
Fixed connecting without a database specified raised an exception in
MysqlIO.changeDatabaseTo().Initial implemention of
ParameterMetadataforPreparedStatement.getParameterMetadata(). Only works fully forCallableStatements, as current server-side prepared statements return every parameter as aVARCHARtype.
Overhaul of character set configuration, everything now lives in a properties file.
Driver now correctly uses CP932 if available on the server for Windows-31J, CP932 and MS932 java encoding names, otherwise it resorts to SJIS, which is only a close approximation. Currently only MySQL-5.0.3 and newer (and MySQL-4.1.12 or .13, depending on when the character set gets backported) can reliably support any variant of CP932.
com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement.ParseInfodoes unnecessary call totoCharArray(). (Bug#9064)Memory leak in
ServerPreparedStatementifserverPrepare()fails. (Bug#10144)Actually write manifest file to correct place so it ends up in the binary jar file.
Added
createDatabaseIfNotExistproperty (default isfalse), which will cause the driver to ask the server to create the database specified in the URL if it doesn't exist. You must have the appropriate privileges for database creation for this to work.Unsigned
SMALLINTtreated as signed forResultSet.getInt(), fixed all cases forUNSIGNEDinteger values and server-side prepared statements, as well asResultSet.getObject()forUNSIGNED TINYINT. (Bug#10156)Double quotes not recognized when parsing client-side prepared statements. (Bug#10155)
Made
enableStreamingResults()visible oncom.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.StatementWrapper.Made
ServerPreparedStatement.asSql()work correctly so auto-explain functionality would work with server-side prepared statements.Made JDBC2-compliant wrappers public in order to allow access to vendor extensions.
Cleaned up logging of profiler events, moved code to dump a profiler event as a string to
com.mysql.jdbc.log.LogUtilsso that third parties can use it.DatabaseMetaData.supportsMultipleOpenResults()now returnstrue. The driver has supported this for some time, DBMD just missed that fact.Driver doesn't support
{?=CALL(...)}for calling stored functions. This involved adding support for function retrieval toDatabaseMetaData.getProcedures()andgetProcedureColumns()as well. (Bug#10310)SQLExceptionthrown when retrievingYEAR(2)withResultSet.getString(). The driver will now always treatYEARtypes asjava.sql.Datesand return the correct values forgetString(). Alternatively, theyearIsDateTypeconnection property can be set tofalseand the values will be treated asSHORTs. (Bug#10485)The datatype returned for
TINYINT(1)columns whentinyInt1isBit=true(the default) can be switched betweenTypes.BOOLEANandTypes.BITusing the new configuration propertytransformedBitIsBoolean, which defaults tofalse. If set tofalse(the default),DatabaseMetaData.getColumns()andResultSetMetaData.getColumnType()will returnTypes.BOOLEANforTINYINT(1)columns. Iftrue,Types.BOOLEANwill be returned instead. Regardless of this configuration property, iftinyInt1isBitis enabled, columns with the typeTINYINT(1)will be returned asjava.lang.Booleaninstances fromResultSet.getObject(...), andResultSetMetaData.getColumnClassName()will returnjava.lang.Boolean.SQLExceptionis thrown when using propertycharacterSetResultswithcp932oreucjpms. (Bug#10496)Reorganized directory layout. Sources now are in
srcfolder. Don't pollute parent directory when building, now output goes to./build, distribution goes to./dist.Added support/bug hunting feature that generates
.sqltest scripts toSTDERRwhenautoGenerateTestcaseScriptis set totrue.0-length streams not sent to server when using server-side prepared statements. (Bug#10850)
Setting
cachePrepStmts=truenow causes theConnectionto also cache the check the driver performs to determine if a prepared statement can be server-side or not, as well as caches server-side prepared statements for the lifetime of a connection. As before, theprepStmtCacheSizeparameter controls the size of these caches.Try to handle
OutOfMemoryErrorsmore gracefully. Although not much can be done, they will in most cases close the connection they happened on so that further operations don't run into a connection in some unknown state. When an OOM has happened, any further operations on the connection will fail with a “Connection closed” exception that will also list the OOM exception as the reason for the implicit connection close event.Don't send
COM_RESET_STMTfor each execution of a server-side prepared statement if it isn't required.Driver detects if you're running MySQL-5.0.7 or later, and does not scan for
LIMIT ?[,?]in statements being prepared, as the server supports those types of queries now.VARBINARYdata corrupted when using server-side prepared statements andResultSet.getBytes(). (Bug#11115)Connection.setCatalog()is now aware of theuseLocalSessionStateconfiguration property, which when set totruewill prevent the driver from sendingUSE ...to the server if the requested catalog is the same as the current catalog.Added the following configuration bundles, use one or many via the
useConfigsconfiguration property:maxPerformance— maximum performance without being recklesssolarisMaxPerformance— maximum performance for Solaris, avoids syscalls where it can3-0-Compat— Compatibility with Connector/J 3.0.x functionality
Added
maintainTimeStatsconfiguration property (defaults totrue), which tells the driver whether or not to keep track of the last query time and the last successful packet sent to the server's time. If set tofalse, removes two syscalls per query.autoReconnectping causes exception on connection startup. (Bug#11259)Connector/J dumping query into
SQLExceptiontwice. (Bug#11360)Fixed
PreparedStatement.setClob()not acceptingnullas a parameter.Production package doesn't include JBoss integration classes. (Bug#11411)
Removed nonsensical “costly type conversion” warnings when using usage advisor.
Fixed
DatabaseMetaData.getTables()returning views when they were not asked for as one of the requested table types.Added support for new precision-math
DECIMALtype in MySQL 5.0.3 and up.Fixed
ResultSet.getTime()on aNULLvalue for server-side prepared statements throws NPE.Made
Connection.ping()a public method.DATE_FORMAT()queries returned asBLOBs fromgetObject(). (Bug#8868)ServerPreparedStatementsnow correctly “stream”BLOB/CLOBdata to the server. You can configure the threshold chunk size using the JDBC URL propertyblobSendChunkSize(the default is 1MB).BlobFromLocatornow uses correct identifier quoting when generating prepared statements.Server-side session variables can be preset at connection time by passing them as a comma-delimited list for the connection property
sessionVariables.Fixed regression in
ping()for users usingautoReconnect=true.PreparedStatement.addBatch()doesn't work with server-side prepared statements and streamingBINARYdata. (Bug#9040)DBMD.supportsMixedCase*Identifiers()returns wrong value on servers running on case-sensitive filesystems. (Bug#8800)Cannot use
UTF-8for characterSetResults configuration property. (Bug#9206)A continuation of Bug#8868, where functions used in queries that should return non-string types when resolved by temporary tables suddenly become opaque binary strings (work-around for server limitation). Also fixed fields with type of
CHAR(n) CHARACTER SET BINARYto return correct/matching classes forRSMD.getColumnClassName()andResultSet.getObject(). (Bug#9236)DBMD.supportsResultSetConcurrency()not returningtruefor forward-only/read-only result sets (we obviously support this). (Bug#8792)DATA_TYPEcolumn fromDBMD.getBestRowIdentifier()causesArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionwhen accessed (and in fact, didn't return any value). (Bug#8803)Check for empty strings (
'') when convertingCHAR/VARCHARcolumn data to numbers, throw exception ifemptyStringsConvertToZeroconfiguration property is set tofalse(for backward-compatibility with 3.0, it is now set totrueby default, but will most likely default tofalsein 3.2).PreparedStatement.getMetaData()inserts blank row in database under certain conditions when not using server-side prepared statements. (Bug#9320)Connection.canHandleAsPreparedStatement()now makes “best effort” to distinguishLIMITclauses with placeholders in them from ones without in order to have fewer false positives when generating work-arounds for statements the server cannot currently handle as server-side prepared statements.Fixed
build.xmlto not compilelog4jlogging iflog4jnot available.Added support for the c3p0 connection pool's (http://c3p0.sf.net/) validation/connection checker interface which uses the lightweight
COM_PINGcall to the server if available. To use it, configure your c3p0 connection pool'sconnectionTesterClassNameproperty to usecom.mysql.jdbc.integration.c3p0.MysqlConnectionTester.Better detection of
LIMITinside/outside of quoted strings so that the driver can more correctly determine whether a prepared statement can be prepared on the server or not.Stored procedures with same name in different databases confuse the driver when it tries to determine parameter counts/types. (Bug#9319)
Added finalizers to
ResultSetandStatementimplementations to be JDBC spec-compliant, which requires that if not explicitly closed, these resources should be closed upon garbage collection.Stored procedures with
DECIMALparameters with storage specifications that contained ‘,’ in them would fail. (Bug#9682)PreparedStatement.setObject(int, Object, int type, int scale)now uses scale value forBigDecimalinstances.Statement.getMoreResults()could throw NPE when existing result set was.close()d. (Bug#9704)The performance metrics feature now gathers information about number of tables referenced in a SELECT.
The logging system is now automatically configured. If the value has been set by the user, via the URL property
loggeror the system propertycom.mysql.jdbc.logger, then use that, otherwise, autodetect it using the following steps:Log4j, if it's available,
Then JDK1.4 logging,
Then fallback to our
STDERRlogging.
DBMD.getTables()shouldn't return tables if views are asked for, even if the database version doesn't support views. (Bug#9778)Fixed driver not returning
truefor-1whenResultSet.getBoolean()was called on result sets returned from server-side prepared statements.Added a
Manifest.MFfile with implementation information to the.jarfile.More tests in
Field.isOpaqueBinary()to distinguish opaque binary (that is, fields with typeCHAR(n)andCHARACTER SET BINARY) from output of various scalar and aggregate functions that return strings.Should accept
nullfor catalog (meaning use current) in DBMD methods, even though it's not JDBC-compliant for legacy's sake. Disable by setting connection propertynullCatalogMeansCurrenttofalse(which will be the default value in C/J 3.2.x). (Bug#9917)Should accept
nullfor name patterns in DBMD (meaning ‘%’), even though it isn't JDBC compliant, for legacy's sake. Disable by setting connection propertynullNamePatternMatchesAlltofalse(which will be the default value in C/J 3.2.x). (Bug#9769)
Timestamp key column data needed
_binarystripped forUpdatableResultSet.refreshRow(). (Bug#7686)Timestamps converted incorrectly to strings with server-side prepared statements and updatable result sets. (Bug#7715)
Detect new
sql_modevariable in string form (it used to be integer) and adjust quoting method for strings appropriately.Added
holdResultsOpenOverStatementCloseproperty (default isfalse), that keeps result sets open over statement.close() or new execution on same statement (suggested by Kevin Burton).Infinite recursion when “falling back” to master in failover configuration. (Bug#7952)
Disable multi-statements (if enabled) for MySQL-4.1 versions prior to version 4.1.10 if the query cache is enabled, as the server returns wrong results in this configuration.
Fixed duplicated code in
configureClientCharset()that preventeduseOldUTF8Behavior=truefrom working properly.Removed
dontUnpackBinaryResultsfunctionality, the driver now always stores results from server-side prepared statements as is from the server and unpacks them on demand.Emulated locators corrupt binary data when using server-side prepared statements. (Bug#8096)
Fixed synchronization issue with
ServerPreparedStatement.serverPrepare()that could cause deadlocks/crashes if connection was shared between threads.By default, the driver now scans SQL you are preparing via all variants of
Connection.prepareStatement()to determine if it is a supported type of statement to prepare on the server side, and if it is not supported by the server, it instead prepares it as a client-side emulated prepared statement. You can disable this by passingemulateUnsupportedPstmts=falsein your JDBC URL. (Bug#4718)Remove
_binaryintroducer from parameters used as in/out parameters inCallableStatement.Always return
byte[]s for output parameters registered as*BINARY.Send correct value for “boolean”
trueto server forPreparedStatement.setObject(n, "true", Types.BIT).Fixed bug with Connection not caching statements from
prepareStatement()when the statement wasn't a server-side prepared statement.Choose correct “direction” to apply time adjustments when both client and server are in GMT time zone when using
ResultSet.get(..., cal)andPreparedStatement.set(...., cal).Added
dontTrackOpenResourcesoption (default isfalse, to be JDBC compliant), which helps with memory use for non-well-behaved apps (that is, applications that don't closeStatementobjects when they should).ResultSet.getString()doesn't maintain format stored on server, bug fix only enabled whennoDatetimeStringSyncproperty is set totrue(the default isfalse). (Bug#8428)Fixed NPE in
ResultSet.realClose()when using usage advisor and result set was already closed.PreparedStatementsnot creating streaming result sets. (Bug#8478)Don't pass
NULLtoString.valueOf()inResultSet.getNativeConvertToString(), as it stringifies it (that is, returnsnull), which is not correct for the method in question.ResultSet.getBigDecimal()throws exception when rounding would need to occur to set scale. The driver now chooses a rounding mode of “half up” if non-roundingBigDecimal.setScale()fails. (Bug#8484)Added
useLocalSessionStateconfiguration property, when set totruethe JDBC driver trusts that the application is well-behaved and only sets autocommit and transaction isolation levels using the methods provided onjava.sql.Connection, and therefore can manipulate these values in many cases without incurring round-trips to the database server.Added
enableStreamingResults()toStatementfor connection pool implementations that checkStatement.setFetchSize()for specification-compliant values. CallStatement.setFetchSize(>=0)to disable the streaming results for that statement.Added support for
BITtype in MySQL-5.0.3. The driver will treatBIT(1-8)as the JDBC standardBITtype (which maps tojava.lang.Boolean), as the server does not currently send enough information to determine the size of a bitfield when < 9 bits are declared.BIT(>9)will be treated asVARBINARY, and will returnbyte[]whengetObject()is called.
Fixed hang on
SocketInputStream.read()withStatement.setMaxRows()and multiple result sets when driver has to truncate result set directly, rather than tacking aLIMITon the end of it.nDBMD.getProcedures()doesn't respect catalog parameter. (Bug#7026)
Fix comparisons made between string constants and dynamic strings that are converted with either
toUpperCase()ortoLowerCase()to useLocale.ENGLISH, as some locales “override” case rules for English. Also useStringUtils.indexOfIgnoreCase()instead of.toUpperCase().indexOf(), avoids creating a very short-lived transientStringinstance.Server-side prepared statements did not honor
zeroDateTimeBehaviorproperty, and would cause class-cast exceptions when usingResultSet.getObject(), as the all-zero string was always returned. (Bug#5235)Fixed batched updates with server prepared statements weren't looking if the types had changed for a given batched set of parameters compared to the previous set, causing the server to return the error “Wrong arguments to mysql_stmt_execute()”.
Handle case when string representation of timestamp contains trailing ‘
.’ with no numbers following it.Inefficient detection of pre-existing string instances in
ResultSet.getNativeString(). (Bug#5706)Don't throw exceptions for
Connection.releaseSavepoint().Use a per-session
Calendarinstance by default when decoding dates fromServerPreparedStatements(set to old, less performant behavior by setting propertydynamicCalendars=true).Added experimental configuration property
dontUnpackBinaryResults, which delays unpacking binary result set values until they're asked for, and only creates object instances for non-numerical values (it is set tofalseby default). For some usecase/jvm combinations, this is friendlier on the garbage collector.UNSIGNED BIGINTunpacked incorrectly from server-side prepared statement result sets. (Bug#5729)ServerSidePreparedStatementallocating short-lived objects unnecessarily. (Bug#6225)Removed unwanted new
Throwable()inResultSetconstructor due to bad merge (caused a new object instance that was never used for every result set created). Found while profiling for Bug#6359.Fixed too-early creation of
StringBufferinEscapeProcessor.escapeSQL(), also returnStringwhen escaping not needed (to avoid unnecessary object allocations). Found while profiling for Bug#6359.Use null-safe-equals for key comparisons in updatable result sets.
SUM()onDECIMALwith server-side prepared statement ignores scale if zero-padding is needed (this ends up being due to conversion toDOUBLEby server, which when converted to a string to parse intoBigDecimal, loses all “padding” zeros). (Bug#6537)Use
DatabaseMetaData.getIdentifierQuoteString()when building DBMD queries.Use 1MB packet for sending file for
LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILEif that is <max_allowed_packeton server.ResultSetMetaData.getColumnDisplaySize()returns incorrect values for multi-byte charsets. (Bug#6399)Make auto-deserialization of
java.lang.Objectsstored inBLOBcolumns configurable viaautoDeserializeproperty (defaults tofalse).Re-work
Field.isOpaqueBinary()to detectCHAR(to support fixed-length binary fields forn) CHARACTER SET BINARYResultSet.getObject().Use our own implementation of buffered input streams to get around blocking behavior of
java.io.BufferedInputStream. Disable this withuseReadAheadInput=false.Failing to connect to the server when one of the addresses for the given host name is IPV6 (which the server does not yet bind on). The driver now loops through all IP addresses for a given host, and stops on the first one that
accepts()asocket.connect(). (Bug#6348)
Connector/J 3.1.3 beta does not handle integers correctly (caused by changes to support unsigned reads in
Buffer.readInt()->Buffer.readShort()). (Bug#4510)Added support in
DatabaseMetaData.getTables()andgetTableTypes()for views, which are now available in MySQL server 5.0.x.ServerPreparedStatement.execute*()sometimes threwArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionwhen unpacking field metadata. (Bug#4642)Optimized integer number parsing, enable “old” slower integer parsing using JDK classes via
useFastIntParsing=falseproperty.Added
useOnlyServerErrorMessagesproperty, which causes message text in exceptions generated by the server to only contain the text sent by the server (as opposed to the SQLState's “standard” description, followed by the server's error message). This property is set totrueby default.ResultSet.wasNull()does not work for primatives if a previousnullwas returned. (Bug#4689)Track packet sequence numbers if
enablePacketDebug=true, and throw an exception if packets received out-of-order.ResultSet.getObject()returns wrong type for strings when using prepared statements. (Bug#4482)Calling
MysqlPooledConnection.close()twice (even though an application error), caused NPE. Fixed.ServerPreparedStatementsdealing with return ofDECIMALtype don't work. (Bug#5012)ResultSet.getObject()doesn't return typeBooleanfor pseudo-bit types from prepared statements on 4.1.x (shortcut for avoiding extra type conversion when using binary-encoded result sets obscured test ingetObject()for “pseudo” bit type). (Bug#5032)You can now use URLs in
LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILEstatements, and the driver will use Java's built-in handlers for retreiving the data and sending it to the server. This feature is not enabled by default, you must set theallowUrlInLocalInfileconnection property totrue.The driver is more strict about truncation of numerics on
ResultSet.get*(), and will throw anSQLExceptionwhen truncation is detected. You can disable this by settingjdbcCompliantTruncationtofalse(it is enabled by default, as this functionality is required for JDBC compliance).Added three ways to deal with all-zero datetimes when reading them from a
ResultSet:exception(the default), which throws anSQLExceptionwith an SQLState ofS1009;convertToNull, which returnsNULLinstead of the date; andround, which rounds the date to the nearest closest value which is'0001-01-01'.Fixed
ServerPreparedStatementto read prepared statement metadata off the wire, even though it's currently a placeholder instead of usingMysqlIO.clearInputStream()which didn't work at various times because data wasn't available to read from the server yet. This fixes sporadic errors users were having withServerPreparedStatementsthrowingArrayIndexOutOfBoundExceptions.Use
com.mysql.jdbc.Message's classloader when loading resource bundle, should fix sporadic issues when the caller's classloader can't locate the resource bundle.
Mangle output parameter names for
CallableStatementsso they will not clash with user variable names.Added support for
INOUTparameters inCallableStatements.Null bitmask sent for server-side prepared statements was incorrect. (Bug#4119)
Use SQL Standard SQL states by default, unless
useSqlStateCodesproperty is set tofalse.Added packet debuging code (see the
enablePacketDebugproperty documentation).Added constants for MySQL error numbers (publicly accessible, see
com.mysql.jdbc.MysqlErrorNumbers), and the ability to generate the mappings of vendor error codes to SQLStates that the driver uses (for documentation purposes).Externalized more messages (on-going effort).
Error in retrieval of
mediumintcolumn with prepared statements and binary protocol. (Bug#4311)Support new time zone variables in MySQL-4.1.3 when
useTimezone=true.Support for unsigned numerics as return types from prepared statements. This also causes a change in
ResultSet.getObject()for thebigint unsignedtype, which used to returnBigDecimalinstances, it now returns instances ofjava.lang.BigInteger.
Fixed stored procedure parameter parsing info when size was specified for a parameter (for example,
char(),varchar()).Enabled callable statement caching via
cacheCallableStmtsproperty.Fixed case when no output parameters specified for a stored procedure caused a bogus query to be issued to retrieve out parameters, leading to a syntax error from the server.
Fixed case when no parameters could cause a
NullPointerExceptioninCallableStatement.setOutputParameters().Removed wrapping of exceptions in
MysqlIO.changeUser().Fixed sending of split packets for large queries, enabled nio ability to send large packets as well.
Added
.toString()functionality toServerPreparedStatement, which should help if you're trying to debug a query that is a prepared statement (it shows SQL as the server would process).Added
gatherPerformanceMetricsproperty, along with properties to control when/where this info gets logged (see docs for more info).ServerPreparedStatementsweren't actually de-allocating server-side resources when.close()was called.Added
logSlowQueriesproperty, along withslowQueriesThresholdMillisproperty to control when a query should be considered “slow.”Correctly map output parameters to position given in
prepareCall()versus. order implied duringregisterOutParameter(). (Bug#3146)Correctly detect initial character set for servers >= 4.1.0.
Cleaned up detection of server properties.
Support placeholder for parameter metadata for server >= 4.1.2.
getProcedures()does not return any procedures in result set. (Bug#3539)getProcedureColumns()doesn't work with wildcards for procedure name. (Bug#3540)DBMD.getSQLStateType()returns incorrect value. (Bug#3520)Added
connectionCollationproperty to cause driver to issueset collation_connection=...query on connection init if default collation for given charset is not appropriate.Fixed
DatabaseMetaData.getProcedures()when run on MySQL-5.0.0 (output ofSHOW PROCEDURE STATUSchanged between 5.0.0 and 5.0.1.getWarnings()returnsSQLWarninginstead ofDataTruncation. (Bug#3804)Don't enable server-side prepared statements for server version 5.0.0 or 5.0.1, as they aren't compatible with the '4.1.2+' style that the driver uses (the driver expects information to come back that isn't there, so it hangs).
Fixed bug with
UpdatableResultSetsnot using client-side prepared statements.Fixed character encoding issues when converting bytes to ASCII when MySQL doesn't provide the character set, and the JVM is set to a multi-byte encoding (usually affecting retrieval of numeric values).
Unpack “unknown” data types from server prepared statements as
Strings.Implemented long data (Blobs, Clobs, InputStreams, Readers) for server prepared statements.
Implemented
Statement.getWarnings()for MySQL-4.1 and newer (usingSHOW WARNINGS).Default result set type changed to
TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY(JDBC compliance).Centralized setting of result set type and concurrency.
Refactored how connection properties are set and exposed as
DriverPropertyInfoas well asConnectionandDataSourceproperties.Support for NIO. Use
useNIO=trueon platforms that support NIO.Support for transaction savepoints (MySQL >= 4.0.14 or 4.1.1).
Support for
mysql_change_user(). See thechangeUser()method incom.mysql.jdbc.Connection.Reduced number of methods called in average query to be more efficient.
Prepared
Statementswill be re-prepared on auto-reconnect. Any errors encountered are postponed until first attempt to re-execute the re-prepared statement.Ensure that warnings are cleared before executing queries on prepared statements, as-per JDBC spec (now that we support warnings).
Support “old”
profileSqlcapitalization inConnectionProperties. This property is deprecated, you should useprofileSQLif possible.Optimized
Buffer.readLenByteArray()to return shared empty byte array when length is 0.Allow contents of
PreparedStatement.setBlob()to be retained between calls to.execute*().Deal with 0-length tokens in
EscapeProcessor(caused by callable statement escape syntax).Check for closed connection on delete/update/insert row operations in
UpdatableResultSet.Fix support for table aliases when checking for all primary keys in
UpdatableResultSet.Removed
useFastDatesconnection property.Correctly initialize datasource properties from JNDI Refs, including explicitly specified URLs.
DatabaseMetaDatanow reportssupportsStoredProcedures()for MySQL versions >= 5.0.0Fixed stack overflow in
Connection.prepareCall()(bad merge).Fixed
IllegalAccessErrortoCalendar.getTimeInMillis()inDateTimeValue(for JDK < 1.4).DatabaseMetaData.getColumns()is not returning correct column ordinal info for non-'%'column name patterns. (Bug#1673)Merged fix of datatype mapping from MySQL type
FLOATtojava.sql.Types.REALfrom 3.0 branch.Detect collation of column for
RSMD.isCaseSensitive().Fixed sending of queries larger than 16M.
Added named and indexed input/output parameter support to
CallableStatement. MySQL-5.0.x or newer.Fixed
NullPointerExceptioninServerPreparedStatement.setTimestamp(), as well as year and month descrepencies inServerPreparedStatement.setTimestamp(),setDate().Added ability to have multiple database/JVM targets for compliance and regression/unit tests in
build.xml.Fixed NPE and year/month bad conversions when accessing some datetime functionality in
ServerPreparedStatementsand their resultant result sets.Display where/why a connection was implicitly closed (to aid debugging).
CommunicationsExceptionimplemented, that tries to determine why communications was lost with a server, and displays possible reasons when.getMessage()is called.NULLvalues for numeric types in binary encoded result sets causingNullPointerExceptions. (Bug#2359)Implemented
Connection.prepareCall(), andDatabaseMetaData.getProcedures()andgetProcedureColumns().Reset
long binaryparameters inServerPreparedStatementwhenclearParameters()is called, by sendingCOM_RESET_STMTto the server.Merged prepared statement caching, and
.getMetaData()support from 3.0 branch.Fixed off-by-1900 error in some cases for years in
TimeUtil.fastDate/TimeCreate()when unpacking results from server-side prepared statements.Fixed charset conversion issue in
getTables(). (Bug#2502)Implemented multiple result sets returned from a statement or stored procedure.
Server-side prepared statements were not returning datatype
YEARcorrectly. (Bug#2606)Enabled streaming of result sets from server-side prepared statements.
Class-cast exception when using scrolling result sets and server-side prepared statements. (Bug#2623)
Merged unbuffered input code from 3.0.
Fixed
ConnectionPropertiesthat weren't properly exposed via accessors, cleaned upConnectionPropertiescode.NULLfields were not being encoded correctly in all cases in server-side prepared statements. (Bug#2671)Fixed rare buffer underflow when writing numbers into buffers for sending prepared statement execution requests.
Use DocBook version of docs for shipped versions of drivers.
Added
requireSSLproperty.Added
useServerPrepStmtsproperty (defaultfalse). The driver will use server-side prepared statements when the server version supports them (4.1 and newer) when this property is set totrue. It is currently set tofalseby default until all bind/fetch functionality has been implemented. Currently only DML prepared statements are implemented for 4.1 server-side prepared statements.Track open
Statements, close all whenConnection.close()is called (JDBC compliance).
Timestamp/Timeconversion goes in the wrong “direction” whenuseTimeZone=trueand server time zone differs from client time zone. (Bug#5874)DatabaseMetaData.getIndexInfo()ignoreduniqueparameter. (Bug#7081)Support new protocol type
MYSQL_TYPE_VARCHAR.Added
useOldUTF8Behavior' configuration property, which causes JDBC driver to act like it did with MySQL-4.0.x and earlier when the character encoding isutf-8when connected to MySQL-4.1 or newer.Statements created from a pooled connection were returning physical connection instead of logical connection when
getConnection()was called. (Bug#7316)PreparedStatementsdon't encode Big5 (and other multi-byte) character sets correctly in static SQL strings. (Bug#7033)Connections starting up failed-over (due to down master) never retry master. (Bug#6966)
PreparedStatement.fixDecimalExponent()adding extra+, making number unparseable by MySQL server. (Bug#7061)Timestamp key column data needed
_binarystripped forUpdatableResultSet.refreshRow(). (Bug#7686)Backported SQLState codes mapping from Connector/J 3.1, enable with
useSqlStateCodes=trueas a connection property, it defaults tofalsein this release, so that we don't break legacy applications (it defaults totruestarting with Connector/J 3.1).PreparedStatement.fixDecimalExponent()adding extra+, making number unparseable by MySQL server. (Bug#7601)Escape sequence {fn convert(..., type)} now supports ODBC-style types that are prepended by
SQL_.Fixed duplicated code in
configureClientCharset()that preventeduseOldUTF8Behavior=truefrom working properly.Handle streaming result sets with more than 2 billion rows properly by fixing wraparound of row number counter.
MS932,SHIFT_JIS, andWindows_31Jnot recognized as aliases forsjis. (Bug#7607)Adding
CP943to aliases forsjis. (Bug#6549, fixed while fixing Bug#7607)Which requires hex escaping of binary data when using multi-byte charsets with prepared statements. (Bug#8064)
NON_UNIQUEcolumn fromDBMD.getIndexInfo()returned inverted value. (Bug#8812)Workaround for server Bug#9098: Default values of
CURRENT_*forDATE,TIME,DATETIME, andTIMESTAMPcolumns can't be distinguished fromstringvalues, soUpdatableResultSet.moveToInsertRow()generates bad SQL for inserting default values.EUCKRcharset is sent asSET NAMES euc_krwhich MySQL-4.1 and newer doesn't understand. (Bug#8629)DatabaseMetaData.supportsSelectForUpdate()returns correct value based on server version.Use hex escapes for
PreparedStatement.setBytes()for double-byte charsets including “aliases”Windows-31J,CP934,MS932.Added support for the
EUC_JP_Solarischaracter encoding, which maps to a MySQL encoding ofeucjpms(backported from 3.1 branch). This only works on servers that supporteucjpms, namely 5.0.3 or later.
Re-issue character set configuration commands when re-using pooled connections and/or
Connection.changeUser()when connected to MySQL-4.1 or newer.Fixed
ResultSetMetaData.isReadOnly()to detect non-writable columns when connected to MySQL-4.1 or newer, based on existence of “original” table and column names.ResultSet.updateByte()when on insert row throwsArrayOutOfBoundsException. (Bug#5664)Fixed
DatabaseMetaData.getTypes()returning incorrect (this is, non-negative) scale for theNUMERICtype.Off-by-one bug in
Buffer.readString(. (Bug#5664)string)Made
TINYINT(1)->BIT/Booleanconversion configurable viatinyInt1isBitproperty (defaulttrueto be JDBC compliant out of the box).Only set
character_set_resultsduring connection establishment if server version >= 4.1.1.Fixed regression where
useUnbufferedInputwas defaulting tofalse.ResultSet.getTimestamp()on a column withTIMEin it fails. (Bug#5664)
StringUtils.escapeEasternUnicodeByteStreamwas still broken for GBK. (Bug#4010)Failover for
autoReconnectnot using port numbers for any hosts, and not retrying all hosts. (Warning: This required a change to theSocketFactoryconnect()method signature, which is nowpublic Socket connect(String host, int portNumber, Properties props); therefore, any third-party socket factories will have to be changed to support this signature. (Bug#4334)Logical connections created by
MysqlConnectionPoolDataSourcewill now issue arollback()when they are closed and sent back to the pool. If your application server/connection pool already does this for you, you can set therollbackOnPooledCloseproperty tofalseto avoid the overhead of an extrarollback().Removed redundant calls to
checkRowPos()inResultSet.DOUBLEmapped twice inDBMD.getTypeInfo(). (Bug#4742)Added FLOSS license exemption.
Calling
.close()twice on aPooledConnectioncauses NPE. (Bug#4808)DBMD.getColumns()returns incorrect JDBC type for unsigned columns. This affects type mappings for all numeric types in theRSMD.getColumnType()andRSMD.getColumnTypeNames()methods as well, to ensure that “like” types fromDBMD.getColumns()match up with whatRSMD.getColumnType()andgetColumnTypeNames()return. (Bug#4138, Bug#4860)“Production” is now “GA” (General Availability) in naming scheme of distributions.
RSMD.getPrecision()returning 0 for non-numeric types (should return max length in chars for non-binary types, max length in bytes for binary types). This fix also fixes mapping ofRSMD.getColumnType()andRSMD.getColumnTypeName()for theBLOBtypes based on the length sent from the server (the server doesn't distinguish betweenTINYBLOB,BLOB,MEDIUMBLOBorLONGBLOBat the network protocol level). (Bug#4880)ResultSetshould releaseField[]instance in.close(). (Bug#5022)ResultSet.getMetaData()should not return incorrectly initialized metadata if the result set has been closed, but should instead throw anSQLException. Also fixed forgetRow()andgetWarnings()and traversal methods by callingcheckClosed()before operating on instance-level fields that are nullified during.close(). (Bug#5069)Parse new time zone variables from 4.1.x servers.
Use
_binaryintroducer forPreparedStatement.setBytes()andset*Stream()when connected to MySQL-4.1.x or newer to avoid misinterpretation during character conversion.
Add unsigned attribute to
DatabaseMetaData.getColumns()output in theTYPE_NAMEcolumn.Added
failOverReadOnlyproperty, to allow end-user to configure state of connection (read-only/writable) when failed over.Backported “change user” and “reset server state” functionality from 3.1 branch, to allow clients of
MysqlConnectionPoolDataSourceto reset server state ongetConnection()on a pooled connection.Don't escape SJIS/GBK/BIG5 when using MySQL-4.1 or newer.
Allow
urlparameter forMysqlDataSourceandMysqlConnectionPoolDataSourceso that passing of other properties is possible from inside appservers.Map duplicate key and foreign key errors to SQLState of
23000.Backport documentation tooling from 3.1 branch.
Return creating statement for
ResultSetscreated bygetGeneratedKeys(). (Bug#2957)Allow
java.util.Dateto be sent in as parameter toPreparedStatement.setObject(), converting it to aTimestampto maintain full precision. (Bug#103).Don't truncate
BLOBorCLOBvalues when usingsetBytes()and/orsetBinary/CharacterStream(). (Bug#2670).Dynamically configure character set mappings for field-level character sets on MySQL-4.1.0 and newer using
SHOW COLLATIONwhen connecting.Map
binarycharacter set toUS-ASCIIto supportDATETIMEcharset recognition for servers >= 4.1.2.Use
SET character_set_resultsduring initialization to allow any charset to be returned to the driver for result sets.Use
charsetnrreturned during connect to encode queries before issuingSET NAMESon MySQL >= 4.1.0.Add helper methods to
ResultSetMetaData(getColumnCharacterEncoding()andgetColumnCharacterSet()) to allow end-users to see what charset the driver thinks it should be using for the column.Only set
character_set_resultsfor MySQL >= 4.1.0.StringUtils.escapeSJISByteStream()not covering all eastern double-byte charsets correctly. (Bug#3511)Renamed
StringUtils.escapeSJISByteStream()to more appropriateescapeEasternUnicodeByteStream().Not specifying database in URL caused
MalformedURLexception. (Bug#3554)Auto-convert MySQL encoding names to Java encoding names if used for
characterEncodingproperty.Added encoding names that are recognized on some JVMs to fix case where they were reverse-mapped to MySQL encoding names incorrectly.
Use
junit.textui.TestRunnerfor all unit tests (to allow them to be run from the command line outside of Ant or Eclipse).UpdatableResultSetnot picking up default values formoveToInsertRow(). (Bug#3557)Inconsistent reporting of data type. The server still doesn't return all types for *BLOBs *TEXT correctly, so the driver won't return those correctly. (Bug#3570)
DBMD.getSQLStateType()returns incorrect value. (Bug#3520)Fixed regression in
PreparedStatement.setString()and eastern character encodings.Made
StringRegressionTest4.1-unicode aware.
Trigger a
SET NAMES utf8when encoding is forced toutf8orutf-8via thecharacterEncodingproperty. Previously, only the Java-style encoding name ofutf-8would trigger this.AutoReconnecttime was growing faster than exponentially. (Bug#2447)Fixed failover always going to last host in list. (Bug#2578)
Added
useUnbufferedInputparameter, and now use it by default (due to JVM issue http://developer.java.sun.com/developer/bugParade/bugs/4401235.html)Detect
on/offor1,2,3form oflower_case_table_namesvalue on server.Return
java.lang.IntegerforTINYINTandSMALLINTtypes fromResultSetMetaData.getColumnClassName(). (Bug#2852)Return
java.lang.DoubleforFLOATtype fromResultSetMetaData.getColumnClassName(). (Bug#2855)Return
[Binstead ofjava.lang.ObjectforBINARY,VARBINARYandLONGVARBINARYtypes fromResultSetMetaData.getColumnClassName()(JDBC compliance).Issue connection events on all instances created from a
ConnectionPoolDataSource.
Don't count quoted IDs when inside a 'string' in
PreparedStatementparsing. (Bug#1511)“Friendlier” exception message for
PacketTooLargeException. (Bug#1534)Backported fix for aliased tables and
UpdatableResultSetsincheckUpdatability()method from 3.1 branch.Fix for
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsexception when usingStatement.setMaxRows(). (Bug#1695)Barge blobs and split packets not being read correctly. (Bug#1576)
Fixed regression of
Statement.getGeneratedKeys()andREPLACEstatements.Subsequent call to
ResultSet.updateFoo()causes NPE if result set is not updatable. (Bug#1630)Fix for 4.1.1-style authentication with no password.
Foreign Keys column sequence is not consistent in
DatabaseMetaData.getImported/Exported/CrossReference(). (Bug#1731)DatabaseMetaData.getSystemFunction()returning bad functionVResultsSion. (Bug#1775)Cross-database updatable result sets are not checked for updatability correctly. (Bug#1592)
DatabaseMetaData.getColumns()should returnTypes.LONGVARCHARfor MySQLLONGTEXTtype.ResultSet.getObject()onTINYINTandSMALLINTcolumns should return Java typeInteger. (Bug#1913)Added
alwaysClearStreamconnection property, which causes the driver to always empty any remaining data on the input stream before each query.Added more descriptive error message
Server Configuration Denies Access to DataSource, as well as retrieval of message from server.Autoreconnect code didn't set catalog upon reconnect if it had been changed.
Implement
ResultSet.updateClob().ResultSetMetaData.isCaseSensitive()returned wrong value forCHAR/VARCHARcolumns.Connection property
maxRowsnot honored. (Bug#1933)Statements being created too many times in
DBMD.extractForeignKeyFromCreateTable(). (Bug#1925)Support escape sequence {fn convert ... }. (Bug#1914)
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundswhen parameter number == number of parameters + 1. (Bug#1958)ResultSet.findColumn()should use first matching column name when there are duplicate column names inSELECTquery (JDBC-compliance). (Bug#2006)Removed static synchronization bottleneck from
PreparedStatement.setTimestamp().Removed static synchronization bottleneck from instance factory method of
SingleByteCharsetConverter.Enable caching of the parsing stage of prepared statements via the
cachePrepStmts,prepStmtCacheSize, andprepStmtCacheSqlLimitproperties (disabled by default).Speed up parsing of
PreparedStatements, try to use one-pass whenever possible.Fixed security exception when used in Applets (applets can't read the system property
file.encodingwhich is needed forLOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE).Use constants for SQLStates.
Map charset
ko18_rutoko18rwhen connected to MySQL-4.1.0 or newer.Ensure that
Buffer.writeString()saves room for the\0.Fixed exception
Unknown character set 'danish'on connect with JDK-1.4.0Fixed mappings in SQLError to report deadlocks with SQLStates of
41000.maxRowsproperty would affect internal statements, so check it for all statement creation internal to the driver, and set to 0 when it is not.
Faster date handling code in
ResultSetandPreparedStatement(no longer usesDatemethods that synchronize on static calendars).Fixed test for end of buffer in
Buffer.readString().Fixed
ResultSet.previous()behavior to move current position to before result set when on first row of result set. (Bug#496)Fixed
StatementandPreparedStatementissuing bogus queries whensetMaxRows()had been used and aLIMITclause was present in the query.refreshRowdidn't work when primary key values contained values that needed to be escaped (they ended up being doubly escaped). (Bug#661)Support
InnoDBcontraint names when extracting foreign key information inDatabaseMetaData(implementing ideas from Parwinder Sekhon). (Bug#517, Bug#664)Backported 4.1 protocol changes from 3.1 branch (server-side SQL states, new field information, larger client capability flags, connect-with-database, and so forth).
Fix
UpdatableResultSetto return values forgetwhen on insert row. (Bug#675)XXX()The
insertRowin anUpdatableResultSetis now loaded with the default column values whenmoveToInsertRow()is called. (Bug#688)DatabaseMetaData.getColumns()wasn't returningNULLfor default values that are specified asNULL.Change default statement type/concurrency to
TYPE_FORWARD_ONLYandCONCUR_READ_ONLY(spec compliance).Don't try and reset isolation level on reconnect if MySQL doesn't support them.
Don't wrap
SQLExceptionsinRowDataDynamic.Don't change timestamp TZ twice if
useTimezone==true. (Bug#774)Fixed regression in large split-packet handling. (Bug#848)
Better diagnostic error messages in exceptions for “streaming” result sets.
Issue exception on
ResultSet.geton empty result set (wasn't caught in some cases).XXX()Don't hide messages from exceptions thrown in I/O layers.
Don't fire connection closed events when closing pooled connections, or on
PooledConnection.getConnection()with already open connections. (Bug#884)Clip +/- INF (to smallest and largest representative values for the type in MySQL) and NaN (to 0) for
setDouble/setFloat(), and issue a warning on the statement when the server does not support +/- INF or NaN.Double-escaping of
'\'when charset is SJIS or GBK and'\'appears in non-escaped input. (Bug#879)When emptying input stream of unused rows for “streaming” result sets, have the current thread
yield()every 100 rows in order to not monopolize CPU time.DatabaseMetaData.getColumns()getting confused about the keyword “set” in character columns. (Bug#1099)Fixed deadlock issue with
Statement.setMaxRows().Fixed
CLOB.truncate(). (Bug#1130)Optimized
CLOB.setChracterStream(). (Bug#1131)Made
databaseName,portNumber, andserverNameoptional parameters forMysqlDataSourceFactory. (Bug#1246)ResultSet.get/setStringmashing char 127. (Bug#1247)Backported authentication changes for 4.1.1 and newer from 3.1 branch.
Added
com.mysql.jdbc.util.BaseBugReportto help creation of testcases for bug reports.Added property to “clobber” streaming results, by setting the
clobberStreamingResultsproperty totrue(the default isfalse). This will cause a “streaming”ResultSetto be automatically closed, and any oustanding data still streaming from the server to be discarded if another query is executed before all the data has been read from the server.
Allow bogus URLs in
Driver.getPropertyInfo().Return list of generated keys when using multi-value
INSERTSwithStatement.getGeneratedKeys().Use JVM charset with filenames and
LOAD DATA [LOCAL] INFILE.Fix infinite loop with
Connection.cleanup().Changed Ant target
compile-coretocompile-driver, and made testsuite compilation a separate target.Fixed result set not getting set for
Statement.executeUpdate(), which affectedgetGeneratedKeys()andgetUpdateCount()in some cases.Unicode character 0xFFFF in a string would cause the driver to throw an
ArrayOutOfBoundsException. (Bug#378).Return correct number of generated keys when using
REPLACEstatements.Fix problem detecting server character set in some cases.
Fix row data decoding error when using very large packets.
Optimized row data decoding.
Issue exception when operating on an already closed prepared statement.
Fixed SJIS encoding bug, thanks to Naoto Sato.
Optimized usage of
EscapeProcessor.Allow multiple calls to
Statement.close().
Fixed
MysqlPooledConnection.close()calling wrong event type.Fixed
StringIndexOutOfBoundsExceptioninPreparedStatement.setClob().4.1 Column Metadata fixes.
Remove synchronization from
Driver.connect()andDriver.acceptsUrl().IOExceptionsduring a transaction now cause theConnectionto be closed.Fixed missing conversion for
YEARtype inResultSetMetaData.getColumnTypeName().Don't pick up indexes that start with
prias primary keys forDBMD.getPrimaryKeys().Throw
SQLExceptionswhen trying to do operations on a forcefully closedConnection(that is, when a communication link failure occurs).You can now toggle profiling on/off using
Connection.setProfileSql(boolean).Fixed charset issues with database metadata (charset was not getting set correctly).
Updatable
ResultSetscan now be created for aliased tables/columns when connected to MySQL-4.1 or newer.Fixed
LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILEbug when file >max_allowed_packet.Fixed escaping of 0x5c (
'\') character for GBK and Big5 charsets.Fixed
ResultSet.getTimestamp()when underlying field is of typeDATE.Ensure that packet size from
alignPacketSize()does not exceedmax_allowed_packet(JVM bug)Don't reset
Connection.isReadOnly()when autoReconnecting.
Fixed
ResultSetMetaDatato return""when catalog not known. FixesNullPointerExceptionswith Sun'sCachedRowSet.Fixed
DBMD.getTypeInfo()andDBMD.getColumns()returning different value for precision inTEXTandBLOBtypes.Allow ignoring of warning for “non transactional tables” during rollback (compliance/usability) by setting
ignoreNonTxTablesproperty totrue.Fixed
SQLExceptionsgetting swallowed on initial connect.Fixed
Statement.setMaxRows()to stop sendingLIMITtype queries when not needed (performance).Clean up
Statementquery/method mismatch tests (that is,INSERTnot allowed with.executeQuery()).More checks added in
ResultSettraversal method to catch when in closed state.Fixed
ResultSetMetaData.isWritable()to return correct value.Add “window” of different
NULLsorting behavior toDBMD.nullsAreSortedAtStart(4.0.2 to 4.0.10, true; otherwise, no).Implemented
Blob.setBytes(). You still need to pass the resultantBlobback into an updatableResultSetorPreparedStatementto persist the changes, because MySQL does not support “locators”.Backported 4.1 charset field info changes from Connector/J 3.1.
Fixed
Buffer.fastSkipLenString()causingArrayIndexOutOfBoundsexceptions with some queries when unpacking fields.Implemented an empty
TypeMapforConnection.getTypeMap()so that some third-party apps work with MySQL (IBM WebSphere 5.0 Connection pool).Added missing
LONGTEXTtype toDBMD.getColumns().Retrieve
TX_ISOLATIONfrom database forConnection.getTransactionIsolation()when the MySQL version supports it, instead of an instance variable.Quote table names in
DatabaseMetaData.getColumns(),getPrimaryKeys(),getIndexInfo(),getBestRowIdentifier().Greatly reduce memory required for
setBinaryStream()inPreparedStatements.Fixed
ResultSet.isBeforeFirst()for empty result sets.Added update options for foreign key metadata.
Added quoted identifiers to database names for
Connection.setCatalog.Added support for quoted identifiers in
PreparedStatementparser.Streamlined character conversion and
byte[]handling inPreparedStatementsforsetByte().Reduce memory footprint of
PreparedStatementsby sharing outbound packet withMysqlIO.Added
strictUpdatesproperty to allow control of amount of checking for “correctness” of updatable result sets. Set this tofalseif you want faster updatable result sets and you know that you create them fromSELECTstatements on tables with primary keys and that you have selected all primary keys in your query.Added support for 4.0.8-style large packets.
Fixed
PreparedStatement.executeBatch()parameter overwriting.
Changed
charsToByteinSingleByteCharConverterto be non-static.Changed
SingleByteCharConverterto use lazy initialization of each converter.Fixed charset handling in
Fields.java.Implemented
Connection.nativeSQL().More robust escape tokenizer: Recognize
--comments, and allow nested escape sequences (seetestsuite.EscapeProcessingTest).DBMD.getImported/ExportedKeys()now handles multiple foreign keys per table.Fixed
ResultSetMetaData.getPrecision()returning incorrect values for some floating-point types.Fixed
ResultSetMetaData.getColumnTypeName()returningBLOBforTEXTandTEXTforBLOBtypes.Fixed
Buffer.isLastDataPacket()for 4.1 and newer servers.Added
CLIENT_LONG_FLAGto be able to get more column flags (isAutoIncrement()being the most important).Because of above, implemented
ResultSetMetaData.isAutoIncrement()to useField.isAutoIncrement().Honor
lower_case_table_nameswhen enabled in the server when doing table name comparisons inDatabaseMetaDatamethods.Some MySQL-4.1 protocol support (extended field info from selects).
Use non-aliased table/column names and database names to fullly qualify tables and columns in
UpdatableResultSet(requires MySQL-4.1 or newer).Allow user to alter behavior of
Statement/PreparedStatement.executeBatch()viacontinueBatchOnErrorproperty (defaults totrue).Check for connection closed in more
Connectionmethods (createStatement,prepareStatement,setTransactionIsolation,setAutoCommit).More robust implementation of updatable result sets. Checks that all primary keys of the table have been selected.
LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE ...now works, if your server is configured to allow it. Can be turned off with theallowLoadLocalInfileproperty (see theREADME).Substitute
'?'for unknown character conversions in single-byte character sets instead of'\0'.NamedPipeSocketFactorynow works (only intended for Windows), seeREADMEfor instructions.
Fixed issue with updatable result sets and
PreparedStatementsnot working.Fixed
ResultSet.setFetchDirection(FETCH_UNKNOWN).Fixed issue when calling
Statement.setFetchSize()when using arbitrary values.Fixed incorrect conversion in
ResultSet.getLong().Implemented
ResultSet.updateBlob().Removed duplicate code from
UpdatableResultSet(it can be inherited fromResultSet, the extra code for each method to handle updatability I thought might someday be necessary has not been needed).Fixed
UnsupportedEncodingExceptionthrown when “forcing” a character encoding via properties.Fixed various non-ASCII character encoding issues.
Added driver property
useHostsInPrivileges. Defaults to true. Affects whether or not@hostnamewill be used inDBMD.getColumn/TablePrivileges.All
DBMDresult set columns describing schemas now returnNULLto be more compliant with the behavior of other JDBC drivers for other database systems (MySQL does not support schemas).Added SSL support. See
READMEfor information on how to use it.Properly restore connection properties when autoReconnecting or failing-over, including
autoCommitstate, and isolation level.Use
SHOW CREATE TABLEwhen possible for determining foreign key information forDatabaseMetaData. Also allows cascade options forDELETEinformation to be returned.Escape
0x5ccharacter in strings for the SJIS charset.Fixed start position off-by-1 error in
Clob.getSubString().Implemented
Clob.truncate().Implemented
Clob.setString().Implemented
Clob.setAsciiStream().Implemented
Clob.setCharacterStream().Added
com.mysql.jdbc.MiniAdminclass, which allows you to sendshutdowncommand to MySQL server. This is intended to be used when “embedding” Java and MySQL server together in an end-user application.Added
connectTimeoutparameter that allows users of JDK-1.4 and newer to specify a maxium time to wait to establish a connection.Failover and
autoReconnectwork only when the connection is in anautoCommit(false)state, in order to stay transaction-safe.Added
queriesBeforeRetryMasterproperty that specifies how many queries to issue when failed over before attempting to reconnect to the master (defaults to 50).Fixed
DBMD.supportsResultSetConcurrency()so that it returns true forResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVEandResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLYorResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE.Fixed
ResultSet.isLast()for empty result sets (should returnfalse).PreparedStatementnow honors stream lengths in setBinary/Ascii/Character Stream() unless you set the connection propertyuseStreamLengthsInPrepStmtstofalse.Removed some not-needed temporary object creation by smarter use of
StringsinEscapeProcessor,ConnectionandDatabaseMetaDataclasses.
Fixed
ResultSet.getRow()off-by-one bug.Fixed
RowDataStatic.getAt()off-by-one bug.Added limited
Clobfunctionality (ResultSet.getClob(),PreparedStatemtent.setClob(),PreparedStatement.setObject(Clob).Added
socketTimeoutparameter to URL.Connection.isClosed()no longer “pings” the server.Connection.close()issuesrollback()whengetAutoCommit()isfalse.Added
paranoidparameter, which sanitizes error messages by removing “sensitive” information from them (such as hostnames, ports, or usernames), as well as clearing “sensitive” data structures when possible.Fixed
ResultSetMetaData.isSigned()forTINYINTandBIGINT.Charsets now automatically detected. Optimized code for single-byte character set conversion.
Implemented
ResultSet.getCharacterStream().Added
LOCAL TEMPORARYto table types inDatabaseMetaData.getTableTypes().Massive code clean-up to follow Java coding conventions (the time had come).
!!! LICENSE CHANGE !!! The driver is now GPL. If you need non-GPL licenses, please contact me
<mark@mysql.com>.JDBC-3.0 functionality including
Statement/PreparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys()andResultSet.getURL().Performance enchancements: Driver is now 50–100% faster in most situations, and creates fewer temporary objects.
Repackaging: New driver name is
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, old name still works, though (the driver is now provided by MySQL-AB).Better checking for closed connections in
StatementandPreparedStatement.Support for streaming (row-by-row) result sets (see
README) Thanks to Doron.Support for large packets (new addition to MySQL-4.0 protocol), see
READMEfor more information.JDBC Compliance: Passes all tests besides stored procedure tests.
Fix and sort primary key names in
DBMetaData(SF bugs 582086 and 582086).Float types now reported as
java.sql.Types.FLOAT(SF bug 579573).ResultSet.getTimestamp()now works forDATEtypes (SF bug 559134).ResultSet.getDate/Time/Timestampnow recognizes all forms of invalid values that have been set to all zeroes by MySQL (SF bug 586058).Testsuite now uses Junit (which you can get from http://www.junit.org.
The driver now only works with JDK-1.2 or newer.
Added multi-host failover support (see
README).General source-code cleanup.
Overall speed improvements via controlling transient object creation in
MysqlIOclass when reading packets.Performance improvements in string handling and field metadata creation (lazily instantiated) contributed by Alex Twisleton-Wykeham-Fiennes.
More code cleanup.
PreparedStatementnow releases resources on.close(). (SF bug 553268)Quoted identifiers not used if server version does not support them. Also, if server started with
--ansior--sql-mode=ANSI_QUOTES, ‘"’ will be used as an identifier quote character, otherwise ‘'’ will be used.ResultSet.getDouble()now uses code built into JDK to be more precise (but slower).LogicalHandle.isClosed()calls through to physical connection.Added SQL profiling (to
STDERR). SetprofileSql=truein your JDBC URL. SeeREADMEfor more information.Fixed typo for
relaxAutoCommitparameter.
More code cleanup.
Fixed unicode chars being read incorrectly. (SF bug 541088)
Faster blob escaping for
PrepStmt.Added
set/getPortNumber()toDataSource(s). (SF bug 548167)Added
setURL()toMySQLXADataSource. (SF bug 546019)PreparedStatement.toString()fixed. (SF bug 534026)ResultSetMetaData.getColumnClassName()now implemented.Rudimentary version of
Statement.getGeneratedKeys()from JDBC-3.0 now implemented (you need to be using JDK-1.4 for this to work, I believe).DBMetaData.getIndexInfo()- bad PAGES fixed. (SF BUG 542201)
General code cleanup.
Added
getIdleFor()method toConnectionandMysqlLogicalHandle.Relaxed synchronization in all classes, should fix 520615 and 520393.
Added
getTable/ColumnPrivileges()to DBMD (fixes 484502).Added new types to
getTypeInfo(), fixed existing types thanks to Al Davis and Kid Kalanon.Added support for
BITtypes (51870) toPreparedStatement.Fixed
getRow()bug (527165) inResultSet.Fixes for
ResultSetupdatability inPreparedStatement.Fixed time zone off-by-1-hour bug in
PreparedStatement(538286, 528785).ResultSet: Fixed updatability (values being set tonullif not updated).DataSources- fixedsetUrlbug (511614, 525565), wrong datasource class name (532816, 528767).Added identifier quoting to all
DatabaseMetaDatamethods that need them (should fix 518108).Added support for
YEARtype (533556).ResultSet.insertRow()should now detect auto_increment fields in most cases and use that value in the new row. This detection will not work in multi-valued keys, however, due to the fact that the MySQL protocol does not return this information.ResultSet.refreshRow()implemented.Fixed
testsuite.TraversalafterLast()bug, thanks to Igor Lastric.
Fixed missing
DELETE_RULEvalue inDBMD.getImported/ExportedKeys()andgetCrossReference().Full synchronization of
Statement.java.More changes to fix
Unexpected end of input streamerrors when readingBLOBvalues. This should be the last fix.
Fixed spurious
Unexpected end of input streamerrors inMysqlIO(bug 507456).Fixed null-pointer-exceptions when using
MysqlConnectionPoolDataSourcewith Websphere 4 (bug 505839).
Ant build was corrupting included
jarfiles, fixed (bug 487669).Fixed extra memory allocation in
MysqlIO.readPacket()(bug 488663).Implementation of
DatabaseMetaData.getExported/ImportedKeys()andgetCrossReference().Full synchronization on methods modifying instance and class-shared references, driver should be entirely thread-safe now (please let me know if you have problems).
DataSourceimplementations moved toorg.gjt.mm.mysql.jdbc2.optionalpackage, and (initial) implementations ofPooledConnectionDataSourceandXADataSourceare in place (thanks to Todd Wolff for the implementation and testing ofPooledConnectionDataSourcewith IBM WebSphere 4).Added detection of network connection being closed when reading packets (thanks to Todd Lizambri).
Fixed quoting error with escape processor (bug 486265).
Report batch update support through
DatabaseMetaData(bug 495101).Fixed off-by-one-hour error in
PreparedStatement.setTimestamp()(bug 491577).Removed concatenation support from driver (the
||operator), as older versions of VisualAge seem to be the only thing that use it, and it conflicts with the logical||operator. You will need to start mysqld with the--ansiflag to use the||operator as concatenation (bug 491680).Fixed casting bug in
PreparedStatement(bug 488663).
Batch updates now supported (thanks to some inspiration from Daniel Rall).
XADataSource/ConnectionPoolDataSourcecode (experimental)PreparedStatement.setAnyNumericType()now handles positive exponents correctly (adds+so MySQL can understand it).DatabaseMetaData.getPrimaryKeys()andgetBestRowIdentifier()are now more robust in identifying primary keys (matches regardless of case or abbreviation/full spelling ofPrimary KeyinKey_typecolumn).
PreparedStatement.setCharacterStream()now implementedFixed dangling socket problem when in high availability (
autoReconnect=true) mode, and finalizer forConnectionwill close any dangling sockets on GC.Fixed
ResultSetMetaData.getPrecision()returning one less than actual on newer versions of MySQL.ResultSet.getBlob()now returnsnullif column value wasnull.Character sets read from database if
useUnicode=trueandcharacterEncodingis not set. (thanks to Dmitry Vereshchagin)Initial transaction isolation level read from database (if avaialable). (thanks to Dmitry Vereshchagin)
Fixed
DatabaseMetaData.supportsTransactions(), andsupportsTransactionIsolationLevel()andgetTypeInfo()SQL_DATETIME_SUBandSQL_DATA_TYPEfields not being readable.Fixed
PreparedStatementgenerating SQL that would end up with syntax errors for some queries.Fixed
ResultSet.isAfterLast()always returningfalse.Fixed time zone issue in
PreparedStatement.setTimestamp(). (thanks to Erik Olofsson)Captialize type names when
captializeTypeNames=trueis passed in URL or properties (for WebObjects. (thanks to Anjo Krank)Updatable result sets now correctly handle
NULLvalues in fields.PreparedStatement.setDouble() now uses full-precision doubles (reverting a fix made earlier to truncate them).
PreparedStatement.setBoolean() will use 1/0 for values if your MySQL version is 3.21.23 or higher.
Fixed
PreparedStatementparameter checking.Fixed case-sensitive column names in
ResultSet.java.
Fixed
ResultSet.getBlob()ArrayIndexout-of-bounds.Fixed
ResultSetMetaData.getColumnTypeNameforTEXT/BLOB.Fixed
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundswhen sending largeBLOBqueries. (Max size packet was not being set)Added
ISOLATIONlevel support toConnection.setIsolationLevel()Fixed NPE on
PreparedStatement.executeUpdate()when all columns have not been set.Fixed data parsing of
TIMESTAMPvalues with 2-digit years.Added
BytetoPreparedStatement.setObject().ResultSet.getBoolean()now recognizes-1astrue.ResultSethas +/-Inf/inf support.ResultSet.insertRow()works now, even if not all columns are set (they will be set toNULL).DataBaseMetaData.getCrossReference()no longerArrayIndexOOB.getObject()onResultSetcorrectly doesTINYINT->ByteandSMALLINT->Short.
Implemented
getBigDecimal()without scale component for JDBC2.Fixed composite key problem with updatable result sets.
Added detection of -/+INF for doubles.
Faster ASCII string operations.
Fixed incorrect detection of
MAX_ALLOWED_PACKET, so sending large blobs should work now.Fixed off-by-one error in
java.sql.Blobimplementation code.Added
ultraDevHackURL parameter, set totrueto allow (broken) Macromedia UltraDev to use the driver.
Fixed
RSMD.isWritable()returning wrong value. Thanks to Moritz Maass.Cleaned up exception handling when driver connects.
Columns that are of type
TEXTnow return asStringswhen you usegetObject().DatabaseMetaData.getPrimaryKeys()now works correctly with respect tokey_seq. Thanks to Brian Slesinsky.No escape processing is done on
PreparedStatementsanymore per JDBC spec.Fixed many JDBC-2.0 traversal, positioning bugs, especially with respect to empty result sets. Thanks to Ron Smits, Nick Brook, Cessar Garcia and Carlos Martinez.
Fixed some issues with updatability support in
ResultSetwhen using multiple primary keys.
Fixes to ResultSet for insertRow() - Thanks to Cesar Garcia
Fix to Driver to recognize JDBC-2.0 by loading a JDBC-2.0 class, instead of relying on JDK version numbers. Thanks to John Baker.
Fixed ResultSet to return correct row numbers
Statement.getUpdateCount() now returns rows matched, instead of rows actually updated, which is more SQL-92 like.
10-29-99
Statement/PreparedStatement.getMoreResults() bug fixed. Thanks to Noel J. Bergman.
Added Short as a type to PreparedStatement.setObject(). Thanks to Jeff Crowder
Driver now automagically configures maximum/preferred packet sizes by querying server.
Autoreconnect code uses fast ping command if server supports it.
Fixed various bugs with respect to packet sizing when reading from the server and when alloc'ing to write to the server.
Now compiles under JDK-1.2. The driver supports both JDK-1.1 and JDK-1.2 at the same time through a core set of classes. The driver will load the appropriate interface classes at runtime by figuring out which JVM version you are using.
Fixes for result sets with all nulls in the first row. (Pointed out by Tim Endres)
Fixes to column numbers in SQLExceptions in ResultSet (Thanks to Blas Rodriguez Somoza)
The database no longer needs to specified to connect. (Thanks to Christian Motschke)
Better Documentation (in progress), in doc/mm.doc/book1.html
DBMD now allows null for a column name pattern (not in spec), which it changes to '%'.
DBMD now has correct types/lengths for getXXX().
ResultSet.getDate(), getTime(), and getTimestamp() fixes. (contributed by Alan Wilken)
EscapeProcessor now handles \{ \} and { or } inside quotes correctly. (thanks to Alik for some ideas on how to fix it)
Fixes to properties handling in Connection. (contributed by Juho Tikkala)
ResultSet.getObject() now returns null for NULL columns in the table, rather than bombing out. (thanks to Ben Grosman)
ResultSet.getObject() now returns Strings for types from MySQL that it doesn't know about. (Suggested by Chris Perdue)
Removed DataInput/Output streams, not needed, 1/2 number of method calls per IO operation.
Use default character encoding if one is not specified. This is a work-around for broken JVMs, because according to spec, EVERY JVM must support "ISO8859_1", but they don't.
Fixed Connection to use the platform character encoding instead of "ISO8859_1" if one isn't explicitly set. This fixes problems people were having loading the character- converter classes that didn't always exist (JVM bug). (thanks to Fritz Elfert for pointing out this problem)
Changed MysqlIO to re-use packets where possible to reduce memory usage.
Fixed escape-processor bugs pertaining to {} inside quotes.
Fixed character-set support for non-Javasoft JVMs (thanks to many people for pointing it out)
Fixed ResultSet.getBoolean() to recognize 'y' & 'n' as well as '1' & '0' as boolean flags. (thanks to Tim Pizey)
Fixed ResultSet.getTimestamp() to give better performance. (thanks to Richard Swift)
Fixed getByte() for numeric types. (thanks to Ray Bellis)
Fixed DatabaseMetaData.getTypeInfo() for DATE type. (thanks to Paul Johnston)
Fixed EscapeProcessor for "fn" calls. (thanks to Piyush Shah at locomotive.org)
Fixed EscapeProcessor to not do extraneous work if there are no escape codes. (thanks to Ryan Gustafson)
Fixed Driver to parse URLs of the form "jdbc:mysql://host:port" (thanks to Richard Lobb)
Fixed Timestamps for PreparedStatements
Fixed null pointer exceptions in RSMD and RS
Re-compiled with jikes for valid class files (thanks ms!)
Fixed escape processor to deal with unmatched { and } (thanks to Craig Coles)
Fixed escape processor to create more portable (between DATETIME and TIMESTAMP types) representations so that it will work with BETWEEN clauses. (thanks to Craig Longman)
MysqlIO.quit() now closes the socket connection. Before, after many failed connections some OS's would run out of file descriptors. (thanks to Michael Brinkman)
Fixed NullPointerException in Driver.getPropertyInfo. (thanks to Dave Potts)
Fixes to MysqlDefs to allow all *text fields to be retrieved as Strings. (thanks to Chris at Leverage)
Fixed setDouble in PreparedStatement for large numbers to avoid sending scientific notation to the database. (thanks to J.S. Ferguson)
Fixed getScale() and getPrecision() in RSMD. (contrib'd by James Klicman)
Fixed getObject() when field was DECIMAL or NUMERIC (thanks to Bert Hobbs)
DBMD.getTables() bombed when passed a null table-name pattern. Fixed. (thanks to Richard Lobb)
Added check for "client not authorized" errors during connect. (thanks to Hannes Wallnoefer)
Result set rows are now byte arrays. Blobs and Unicode work bidriectonally now. The useUnicode and encoding options are implemented now.
Fixes to PreparedStatement to send binary set by setXXXStream to be sent untouched to the MySQL server.
Fixes to getDriverPropertyInfo().
Changed all ResultSet fields to Strings, this should allow Unicode to work, but your JVM must be able to convert between the character sets. This should also make reading data from the server be a bit quicker, because there is now no conversion from StringBuffer to String.
Changed PreparedStatement.streamToString() to be more efficient (code from Uwe Schaefer).
URL parsing is more robust (throws SQL exceptions on errors rather than NullPointerExceptions)
PreparedStatement now can convert Strings to Time/Date values via setObject() (code from Robert Currey).
IO no longer hangs in Buffer.readInt(), that bug was introduced in 1.1d when changing to all byte-arrays for result sets. (Pointed out by Samo Login)
Fixes to DatabaseMetaData to allow both IBM VA and J-Builder to work. Let me know how it goes. (thanks to Jac Kersing)
Fix to ResultSet.getBoolean() for NULL strings (thanks to Barry Lagerweij)
Beginning of code cleanup, and formatting. Getting ready to branch this off to a parallel JDBC-2.0 source tree.
Added "final" modifier to critical sections in MysqlIO and Buffer to allow compiler to inline methods for speed.
9-29-98
If object references passed to setXXX() in PreparedStatement are null, setNull() is automatically called for you. (Thanks for the suggestion goes to Erik Ostrom)
setObject() in PreparedStatement will now attempt to write a serialized representation of the object to the database for objects of Types.OTHER and objects of unknown type.
Util now has a static method readObject() which given a ResultSet and a column index will re-instantiate an object serialized in the above manner.
Got rid of "ugly hack" in MysqlIO.nextRow(). Rather than catch an exception, Buffer.isLastDataPacket() was fixed.
Connection.getCatalog() and Connection.setCatalog() should work now.
Statement.setMaxRows() works, as well as setting by property maxRows. Statement.setMaxRows() overrides maxRows set via properties or url parameters.
Automatic re-connection is available. Because it has to "ping" the database before each query, it is turned off by default. To use it, pass in "autoReconnect=true" in the connection URL. You may also change the number of reconnect tries, and the initial timeout value via "maxReconnects=n" (default 3) and "initialTimeout=n" (seconds, default 2) parameters. The timeout is an exponential backoff type of timeout; for example, if you have initial timeout of 2 seconds, and maxReconnects of 3, then the driver will timeout 2 seconds, 4 seconds, then 16 seconds between each re-connection attempt.
Fixed handling of blob data in Buffer.java
Fixed bug with authentication packet being sized too small.
The JDBC Driver is now under the LPGL
8-14-98
Fixed Buffer.readLenString() to correctly read data for BLOBS.
Fixed PreparedStatement.stringToStream to correctly read data for BLOBS.
Fixed PreparedStatement.setDate() to not add a day. (above fixes thanks to Vincent Partington)
Added URL parameter parsing (?user=... and so forth).
Big news! New package name. Tim Endres from ICE Engineering is starting a new source tree for GNU GPL'd Java software. He's graciously given me the org.gjt.mm package directory to use, so now the driver is in the org.gjt.mm.mysql package scheme. I'm "legal" now. Look for more information on Tim's project soon.
Now using dynamically sized packets to reduce memory usage when sending commands to the DB.
Small fixes to getTypeInfo() for parameters, and so forth.
DatabaseMetaData is now fully implemented. Let me know if these drivers work with the various IDEs out there. I've heard that they're working with JBuilder right now.
Added JavaDoc documentation to the package.
Package now available in .zip or .tar.gz.
Implemented getTypeInfo(). Connection.rollback() now throws an SQLException per the JDBC spec.
Added PreparedStatement that supports all JDBC API methods for PreparedStatement including InputStreams. Please check this out and let me know if anything is broken.
Fixed a bug in ResultSet that would break some queries that only returned 1 row.
Fixed bugs in DatabaseMetaData.getTables(), DatabaseMetaData.getColumns() and DatabaseMetaData.getCatalogs().
Added functionality to Statement that allows executeUpdate() to store values for IDs that are automatically generated for AUTO_INCREMENT fields. Basically, after an executeUpdate(), look at the SQLWarnings for warnings like "LAST_INSERTED_ID = 'some number', COMMAND = 'your SQL query'". If you are using AUTO_INCREMENT fields in your tables and are executing a lot of executeUpdate()s on one Statement, be sure to clearWarnings() every so often to save memory.
Split MysqlIO and Buffer to separate classes. Some ClassLoaders gave an IllegalAccess error for some fields in those two classes. Now mm.mysql works in applets and all classloaders. Thanks to Joe Ennis <jce@mail.boone.com> for pointing out the problem and working on a fix with me.
Fixed DatabaseMetadata problems in getColumns() and bug in switch statement in the Field constructor. Thanks to Costin Manolache <costin@tdiinc.com> for pointing these out.
Incorporated efficiency changes from Richard Swift <Richard.Swift@kanatek.ca> in
MysqlIO.javaandResultSet.java:We're now 15% faster than gwe's driver.
Started working on
DatabaseMetaData.The following methods are implemented:
getTables()getTableTypes()getColumnsgetCatalogs()
- 23.4.1. Introduction
- 23.4.2. Supported Platforms
- 23.4.3. JUnit Test Requirements
- 23.4.4. Running the JUnit Tests
- 23.4.5. Running as part of the JDBC Driver
- 23.4.6. Running within a Java Object
- 23.4.7. The MysqldResource API
- 23.4.8. Running within a JMX Agent (custom)
- 23.4.9. Deployment in a standard JMX Agent environment (JBoss)
- 23.4.10. Installation
MySQL Connector/MXJ is a Java Utility package for deploying and managing a MySQL database. Connector/MXJ may be bundled in to an existing Java application or may be deployed as a JMX MBean. Deploying and using MySQL can be as easy as adding an additional parameter to the JDBC connection url, which will result in the database being started when the first connection is made. This makes it easy for Java developers to deploy applications which require a database by reducing installation barriers for their end-users.
MySQL Connector/MXJ makes the MySQL database appear to be a java-based component. It does this by determining what platform the system is running on, selecting the appropriate binary, and launching the executable. It will also optionally deploy an initial database, with any specified parameters.
As a JMX MBean, MySQL Connector/MXJ requires a JMX v1.2 compliant MBean container, such as JBoss version 4. The MBean will uses the standard JMX management APIs to present (and allow the setting of) parameters which are appropriate for that platform.
Included are instructions for use with a JDBC driver and deploying as a JMX MBean to JBoss.
You can download sources and binaries from: http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/mxj/
This a beta release and feedback is welcome and encouraged.
Please send questions or comments to java@lists.mysql.com.
Linux, i386
Windows NT, x86
Windows 2000, x86
Windows XP, x86
Solaris 9, SPARC 32
The best way to ensure that your platform is supported is to run the JUnit tests.
The first thing to do is make sure that the components will work
on the platform. The MysqldResource class
is really a wrapper for a native version of MySQL, so not all
platforms are supported. At the time of this writing, Linux on the
i386 architecture has been tested and seems to work quite well, as
does OS X v10.3. There has been limited testing on Windows and
Solaris.
Requirements:
JDK-1.4 or newer (or the JRE if you aren't going to be compiling the source or JSPs).
MySQL Connector/J version 3.1 or newer (from http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/j/) installed and available via your CLASSPATH.
The
javax.managementclasses for JMX version 1.2.1, these are present in the following application servers:JBoss - 4.0rc1 or newer
Apache Tomcat - 5.0 or newer
Sun's JMX reference implementation version 1.2.1 (from http://java.sun.com/products/JavaManagement/)
Junit 3.8.1 (from http://www.junit.org/)
If building from source, All of the requirements from above, plus:
Ant version 1.5 or newer (download from http://ant.apache.org/)
The tests attempt to launch MySQL on the port 3336. If you have a MySQL running, it may conflict, but this isn't very likely because the default port for MySQL is 3306. However, You may set the "c-mxj_test_port" Java property to a port of your choosing. Alternatively, you may wish to start by shutting down any instances of MySQL you have running on the target machine.
The tests surpress output to the console by default. For verbose output, you may set the "c-mxj_test_silent" Java property to "false".
To run the JUnit test suite, the $CLASSPATH must include the following:
JUnit
JMX
Connector/J
MySQL Connector/MXJ
If
connector-mxj.jaris not present in your download, unzip MySQL Connector/MXJ source archive.cd mysqldjmx ant distThen add
$TEMP/cmxj/stage/connector-mxj/connector-mxj.jarto the CLASSPATH.if you have
junit, execute the unit tests. From the command line, type:java junit.textui.TestRunner com.mysql.management.AllTestsSuiteThe output should look something like this:
......................................... ......................................... .......... Time: 259.438 OK (101 tests)
Note that the tests are a bit slow near the end, so please be patient.
A feature of the MySQL Connector/J JDBC driver is the ability to specify a ''SocketFactory'' as a parameter in the JDBC connection string. MySQL Connector/MXJ includes a custom SocketFactory. The SocketFactory will, upon the first connection, deploy and launch the MySQL database. The SocketFactory also exposes a ''shutdown'' method.
To try it specify the ''socketFactory'' parameter on the JDBC connection string with a value equal to ''com.mysql.management.driverlaunched.ServerLauncherSocketFactory''
In the following example, we have a program which creates a connection, executes a query, and prints the result to the System.out. The MySQL database will be deployed and started as part of the connection process, and shutdown as part of the finally block.
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import com.mysql.management.driverlaunched.ServerLauncherSocketFactory;
public class ConnectorMXJTestExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String hostColonPort = "localhost:3336";
String driver = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver.class.getName();
String url = "jdbc:mysql://" + hostColonPort + "/" + "?"
+ "socketFactory="
+ ServerLauncherSocketFactory.class.getName();
String userName = "root";
String password = "";
Class.forName(driver);
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, password);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT VERSION()");
rs.next();
String version = rs.getString(1);
rs.close();
stmt.close();
System.out.println("------------------------");
System.out.println(version);
System.out.println("------------------------");
} finally {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ServerLauncherSocketFactory.shutdown(hostColonPort);
}
}
}
To run the above program, be sure to have connector-mxj.jar and Connector/J in the CLASSPATH. Then type:
java ConnectorMXJTestExample
Of course there are many options we may wish to set for a MySQL database. These options may be specified as part of the JDBC connection string simply by prefixing each server option with ''server.''. In the following example we set three driver parameters and two server parameters:
String url = "jdbc:mysql://" + hostColonPort + "/"
+ "?"
+ "socketFactory="
+ ServerLauncherSocketFactory.class.getName();
+ "&"
+ "cacheServerConfiguration=true"
+ "&"
+ "useLocalSessionState=true"
+ "&"
+ "server.basedir=/opt/myapp/db"
+ "&"
+ "server.datadir=/mnt/bigdisk/myapp/data";
If you have a java application and wish to “embed” a MySQL database, make use of the com.mysql.management.MysqldResource class directly. This class may be instantiated with the default (no argument) constructor, or by passing in a java.io.File object representing the directory you wish the server to be "unzipped" into. It may also be instantiated with printstreams for "stdout" and "stderr" for logging.
Once instantiated, a java.util.Map, the object will be able to provide a java.util.Map of server options appropriate for the platform and version of MySQL which you will be using.
The MysqldResource enables you to "start" MySQL with a java.util.Map of server options which you provide, as well as "shutdown" the database. The following example shows a simplistic way to embed MySQL in an application using plain java objects:
import com.mysql.management.MysqldResource;
...
public void startMySQL() {
File baseDir = new File(ourAppDir, "mysql");
mysqldResource = new MysqldResource(baseDir);
Map options = new HashMap();
options.put("port", "3336");
String threadName = "OurApp MySQL";
mysqldResource.start(threadName, options);
}
public void stopMySQL() {
if (mysqldResource != null) {
mysqldResource.shutdown();
}
mysqldResource = null;
}
public java.sql.Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
String db = "test";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3336/" + db;
String userName = "root";
String password = "";
Class.forName(com.mysql.jdbc.Driver.class.getName());
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, password);
}
Constructors:
public MysqldResource(File baseDir, PrintStream out, PrintStream err);
Allows the setting of the "basedir" to deploy the MySQL files to, as well as out put streams for standard out and standard err.
public MysqldResource(File baseDir);
Allows the setting of the "basedir" to deploy the MySQL files to. Output for standard out and standard err are directed to System.out and System.err.
public MysqldResource();
The basedir is defaulted to a subdirectory of the java.io.tempdir. Output for standard out and standard err are directed to System.out and System.err;
MysqldResource API includes the following methods:
void start(String threadName, Map mysqldArgs);
Deploys and starts MySQL. The "threadName" string is used to name the thread which actually performs the execution of the MySQL command line. The map is the set of arguments and their values to be passed to the command line.
void shutdown();
Shuts down the MySQL instance managed by the MysqldResource object.
Map getServerOptions();
Returns a map of all the options and their current (or default, if not running) options available for the MySQL database.
boolean isRunning();
Returns true if the MySQL database is running.
boolean isReadyForConnections();
Returns true once the database reports that is ready for connections.
void setKillDelay(int millis);
The default “Kill Delay” is 30 seconds. This represents the amount of time to wait between the initial request to shutdown and issuing a “force kill” if the database has not shutdown by itself.
void addCompletionListenser(Runnable listener);
Allows for applications to be notified when the server process completes. Each ''listener'' will be fired off in its own thread.
String getVersion();
returns the version of MySQL.
void setVersion(int MajorVersion, int minorVersion, int patchLevel);
The standard distribution comes with only one version of MySQL packaged. However, it is possible to package multiple versions, and specify which version to use.
If you are not using the SUN Reference implementation of the JMX libraries, you should skip this section. Or, if you are deploying to JBoss, you also may wish to skip to the next section.
We want to see the MysqldDynamicMBean in action inside of a JMX
agent. In the com.mysql.management.jmx.sunri
package is a custom JMX agent with two MBeans:
the MysqldDynamicMBean, and
a com.sun.jdmk.comm.HtmlAdaptorServer, which provides a web interface for manipulating the beans inside of a JMX agent.
When this very simple agent is started, it will allow a MySQL database to be started and stopped with a web browser.
Complete the testing of the platform as above.
current JDK, JUnit, Connector/J, MySQL Connector/MXJ
this section requires the SUN reference implementation of JMX
PATH, JAVA_HOME, ANT_HOME, CLASSPATH
If not building from source, skip to next step
rebuild with the "sunri.present"
ant -Dsunri.present=true dist re-run tests: java junit.textui.TestRunner com.mysql.management.AllTestsSuite
launch the test agent from the command line:
java com.mysql.management.jmx.sunri.MysqldTestAgentSunHtmlAdaptor &from a browser:
http://localhost:9092/under MysqldAgent,
select "name=mysqld"Observe the MBean View
scroll to the bottom of the screen press the button
click
Back to MBean Viewscroll to the bottom of the screen press button
kill the java process running the Test Agent (jmx server)
Once there is confidence that the MBean will function on the platform, deploying the MBean inside of a standard JMX Agent is the next step. Included are instructions for deploying to JBoss.
Ensure a current version of java development kit (v1.4.x), see above.
Ensure
JAVA_HOMEis set (JBoss requiresJAVA_HOME)Ensure
JAVA_HOME/binis in thePATH(You will NOT need to set your CLASSPATH, nor will you need any of the jars used in the previous tests).
Ensure a current version of JBoss (v4.0RC1 or better)
http://www.jboss.org/index.html select "Downloads" select "jboss-4.0.zip" pick a mirror unzip ~/dload/jboss-4.0.zip create a JBOSS_HOME environment variable set to the unzipped directory unix only: cd $JBOSS_HOME/bin chmod +x *.sh
Deploy (copy) the
connector-mxj.jarto$JBOSS_HOME/server/default/lib.Deploy (copy)
mysql-connector-java-3.1.4-beta-bin.jarto$JBOSS_HOME/server/default/lib.Create a
mxjtest.wardirectory in$JBOSS_HOME/server/default/deploy.Deploy (copy)
index.jspto$JBOSS_HOME/server/default/deploy/mxjtest.war.Create a
mysqld-service.xmlfile in$JBOSS_HOME/server/default/deploy.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <server> <mbean code="com.mysql.management.jmx.jboss.JBossMysqldDynamicMBean" name="mysql:type=service,name=mysqld"> <attribute name="datadir">/tmp/xxx_data_xxx</attribute> <attribute name="autostart">true</attribute> </mbean> </server>Start jboss:
on unix: $JBOSS_HOME/bin/run.sh
on windows: %JBOSS_HOME%\bin\run.bat
Be ready: JBoss sends a lot of output to the screen.
When JBoss seems to have stopped sending output to the screen, open a web browser to:
http://localhost:8080/jmx-consoleScroll down to the bottom of the page in the
mysqlsection, select the bulletedmysqldlink.Observe the JMX MBean View page. MySQL should already be running.
(If "autostart=true" was set, you may skip this step.) Scroll to the bottom of the screen. You may press the button to stop (or start) MySQL observe
Operation completed successfully without a return value.ClickBack to MBean ViewTo confirm MySQL is running, open a web browser to
http://localhost:8080/mxjtest/and you should see thatSELECT 1
returned with a result of
1
Guided by the
$JBOSS_HOME/server/default/deploy/mxjtest.war/index.jspyou will be able to use MySQL in your Web Application. There is atestdatabase and arootuser (no password) ready to expirement with. Try creating a table, inserting some rows, and doing some selects.Shut down MySQL. MySQL will be stopped automatically when JBoss is stopped, or: from the browser, scroll down to the bottom of the MBean View press the stop service button to halt the service. Observe
Operation completed successfully without a return value.Usingpsortask managersee that MySQL is no longer running
As of 1.0.6-beta version is the ability to have the MBean start the MySQL database upon start up. Also, we've taken advantage of the JBoss life-cycle extension methods so that the database will gracefully shut down when JBoss is shutdown.
If you've worked through the above sections, you've arleady performed these steps. But we list them here for quick reference.
Driver Launched:
Download and unzip Connector/MXJ, add connector-mxj.jar to the CLASSPATH
To the JDBC connection string add the following parameter: "socketFactory=" + ServerLauncherSocketFactory.class.getName()
JBoss:
Download Connector/MXJ copy the
connector-mxj.jarfile to the$JBOSS_HOME/server/default/libdiretory.Download Connector/J copy the
connector-mxj.jarfile to the$JBOSS_HOME/server/default/libdiretory.Create an MBean service xml file in the
$JBOSS_HOME/server/default/deploydirectory with any attributes set, for instance thedatadirandautostart.Set the JDBC parameters of your web application to use:
String driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; String url = "jdbc:mysql:///test?propertiesTransform="+ "com.mysql.management.jmx.ConnectorMXJPropertiesTransform"; String user = "root"; String password = ""; Class.forName(driver); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
You may wish to create a separate users and database table spaces for each application, rather than using "root and test".
We highly suggest having a routine backup procedure for backing up
the database files in the datadir.
The PHP distribution and documentation are available from the PHP
Web site. MySQL provides the mysql and
mysqli extensions for the Windows operating
system for MySQL versions as of 5.0.18 on
http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/php/. You
can find information why you should preferably use the extensions
provided by MySQL on that page. For platforms other than Windows,
you should use the mysql or
mysqli extensions shipped with the PHP sources.
See Section 22.3, “MySQL PHP API”.